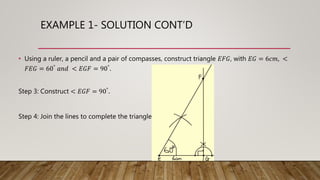
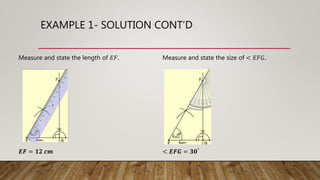
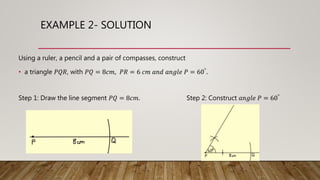
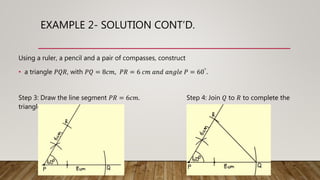
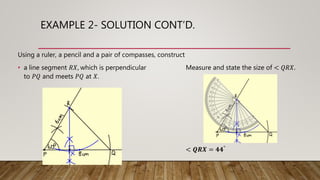
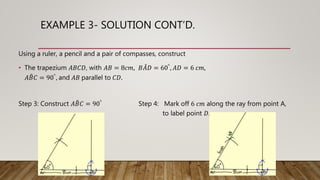
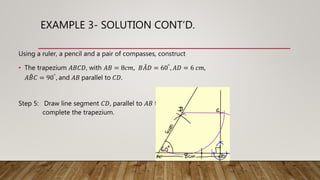
This document provides worked examples for constructing geometric shapes using a ruler, pencil, and compass. It includes three examples of constructing different shapes step-by-step: 1) a triangle with given side lengths and angles, 2) a triangle with a perpendicular line segment, and 3) a trapezoid with given side lengths and angles. The examples show the step-by-step construction of each shape and measure any required lengths or angles.