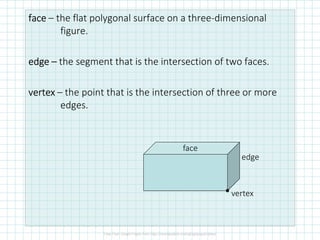
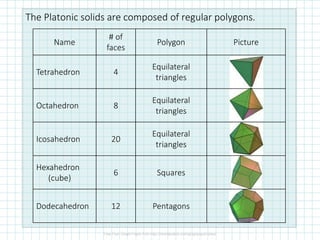
Solid geometry involves classifying and analyzing three-dimensional shapes. Key concepts include polyhedra composed of polygons, prisms with two parallel congruent bases, pyramids with a polygonal base meeting at a common vertex, and using nets which can be folded to form three-dimensional shapes. Formulas relate the number of vertices, edges and faces of polyhedra. Surface area calculations involve finding the total area of each face.