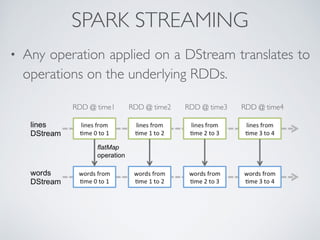
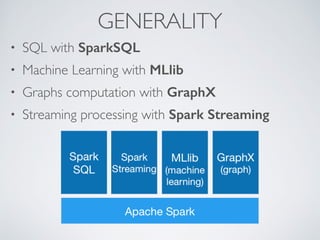
Apache Spark is a fast and general engine for large-scale data processing. It was originally developed in 2009 and is now supported by Databricks. Spark provides APIs in Java, Scala, Python and can run on Hadoop, Mesos, standalone or in the cloud. It provides high-level APIs like Spark SQL, MLlib, GraphX and Spark Streaming for structured data processing, machine learning, graph analytics and stream processing.









![SCHEMA RDD
• To work with SparkSQL you need SQLContext
(or HiveContext)
from spark.sql import SQLContext
sqlCtx = SQLContext(sc)
records = sc.textFile(“customers.csv”)
customers = records.map(lambda line: line.split(“,”))
.map(lambda r: Row(name=r[0], age=int(r[1])))
customersTable = sqlCtx.inferSchema(customers)
customersTable.registerAsTable(“customers”)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark-overview-ferret-141216165437-conversion-gate01/85/Apache-Spark-Overview-ferret-11-320.jpg)






![MACHINE LEARNING LIBRARY
• LinearRegression with stochastic gradient descent (SGD)
example on Spark:
def parsePoint(line):
values = [float(x) for x in line.replace(',', ' ').split(' ')]
return LabeledPoint(values[0], values[1:])
parsedData = data.map(parsePoint)
model = LinearRegressionWithSGD.train(parsedData)
valuesAndPreds = parsedData.map(
lambda p: (p.label, model.predict(p.features)))
MSE = valuesAndPreds.map(lambda (v, p): (v - p)**2)
.reduce(lambda x, y: x + y) / valuesAndPreds.count()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark-overview-ferret-141216165437-conversion-gate01/85/Apache-Spark-Overview-ferret-18-320.jpg)