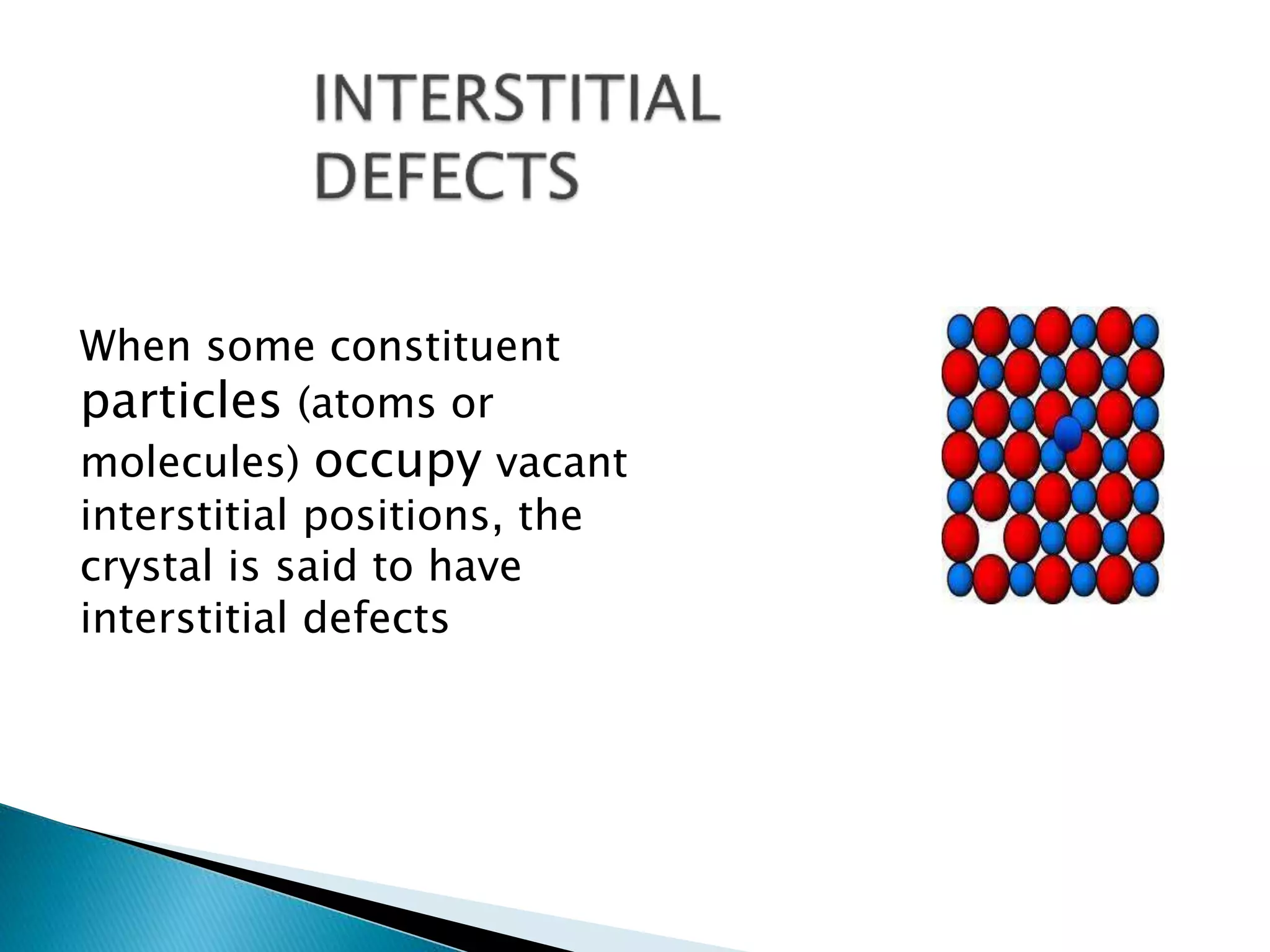
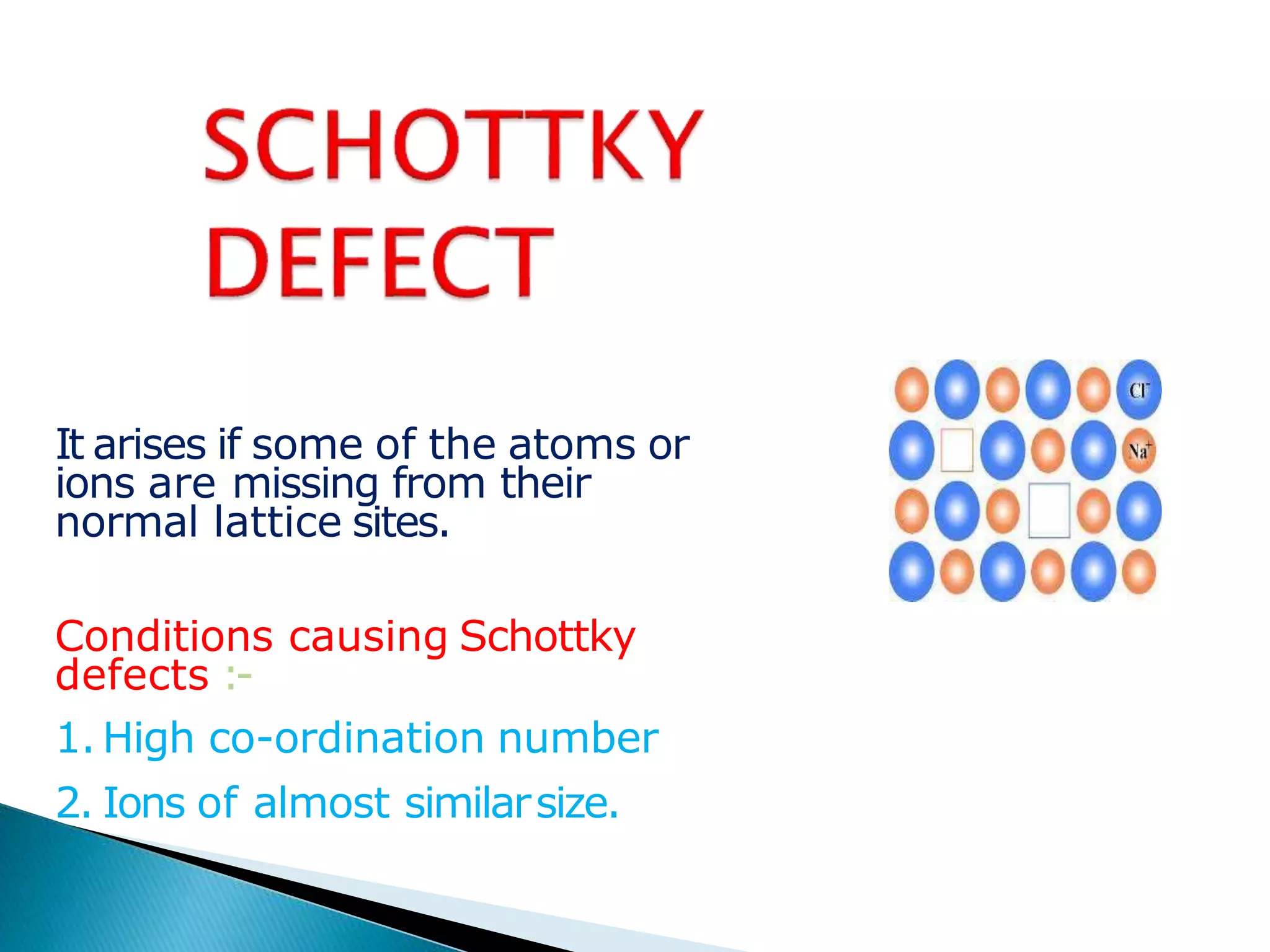
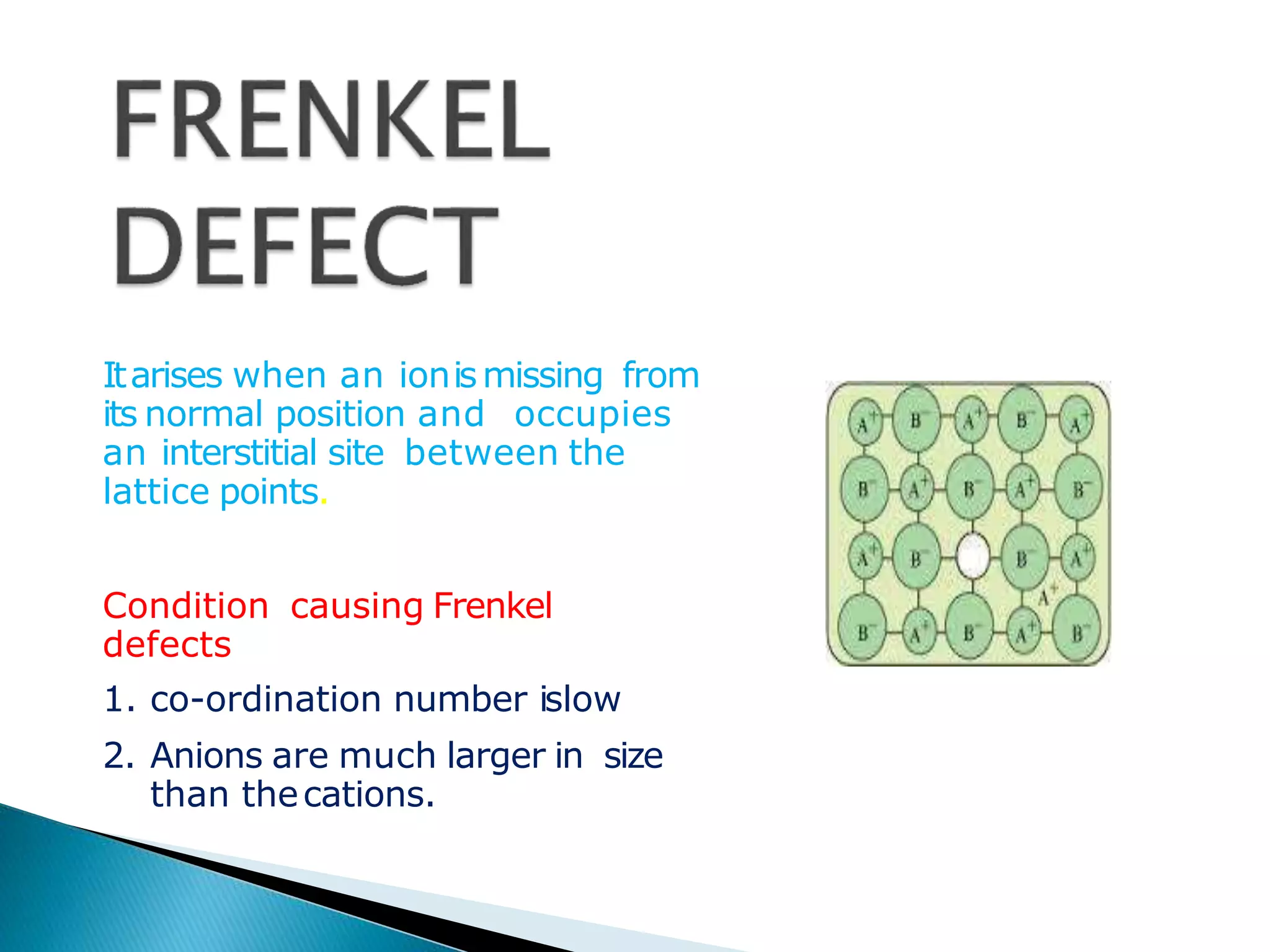
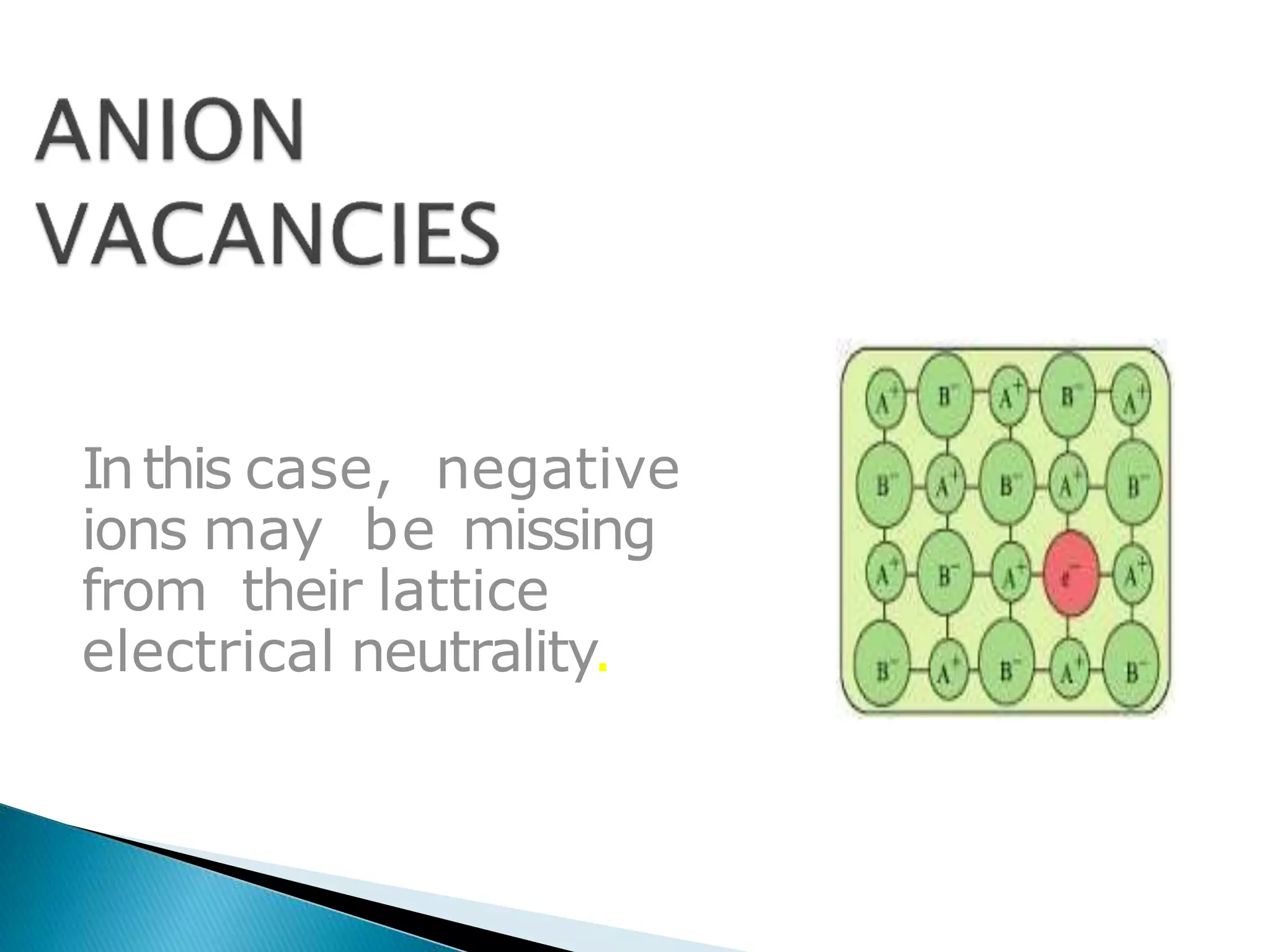
