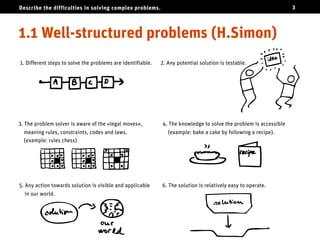
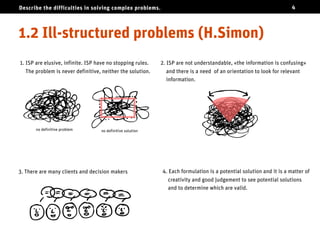
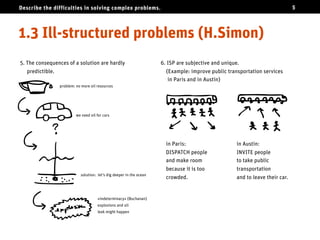
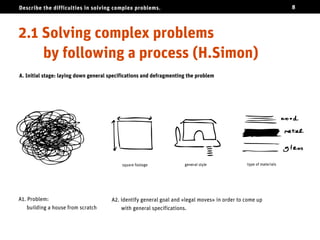
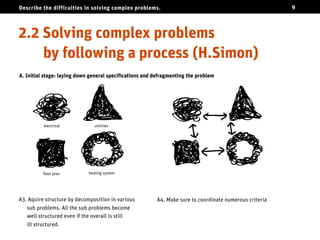
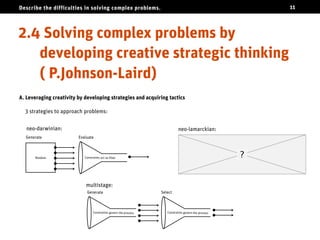
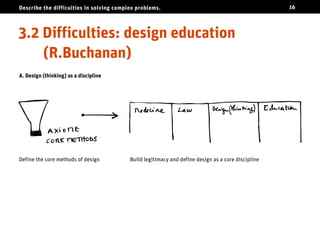
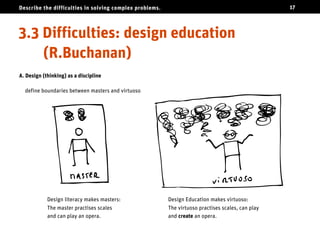
The document discusses the challenges of solving complex problems, classifying them into well-structured, ill-structured, and wicked types, each with distinct characteristics and difficulties. It emphasizes the need for design literacy and education, advocating for design thinking to be established as a core discipline and integrated into educational curricula. The conclusion suggests a shift towards teaching design skills early and equipping individuals with both logical and emotional tools to tackle these complex issues.