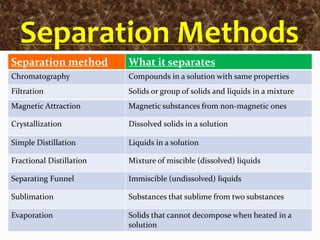
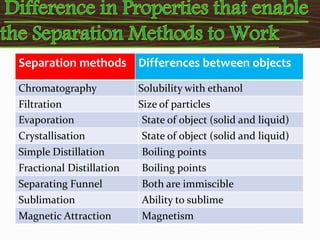
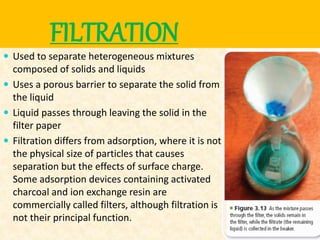
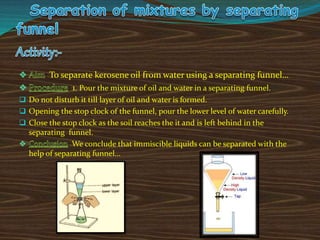
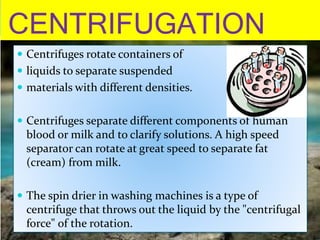
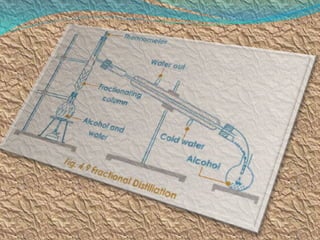
Filtration can be used to separate an insoluble substance from a soluble substance. It uses a porous barrier such as filter paper to separate solids from liquids, allowing the liquid to pass through while retaining the solid. Chromatography separates components of a mixture based on how strongly they interact with and move across a stationary material like chromatography paper. Distillation separates mixtures based on differences in boiling points, heating the mixture until it vaporizes then cooling the vapors to condense them.