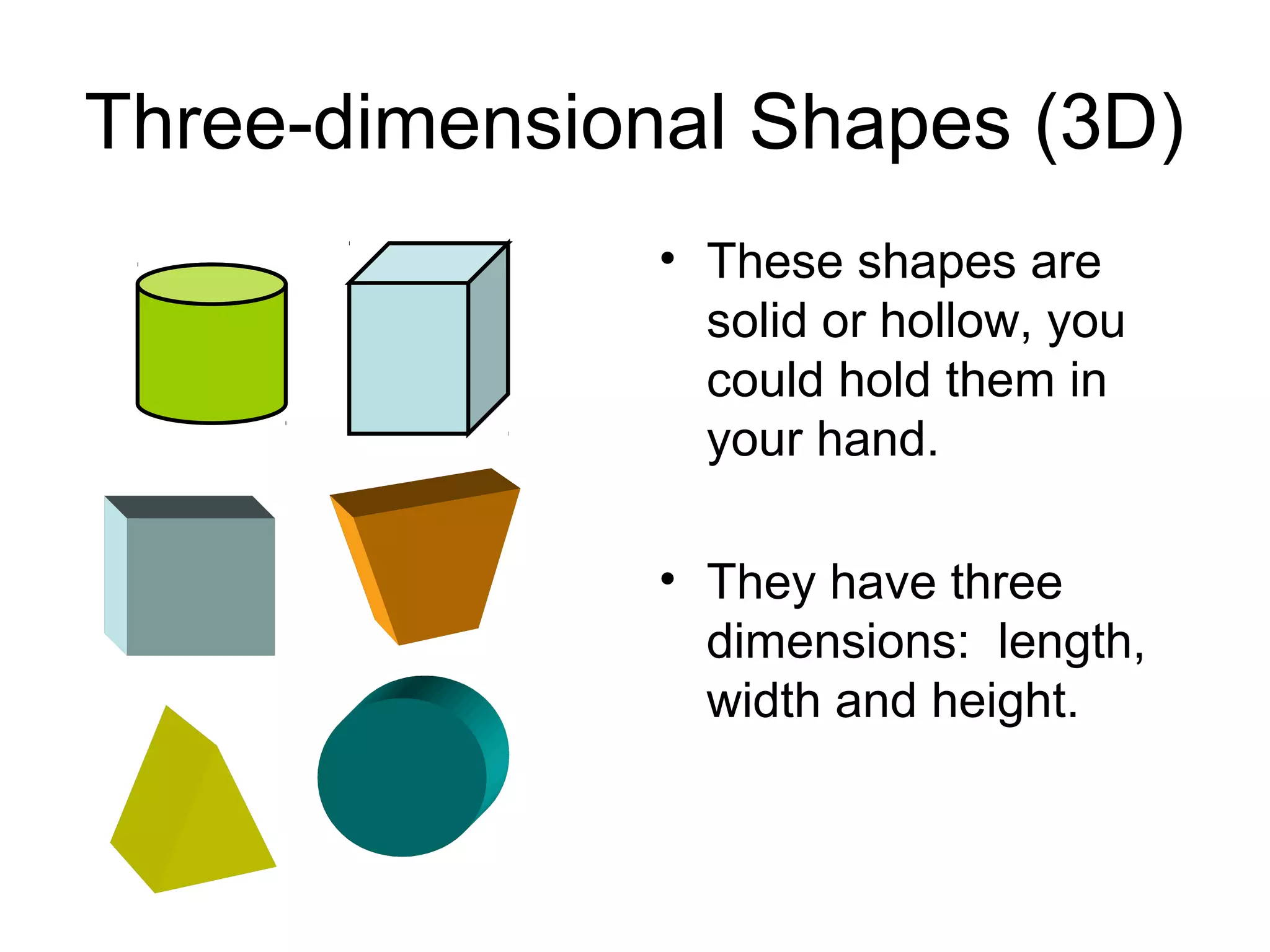
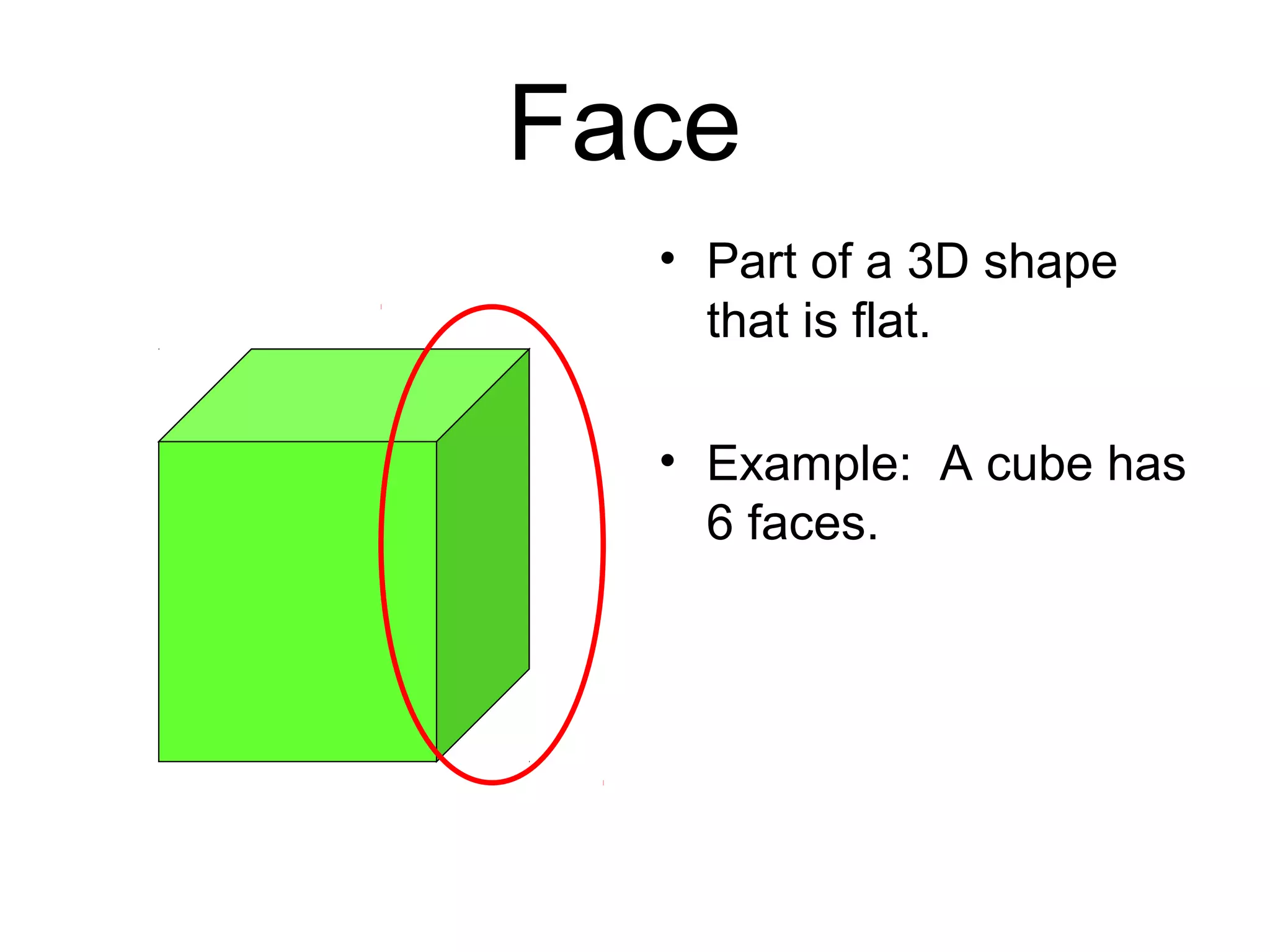
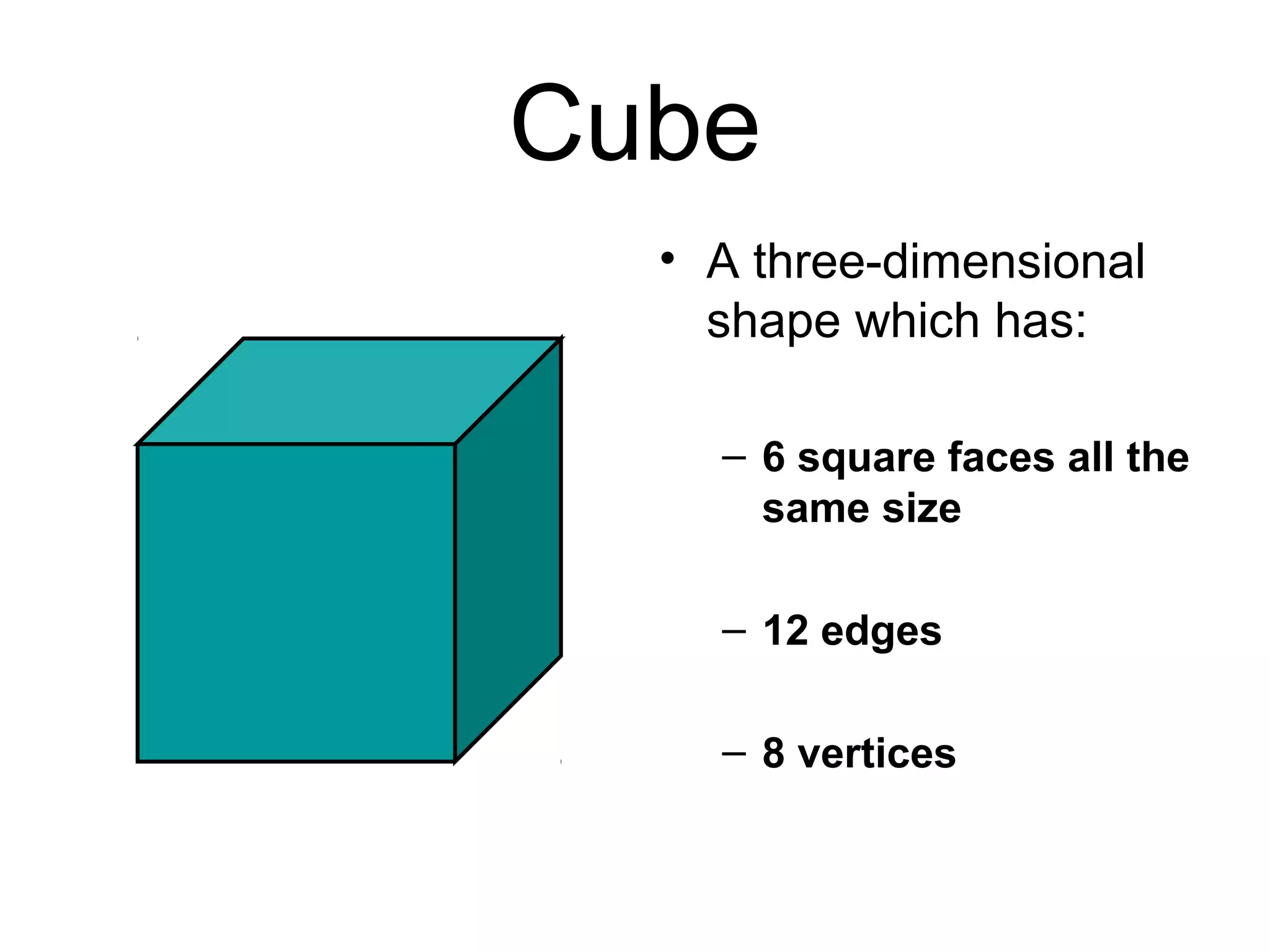
