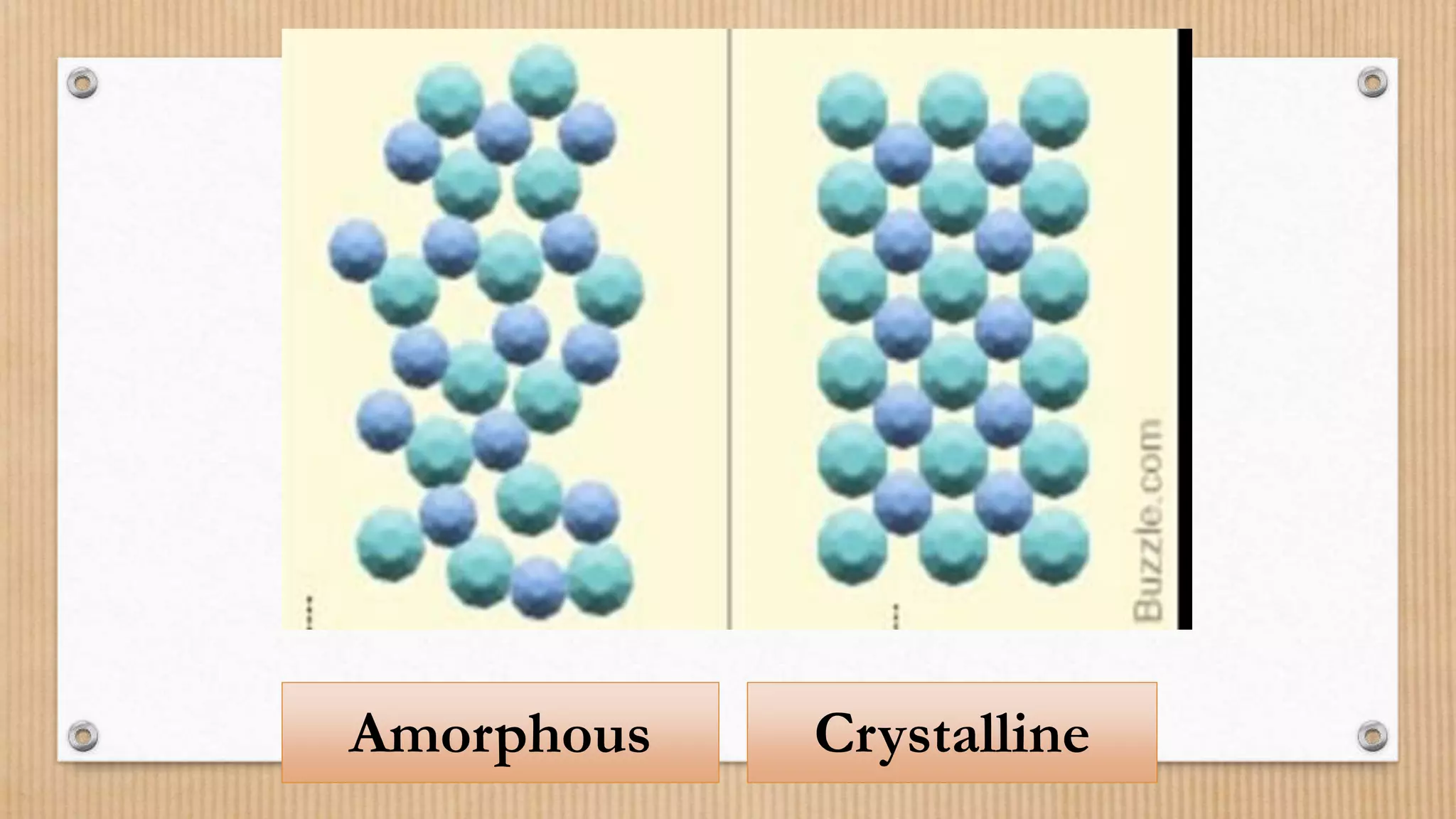
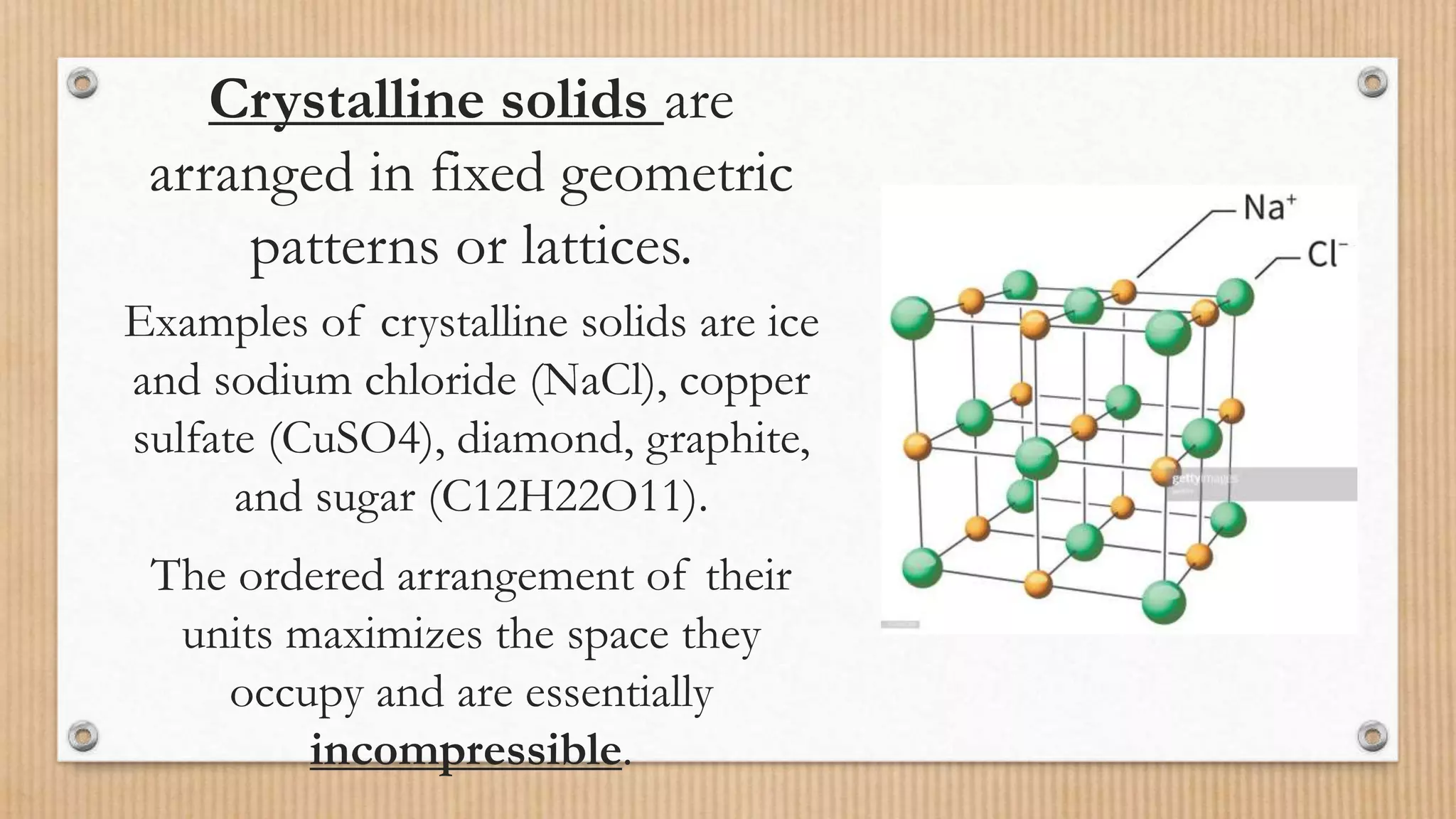
Crystalline and amorphous solids differ in their arrangement of particles. Crystalline solids have a regular repeating three-dimensional structure with particles arranged in fixed geometric patterns or lattices. They have sharp melting points. Amorphous solids have a random orientation of particles and do not have a defined structure, resembling liquids. They melt over a wide range of temperatures rather than at a distinct melting point. Examples of crystalline solids are NaCl and CuSO4, while glass and rubber are amorphous solids.