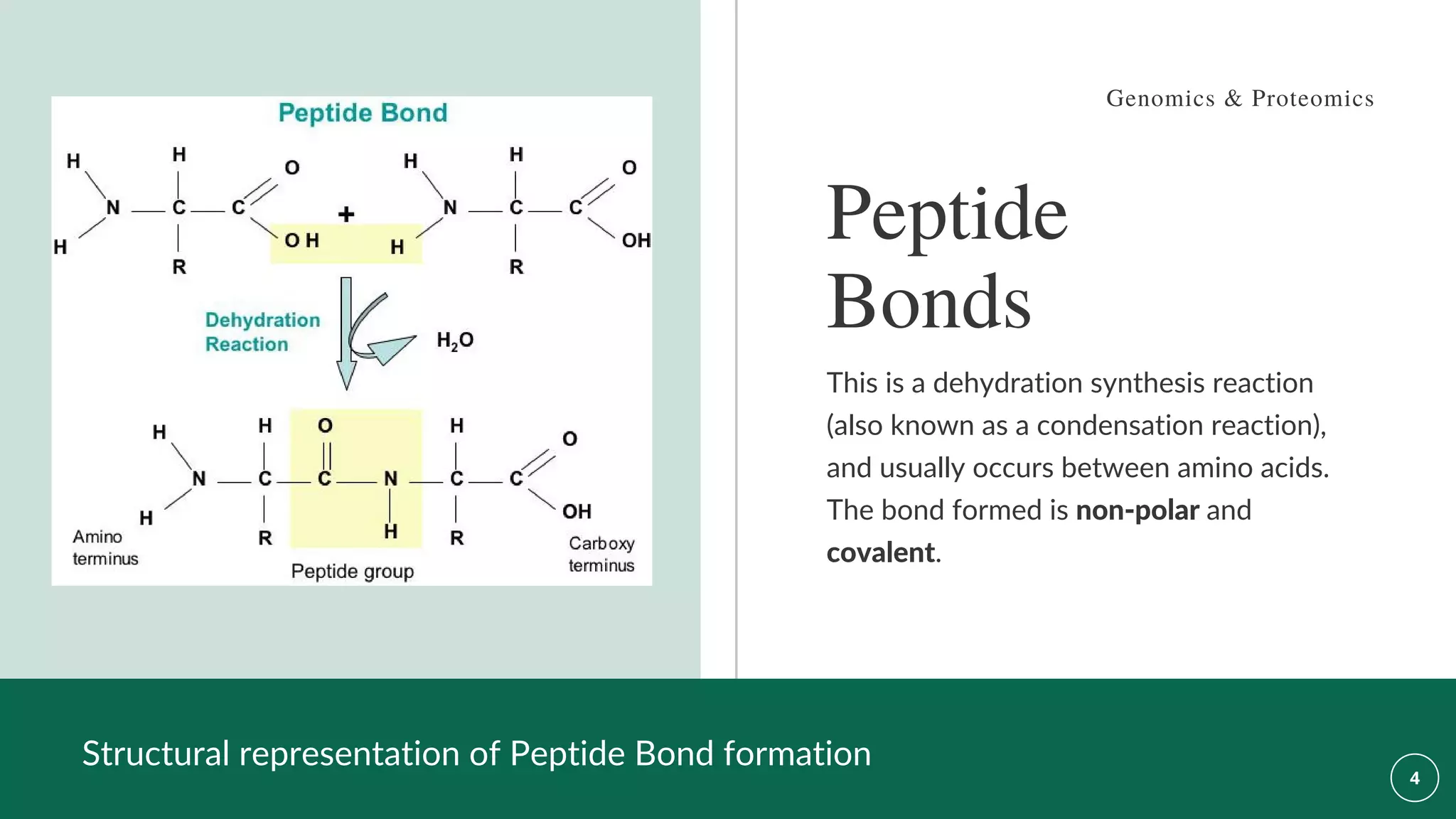
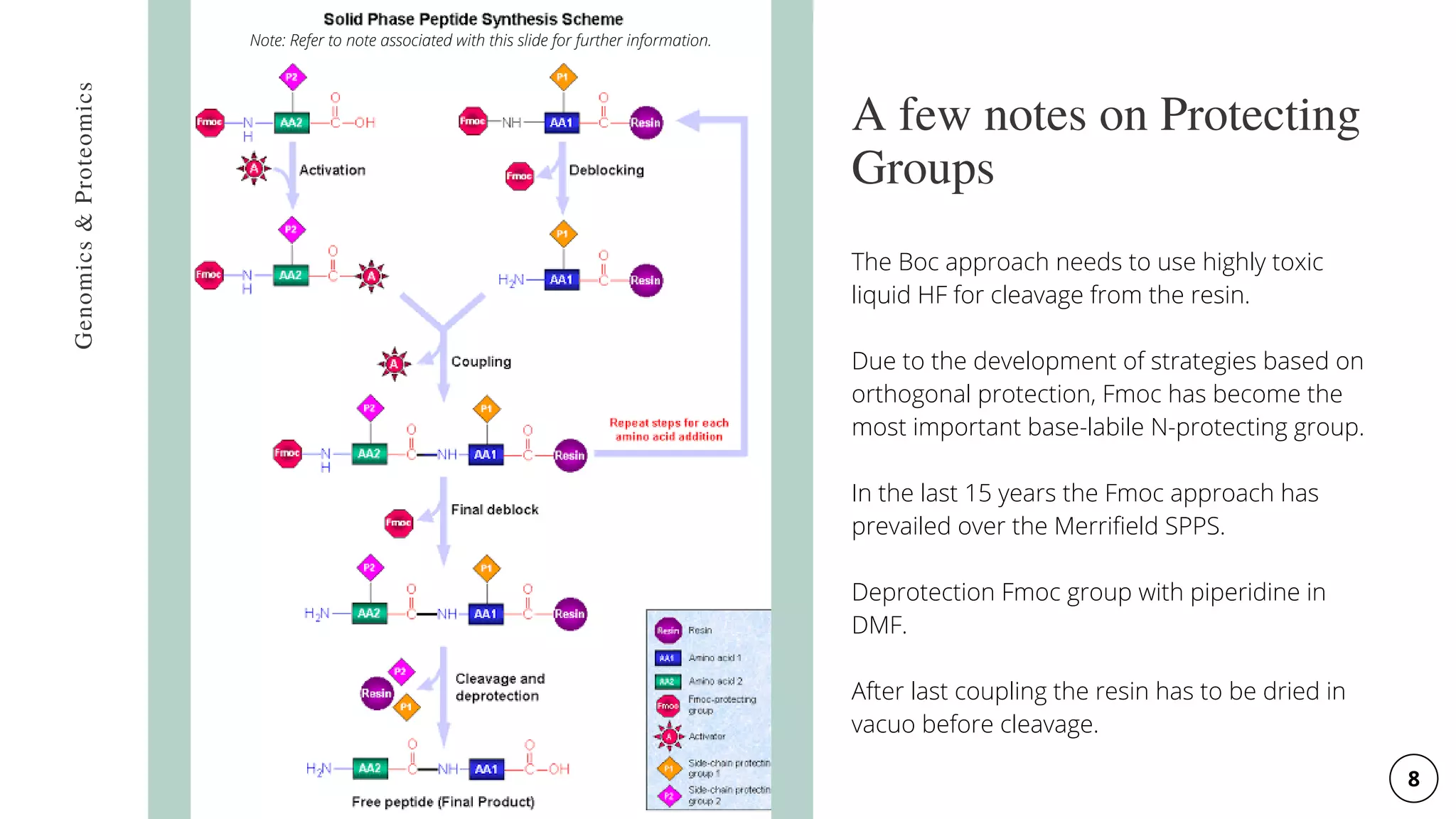
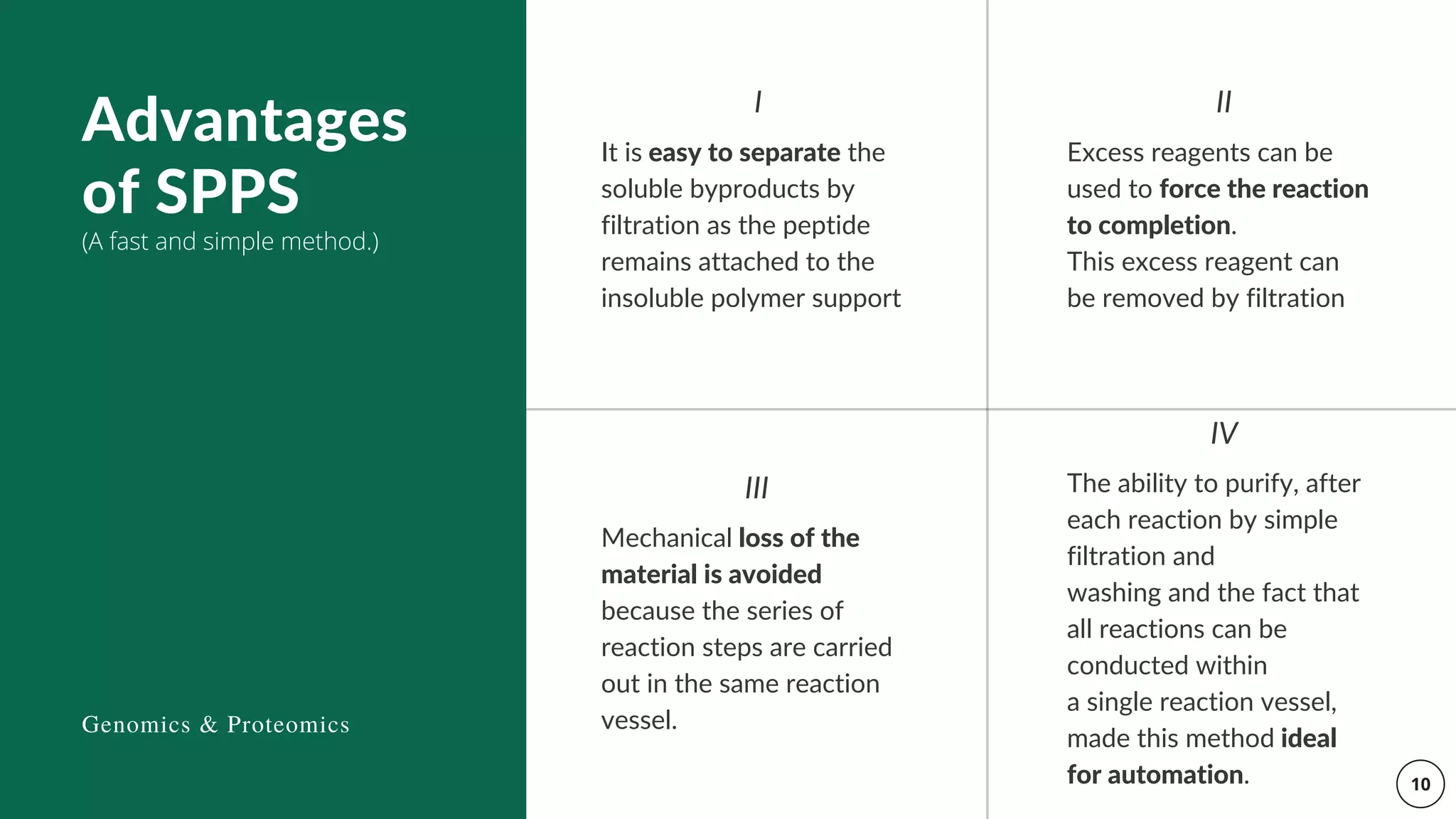
