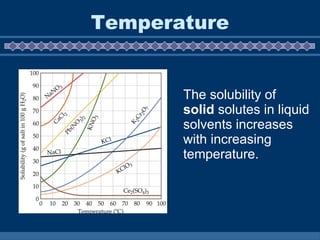
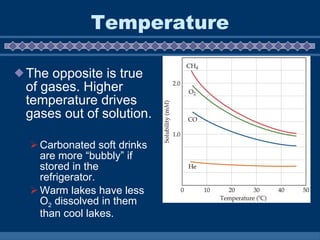
A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances, with a solute dissolved in a solvent. Water is the universal solvent, dissolving most other substances to form aqueous solutions. The rate at which a substance dissolves, or its solubility, depends on factors like temperature, surface area, movement, and pressure. Higher temperatures increase solubility of solids but decrease gases, while increased surface area, movement, and pressure also generally increase solubility.