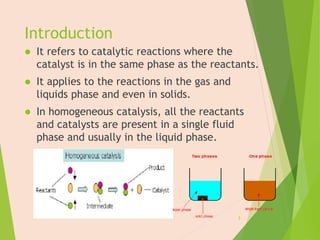
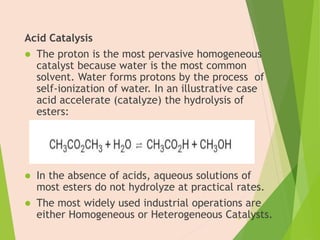
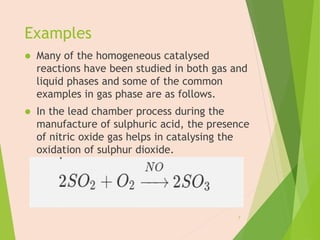
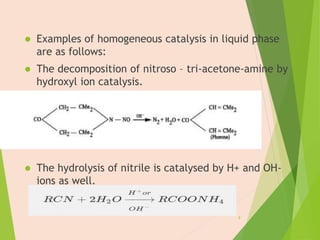
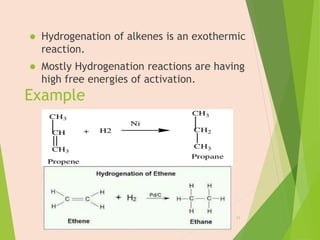
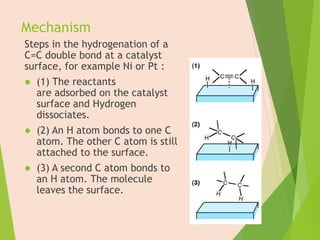
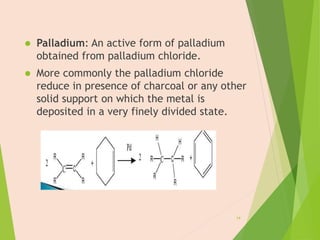
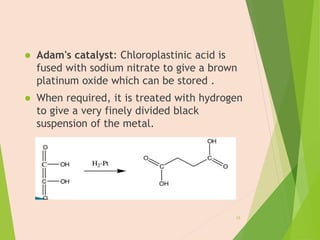
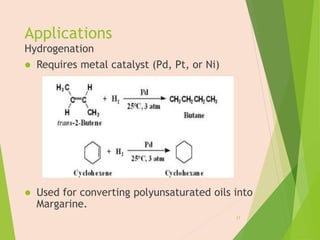
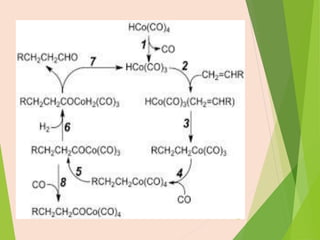
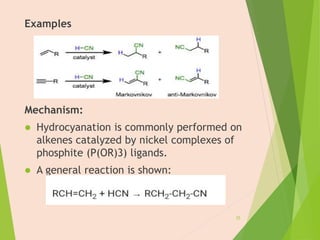
The document discusses homogeneous catalysis where the catalyst is in the same phase as the reactants. It provides examples of important homogeneous catalytic reactions like hydrogenation, hydroformylation, and hydrocyanation. Hydrogenation involves using metal catalysts like palladium, platinum, or nickel to reduce double and triple bonds. Hydroformylation uses cobalt or rhodium catalysts to add a formyl group and hydrogen to an alkene to produce an aldehyde. Hydrocyanation employs nickel phosphite catalysts to add hydrogen cyanide to an alkene to yield a nitrile, with an important application being the production of adiponitrile.