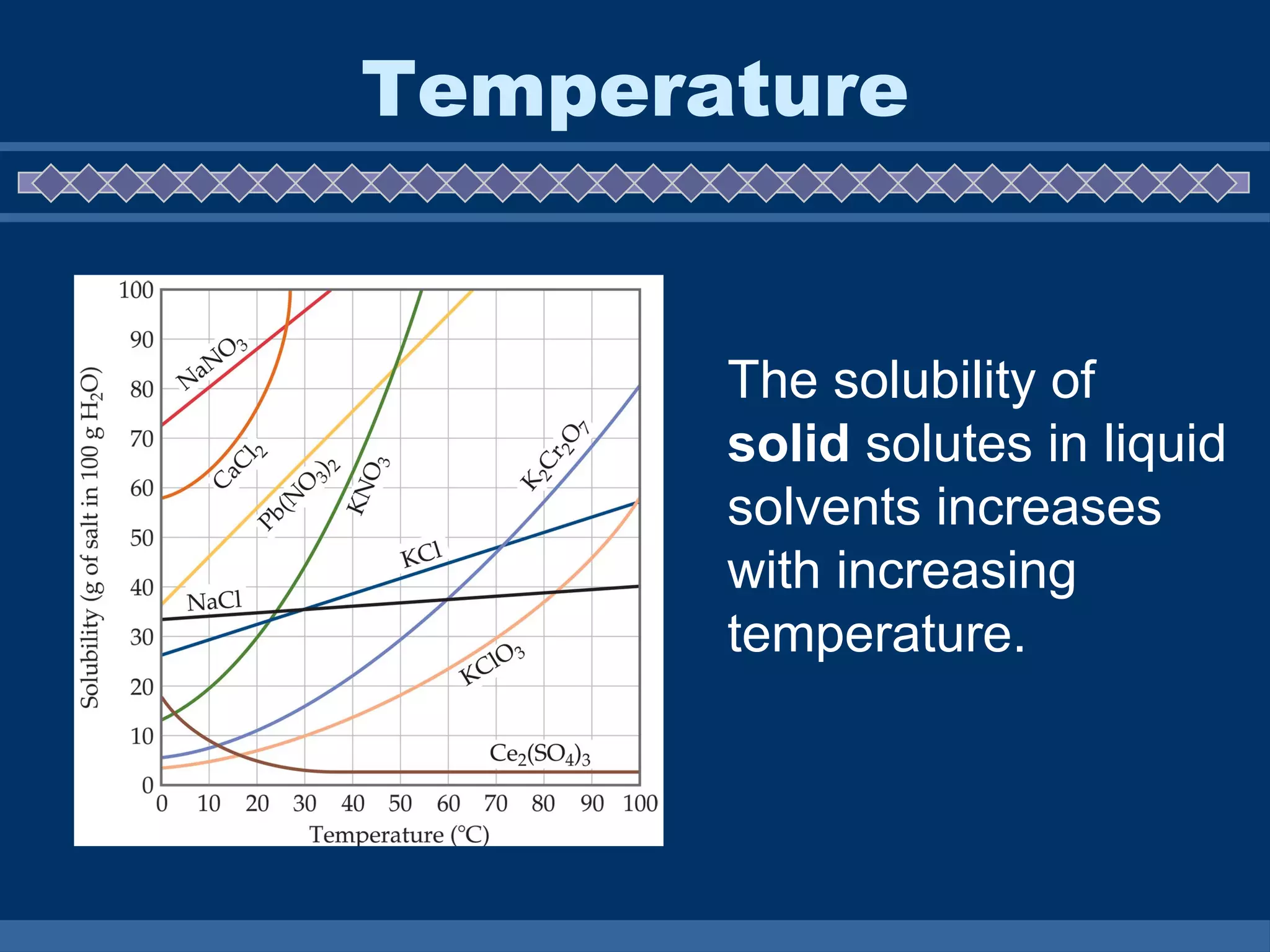
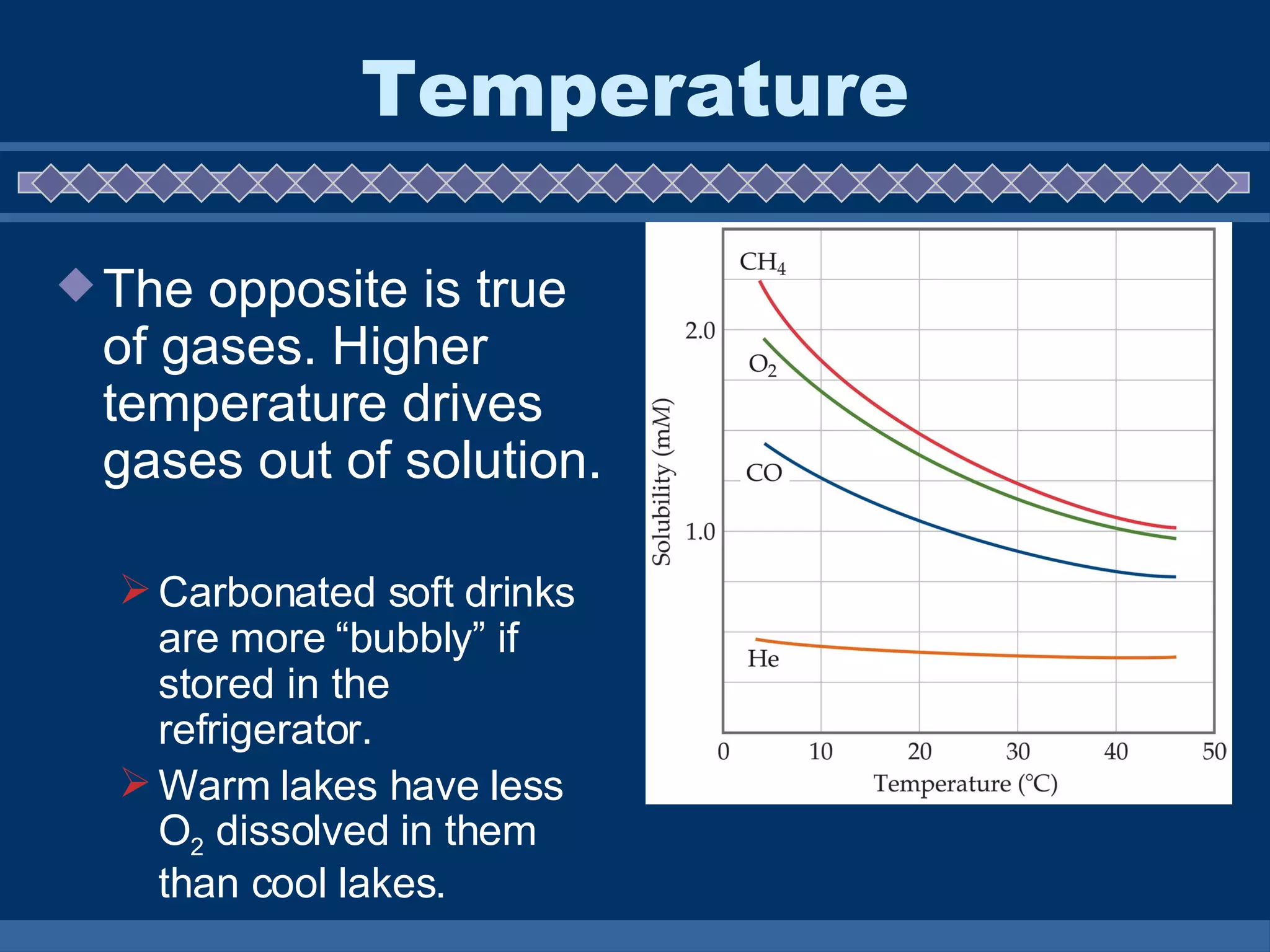
A solution is a homogeneous mixture composed of a solute dissolved in a solvent. The solute is the substance that is dissolved, while the solvent does the dissolving. Water is the most common solvent and solutions using water are called aqueous solutions. The rate of solubility, or how quickly a substance will dissolve, can be affected by several factors including temperature, surface area, movement, and pressure. Higher temperatures increase the solubility of solids but decrease gases, while increased surface area, movement, and pressure can also increase dissolution rates.