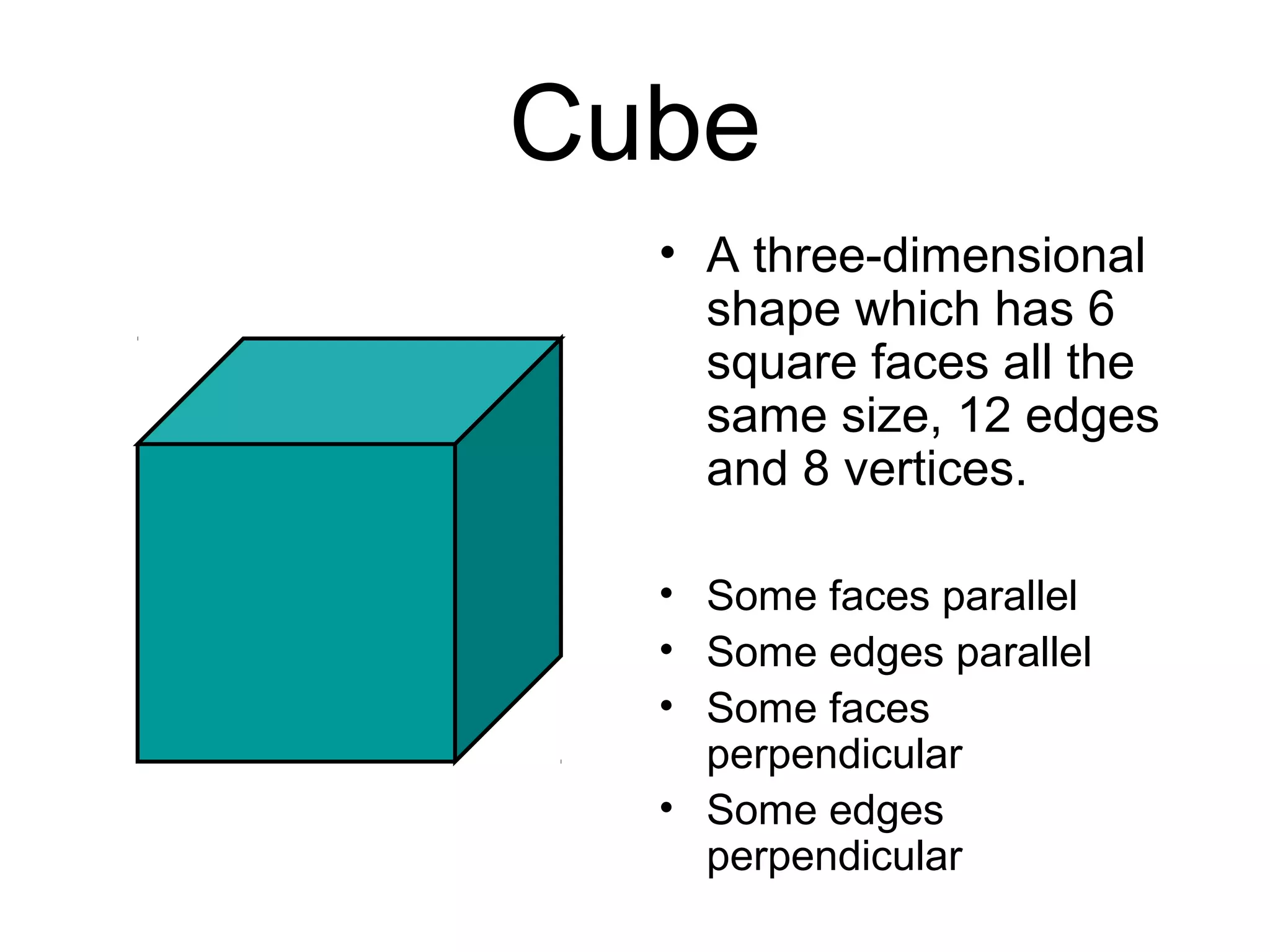
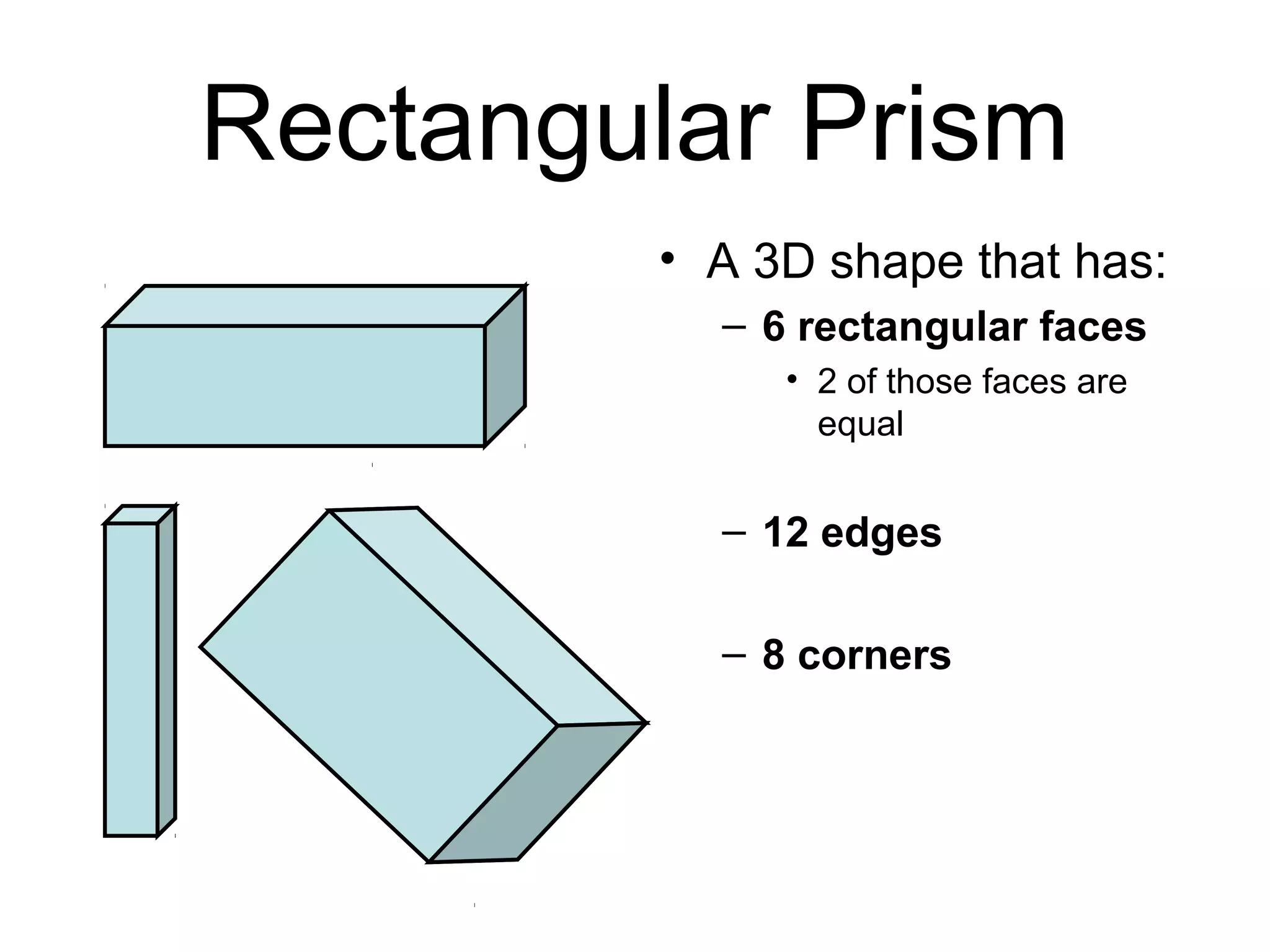
