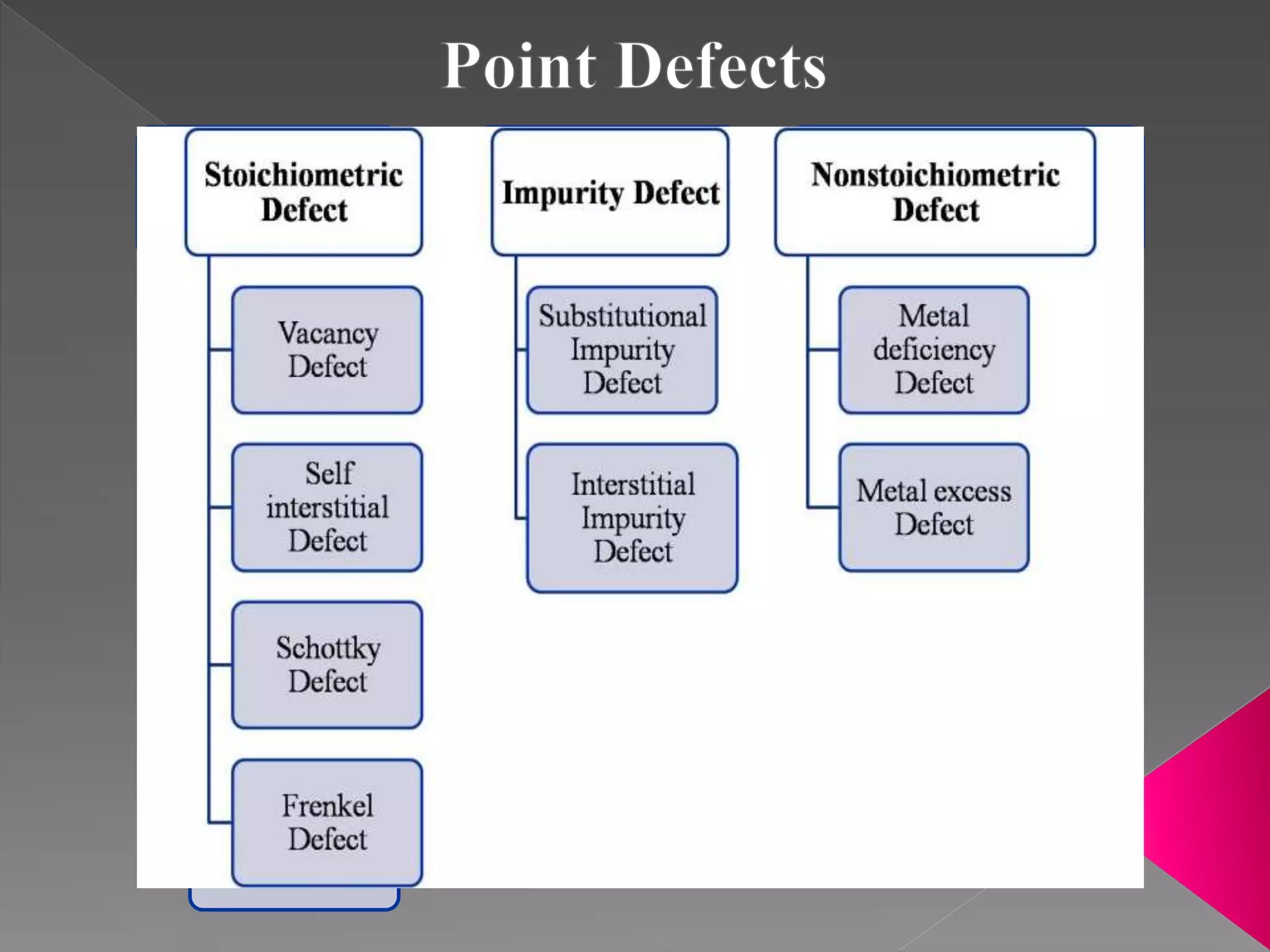
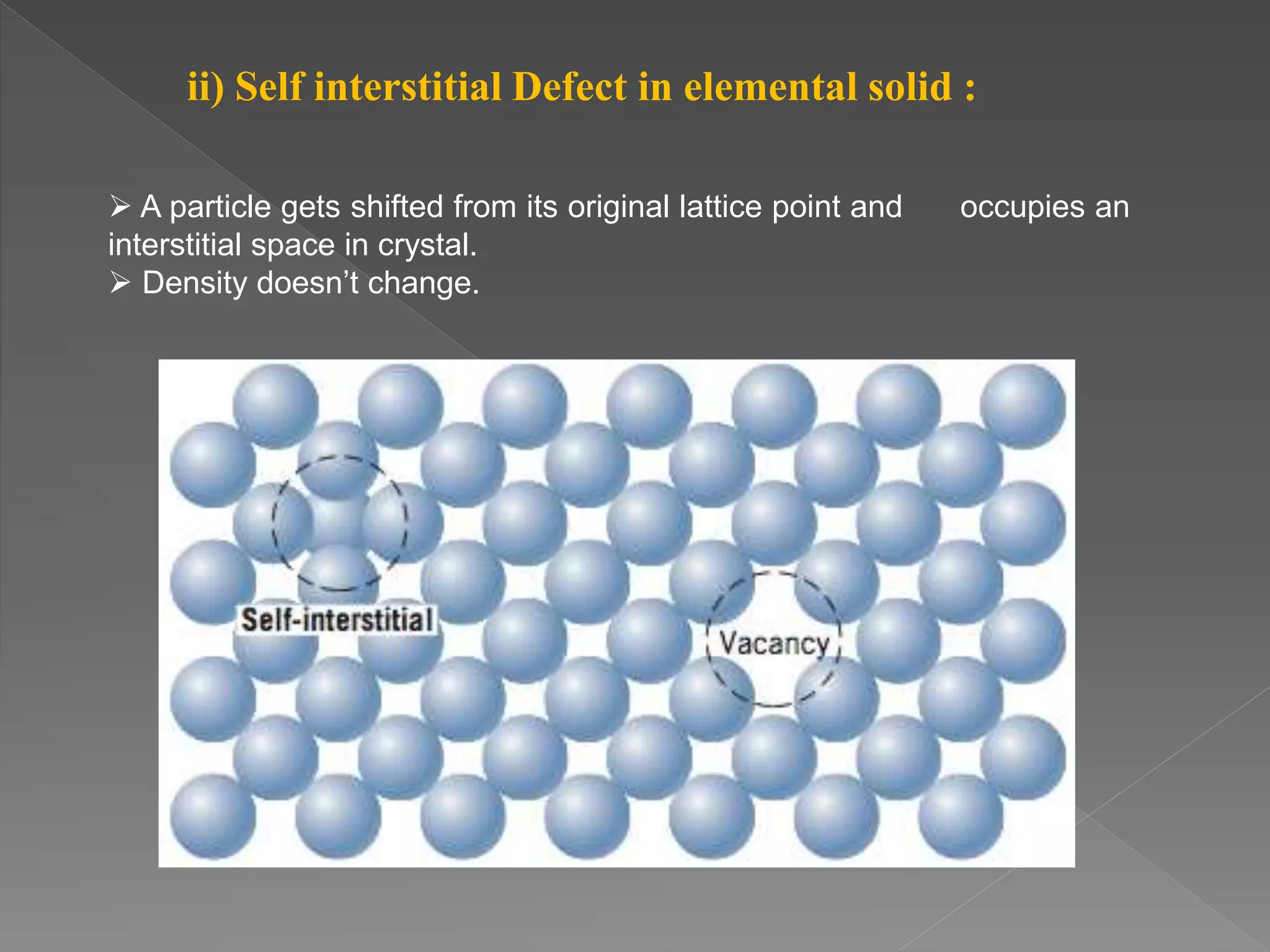
This document discusses different types of crystal defects including point defects like vacancies and interstitials, and line and plane defects. It describes specific point defects in detail such as vacancy defects, self-interstitial defects, Schottky defects, and Frenkel defects. The key differences between Schottky and Frenkel defects are outlined. Impurity defects caused by foreign atoms substituting into the crystal lattice or occupying interstitial sites are also summarized. Finally, non-stoichiometric defects resulting from a metal deficiency or excess are mentioned.