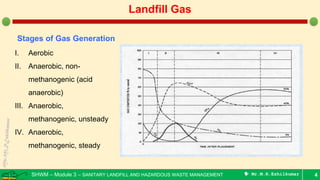
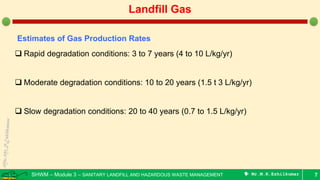
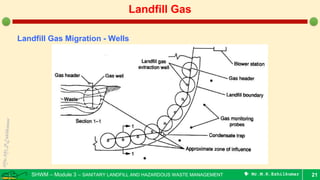
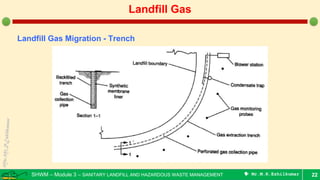
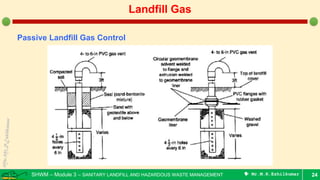
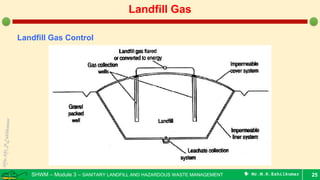
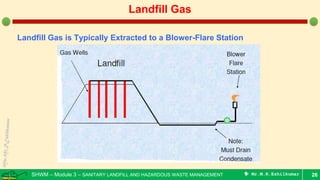
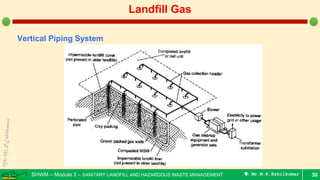
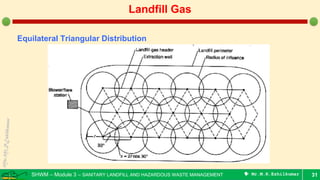
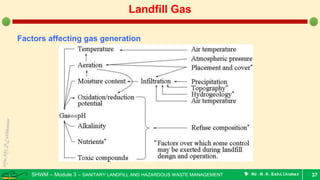
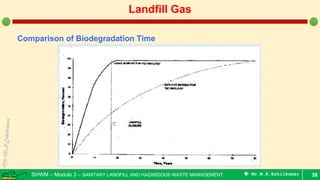
This document is a lecture on landfill gas management by Prof. M.R. Ezhilkumar from Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology. It discusses the stages of landfill gas generation, composition of landfill gas, methods for estimating gas production rates, techniques for enhancing gas generation, and systems for controlling landfill gas migration. It provides details on the design of landfill gas collection systems, including the layout of gas extraction wells and headers, sizing calculations, and rules of thumb. Passive and active landfill gas control methods are also covered.