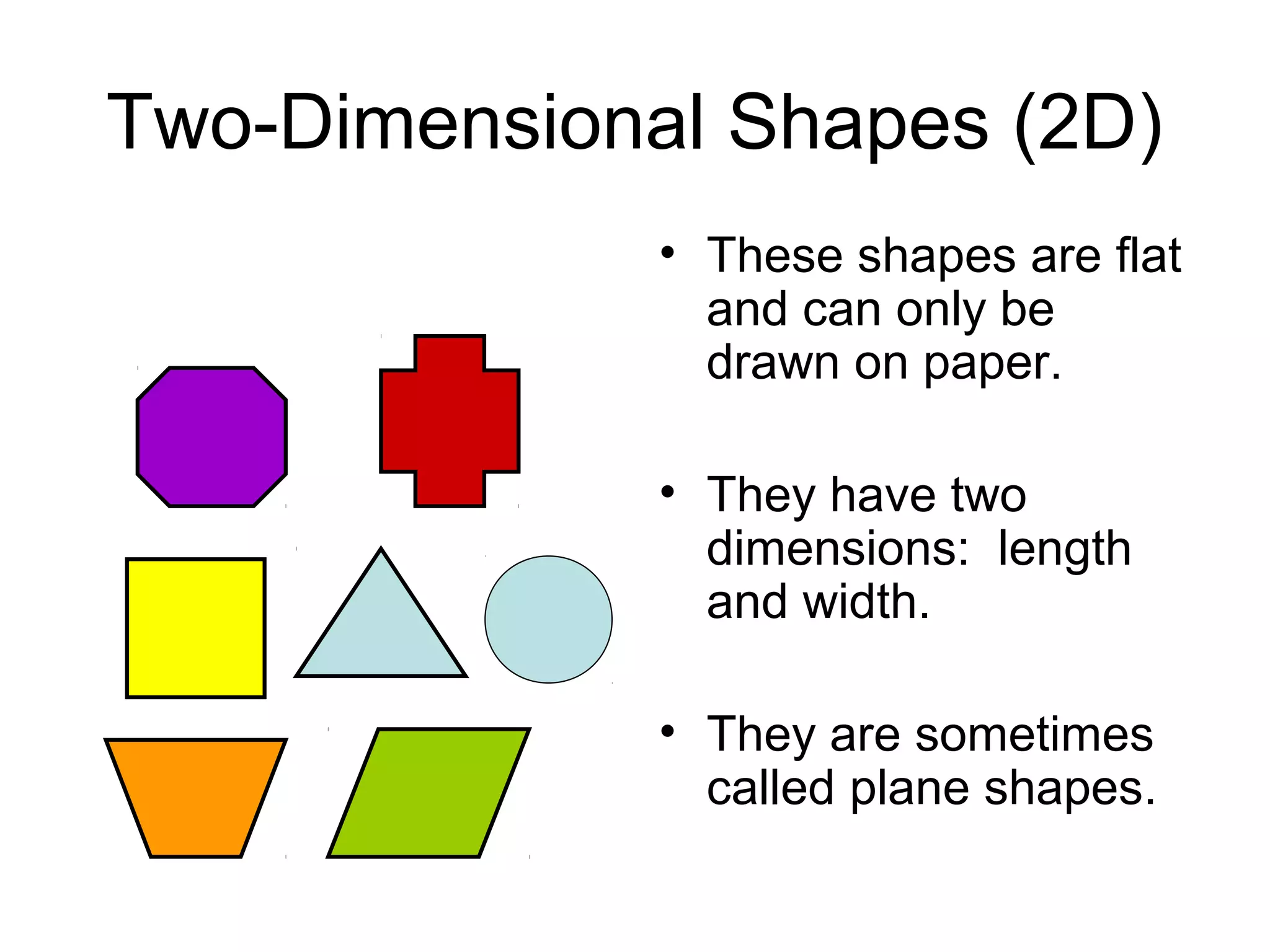
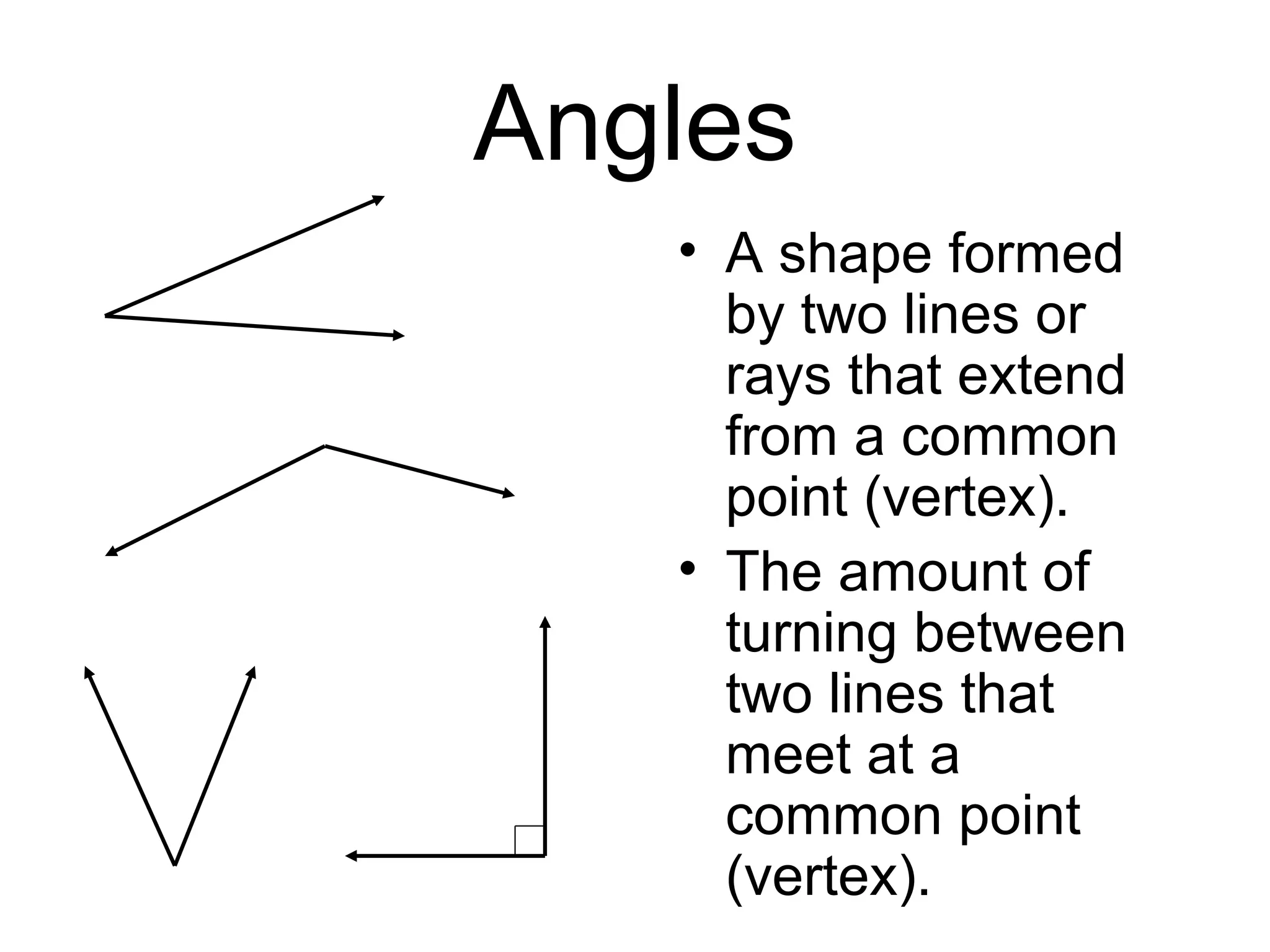
This document defines and provides examples of various 3D and 2D shapes. It discusses 3D shapes like cubes, spheres, cones and cylinders. It explains they have dimensions of length, width, height and describes features like faces, edges, vertices and surfaces. It also defines 2D shapes such as triangles, rectangles, circles and discusses their sides, angles and other properties. Various properties of lines, angles and symmetry are also outlined.