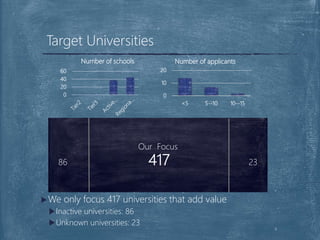
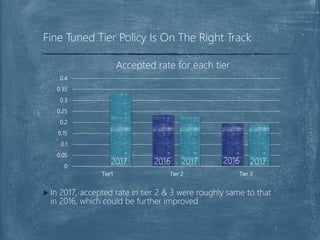
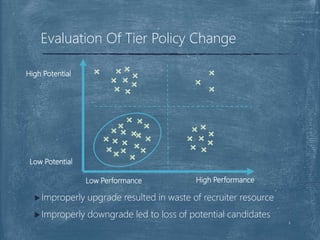
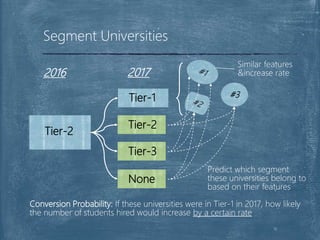
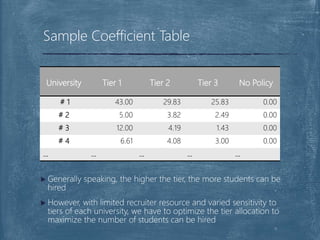
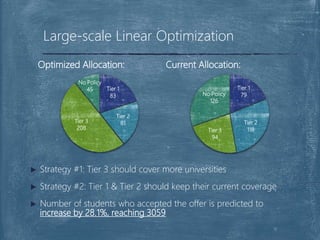
The document discusses a case competition project focused on optimizing university tier assignments for improved recruiter resource allocation and increased acceptance rates of qualified candidates. Key findings suggest that tier 3 should cover more universities while tiers 1 and 2 maintain current coverage, with recommendations to optimize resource allocation using a fine-tuned lead scoring model. The analysis indicates that proper tier assignments can enhance the number of students hired and improve acceptance rates across various tiers.