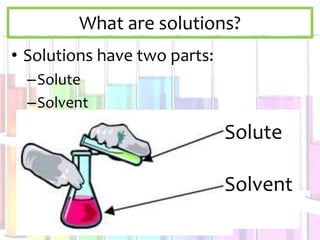
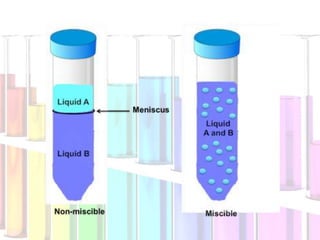
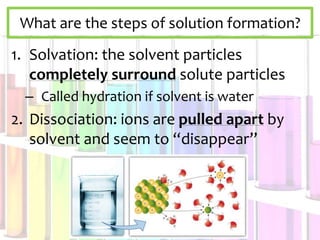
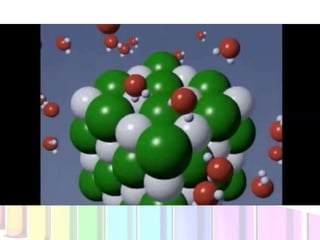
Solutions are homogeneous mixtures composed of a solute dissolved in a solvent. The solute is the substance being dissolved and is always present in smaller amounts, while the solvent does the dissolving and is present in larger amounts. Examples of solutions include cola, gasoline, and cleaners. Solutions can be solid, liquid, or gas depending on the state of matter of the solvent. For a solid solute to dissolve in a liquid to form a solution, it must be soluble, while if two liquids dissolve in each other they are miscible. The formation of solutions involves solvation and dissociation processes. Whether a substance dissolves depends on if it is polar or nonpolar, following the "like dissolves like"