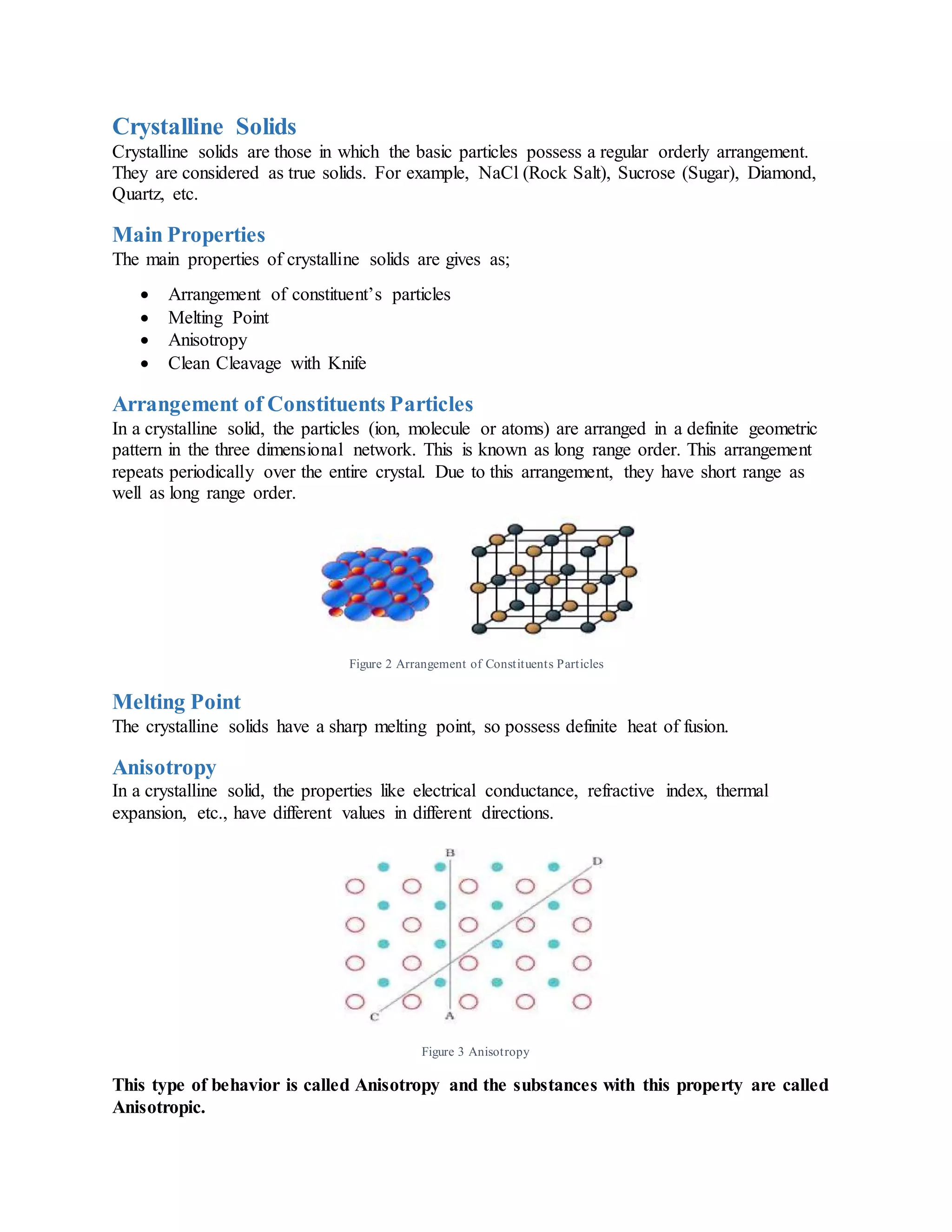
A solid is a state of matter characterized by particles arranged in a stable, close-packed structure that gives solids a definite shape and volume. Solids can be crystalline or amorphous. Crystalline solids have particles arranged in a regular, repeating pattern throughout the crystal lattice. Amorphous solids lack long-range order and have particles arranged irregularly over short distances. The crystal lattice is made up of repeating units called unit cells, which define the symmetry and geometry of the crystal structure. Unit cells come in seven main types depending on their parameters. Crystalline solids are further classified based on the type of bonds between particles as ionic, covalent, metallic, or molecular solids.