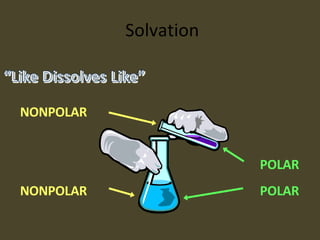
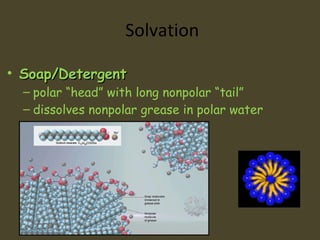
1. A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances, where the solute is evenly distributed throughout the solvent.
2. The solute is the substance being dissolved and is present in smaller amounts, while the solvent is the dissolving medium and makes up the majority of the solution.
3. Solutions are distinguished from suspensions and colloids by having particles small enough to not be visible, and that can be separated by evaporation but not filtration.