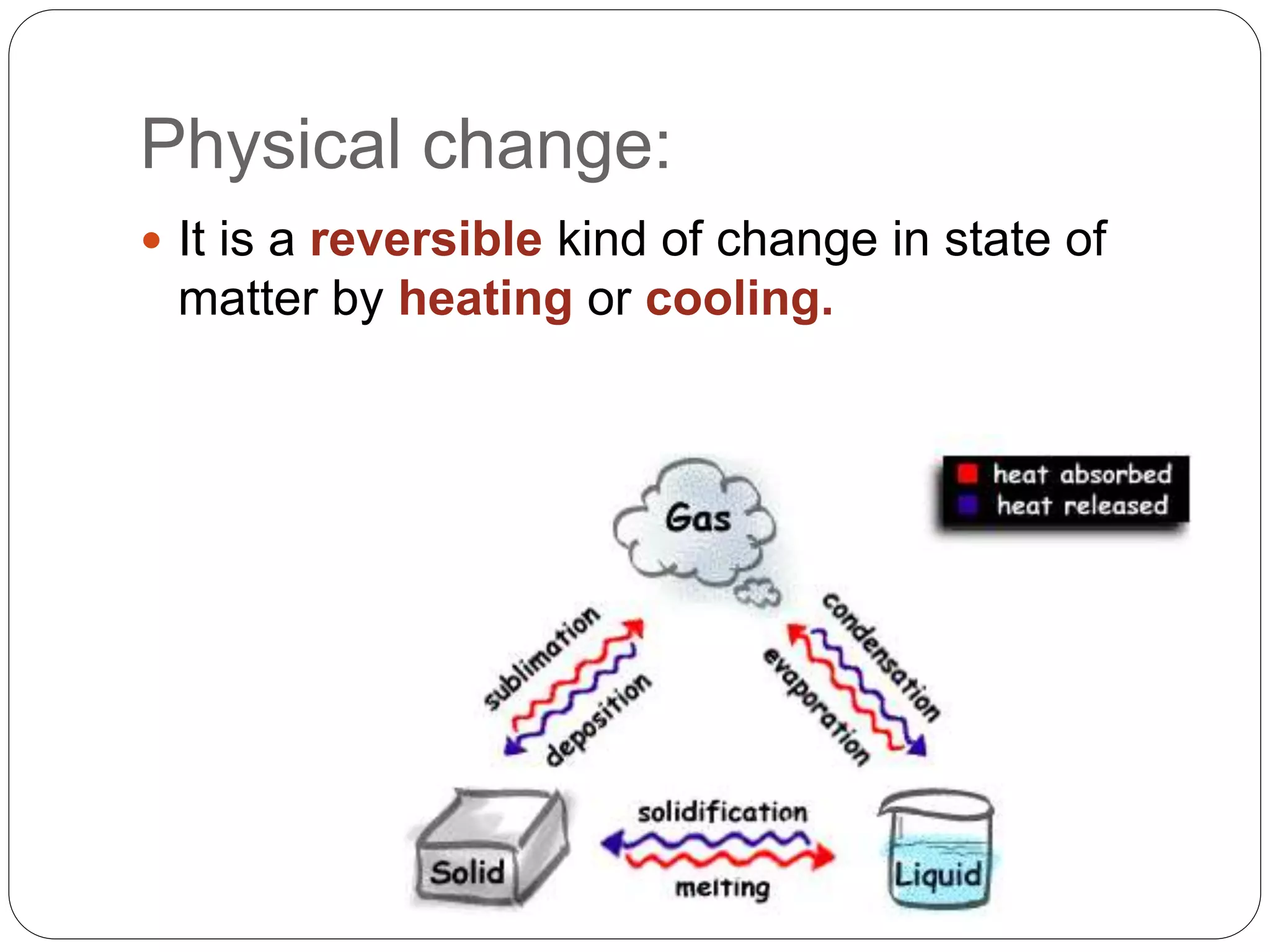
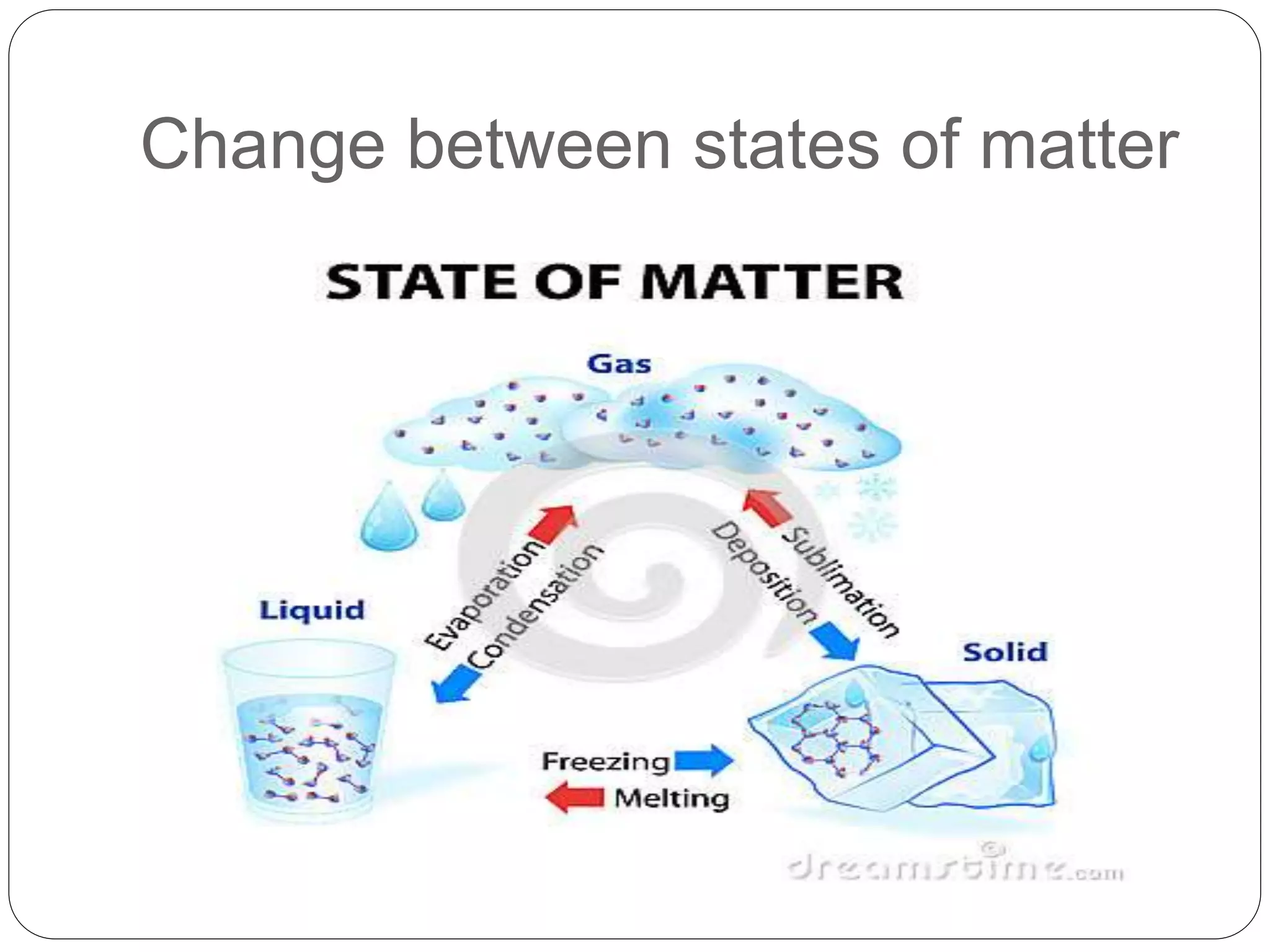
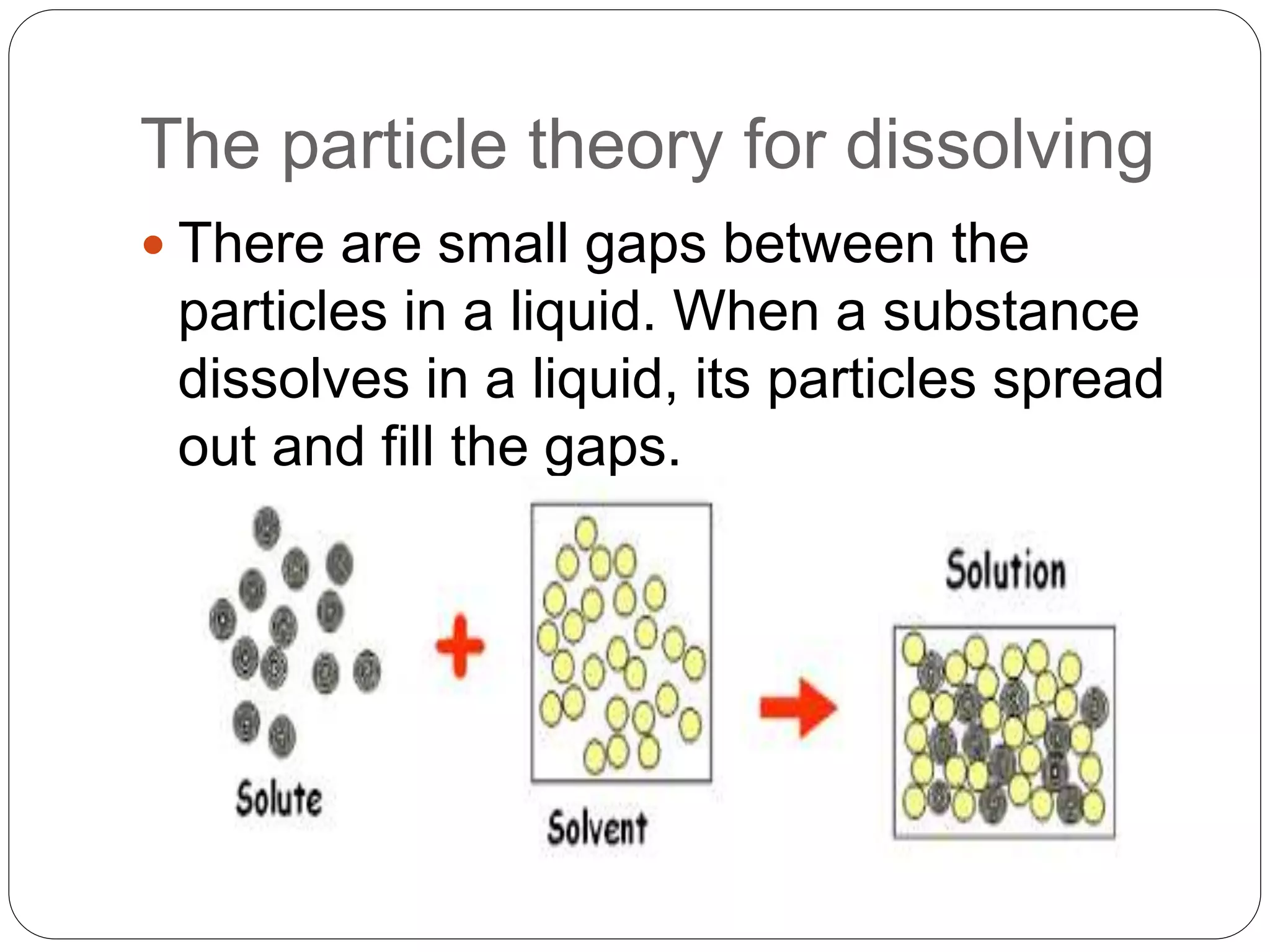
This document discusses the three common states of matter - solids, liquids, and gases. It explains their key properties including definite mass and varying volume and shape. The document then introduces the particle theory of matter, which states that all matter is made up of tiny particles that are in constant motion. It describes how the motion and interaction of these particles determines whether a substance is a solid, liquid or gas, and how physical changes like melting, boiling and condensation occur as particles gain or lose energy.