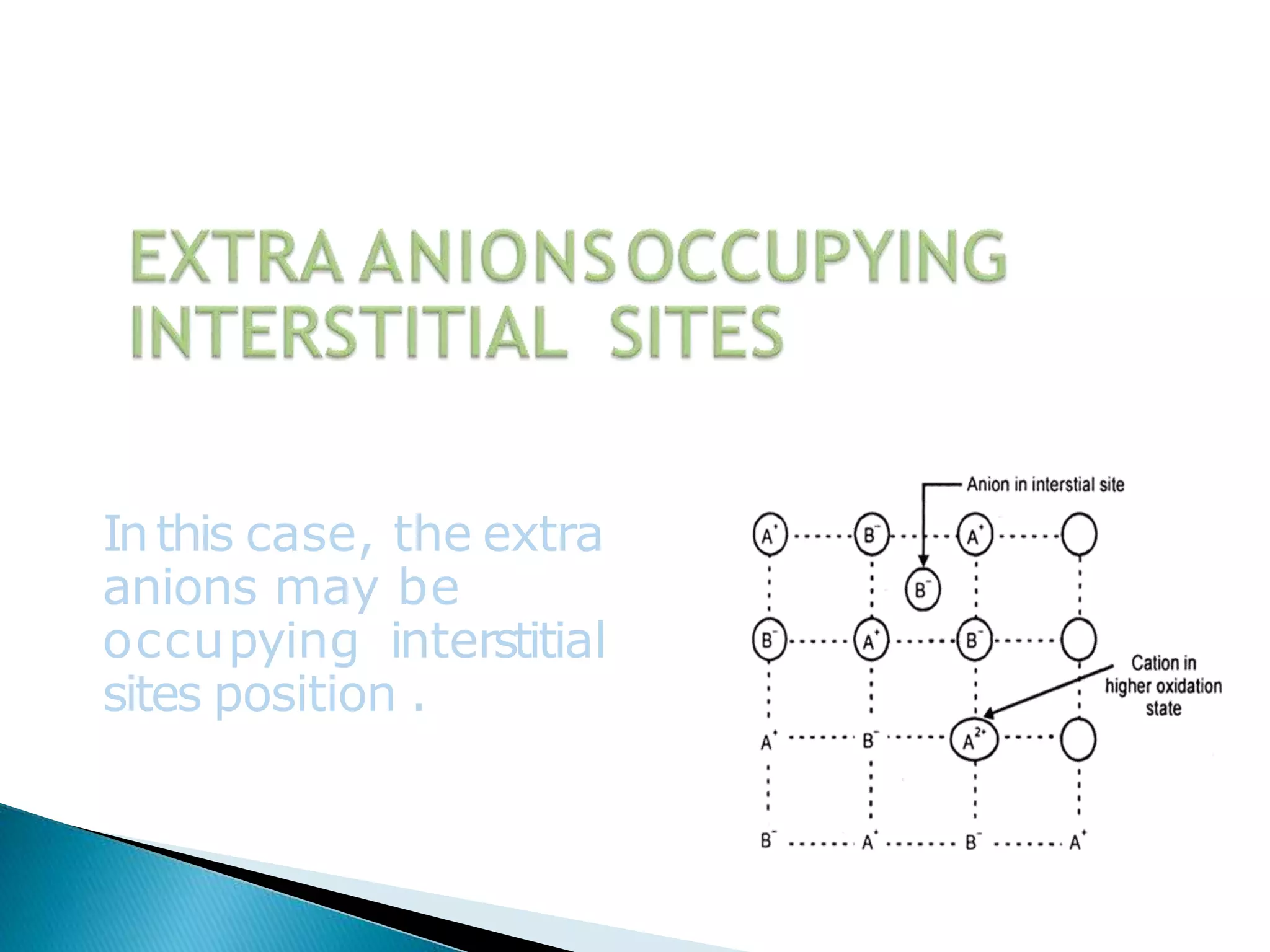
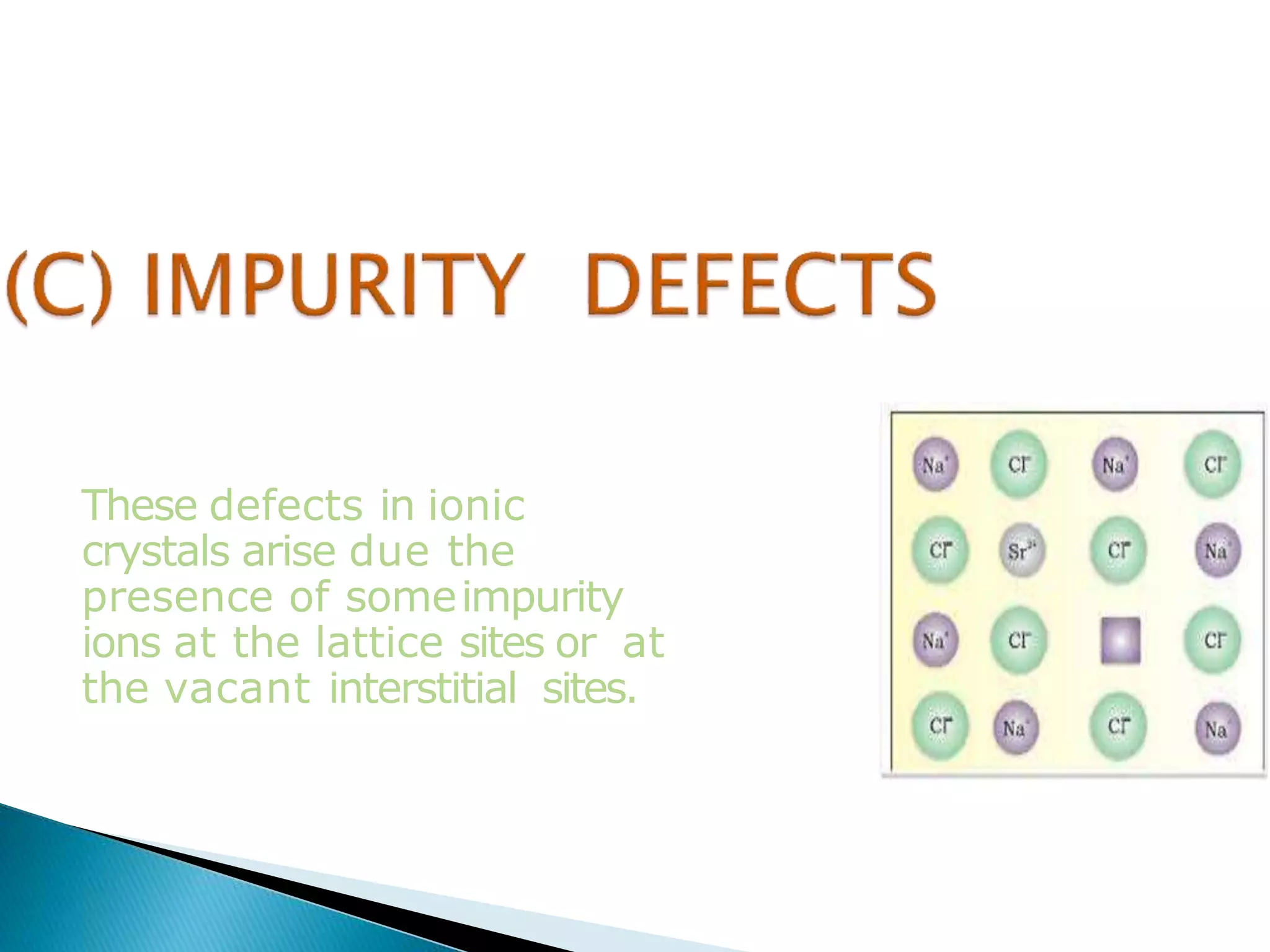
This document discusses different types of defects that can occur in crystalline materials. There are two main types of defects - point defects and line defects. Point defects include vacancy defects, where lattice sites are vacant, and interstitial defects, where atoms occupy interstitial positions between lattice sites. Vacancy and interstitial defects can both occur as Schottky or Frenkel defects in stoichiometric compounds. Non-stoichiometric compounds can exhibit metal excess or metal deficient defects due to anionic/cationic vacancies or interstitial atoms. Impurity defects also arise from the presence of impurity ions in the crystal lattice or interstitial sites. These various defects impact the macroscopic properties of materials and some