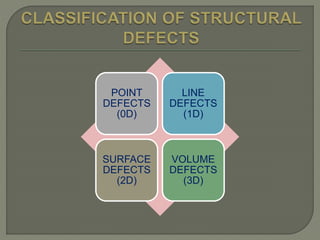
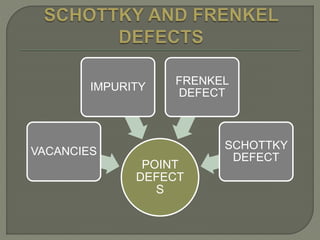
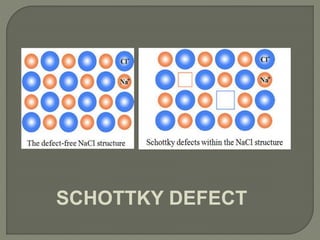
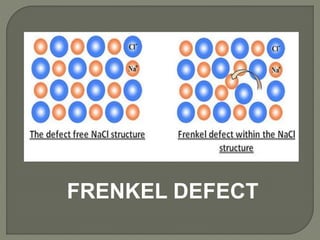
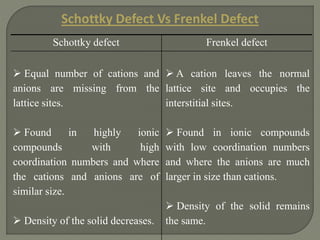
This document discusses different types of lattice defects in crystals. It describes Schottky and Frenkel defects. A Schottky defect occurs in ionic crystals when equal numbers of oppositely charged ions leave their lattice sites, creating vacancies while maintaining overall charge neutrality. A Frenkel defect occurs when an atom moves from its lattice site to an interstitial site, producing a vacancy and interstitial. Schottky defects lower the crystal's density while Frenkel defects do not change density.