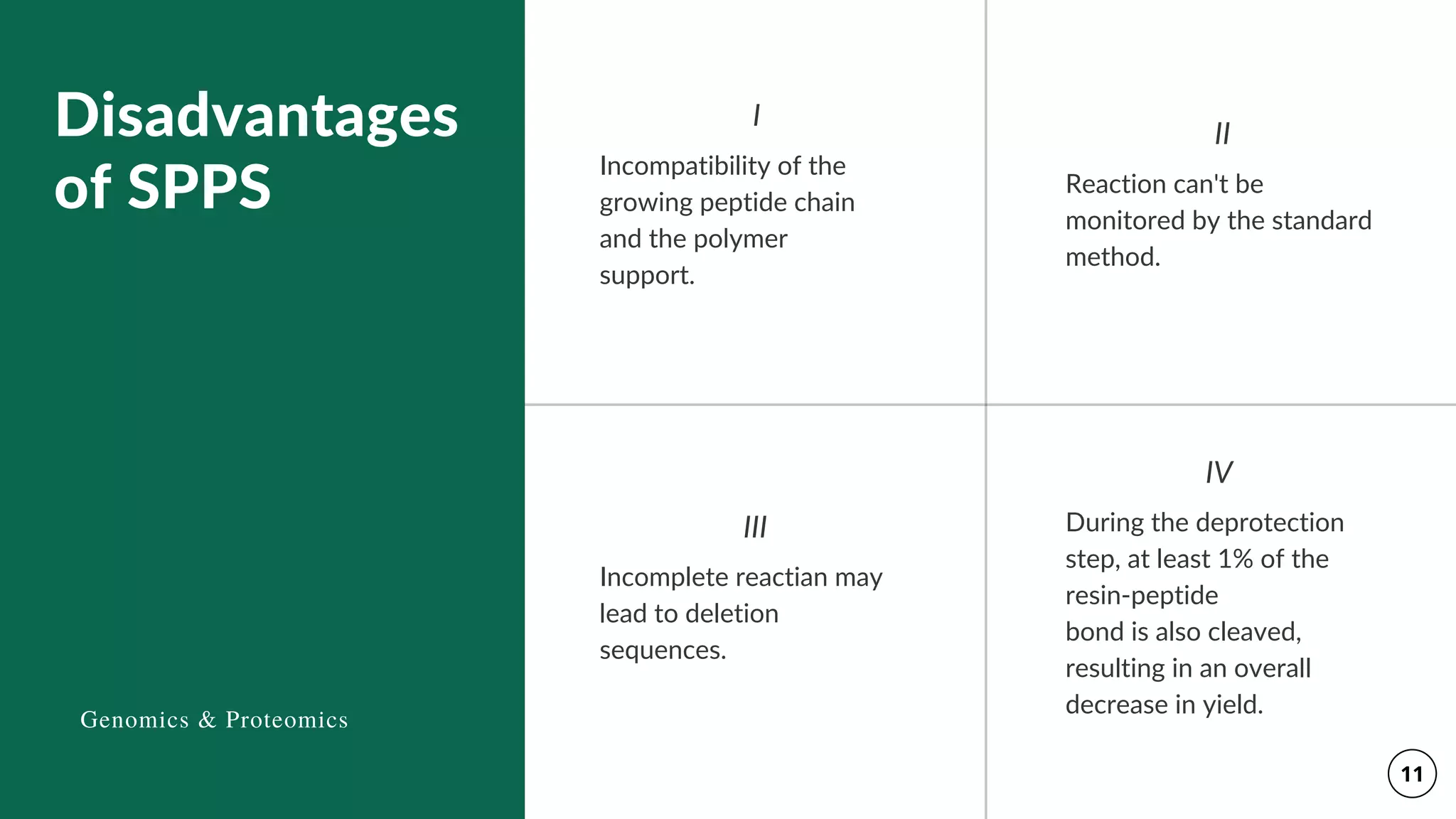
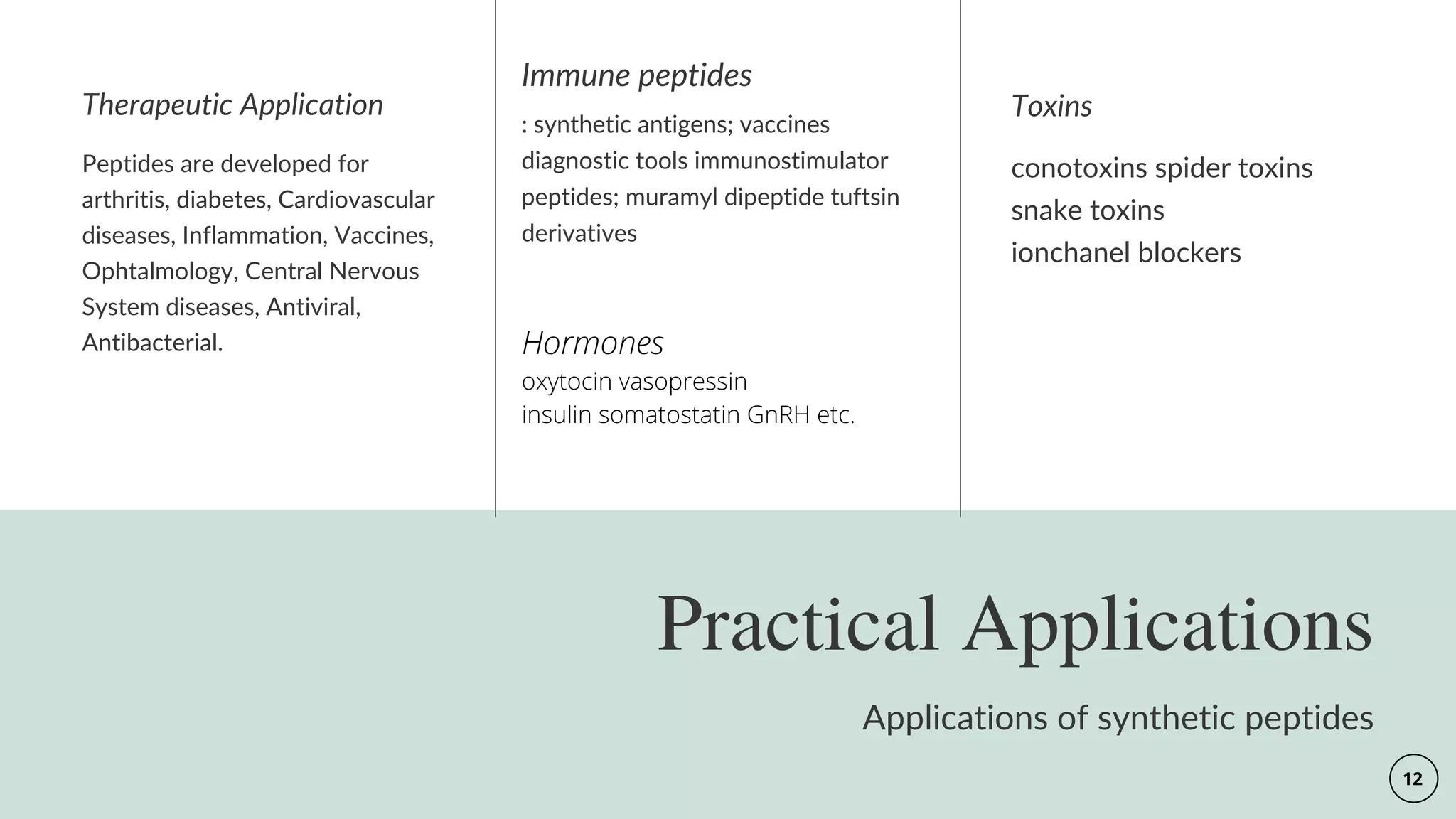
The document discusses the Merrifield solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) methodology, detailing its principles, advantages, disadvantages, and applications in various therapeutic areas. It describes the importance of peptide bonds, the use of solid supports, and the challenges of reaction compatibility and monitoring. The document also emphasizes the relevance of synthetic peptides in medicine, including potential treatments and diagnostic tools.