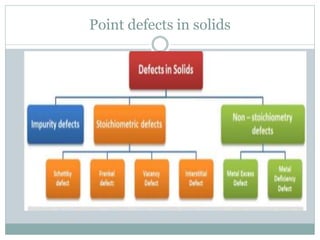
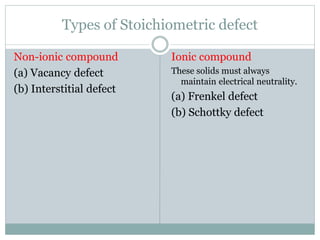
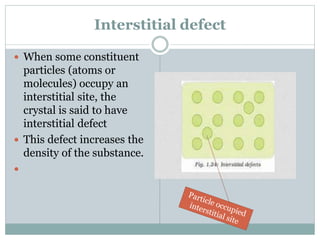
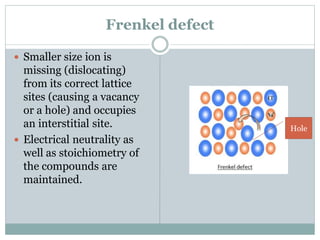
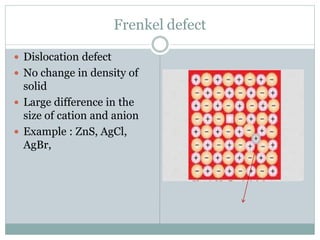
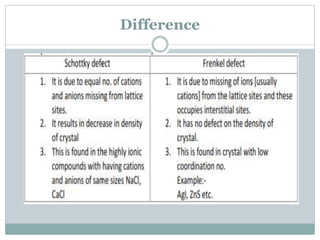
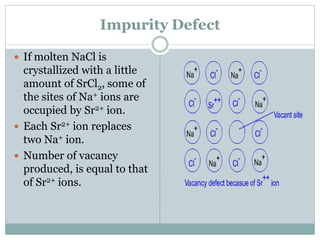
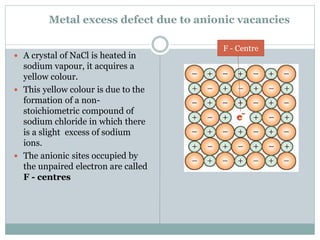
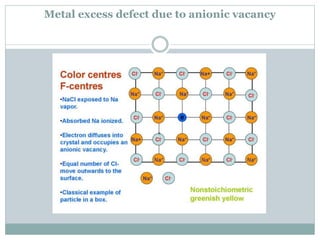
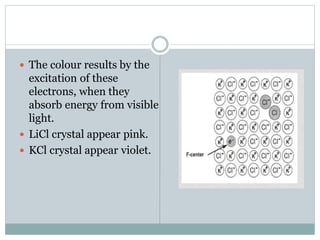
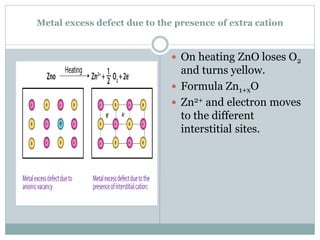
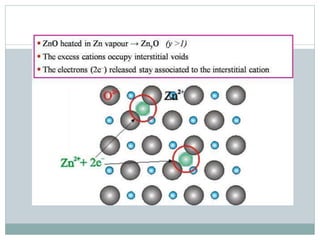
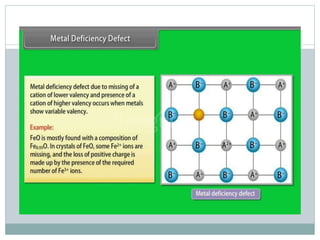
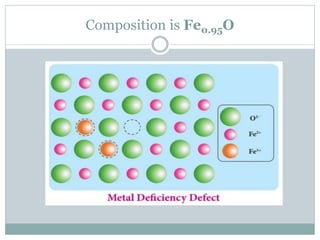
The document discusses defects in solids, categorizing them into stoichiometric and non-stoichiometric defects, which include vacancy and interstitial defects. Stoichiometric defects maintain the balance of constituent particles, while non-stoichiometric defects result from an imbalance, such as metal excess or deficiency due to cation or anionic vacancies. Examples like Frenkel and Schottky defects illustrate how these structural anomalies affect the material properties and composition of crystals.