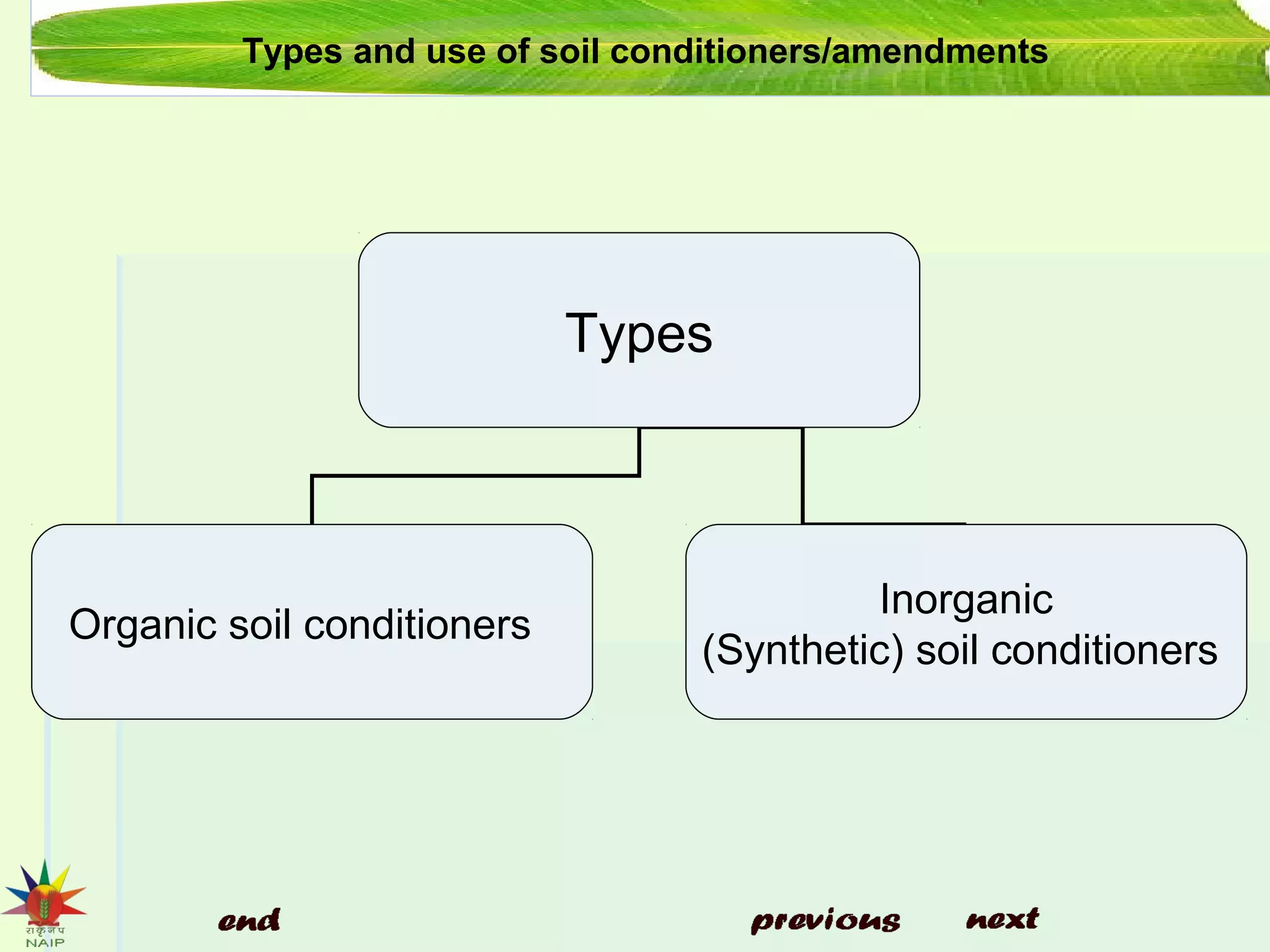
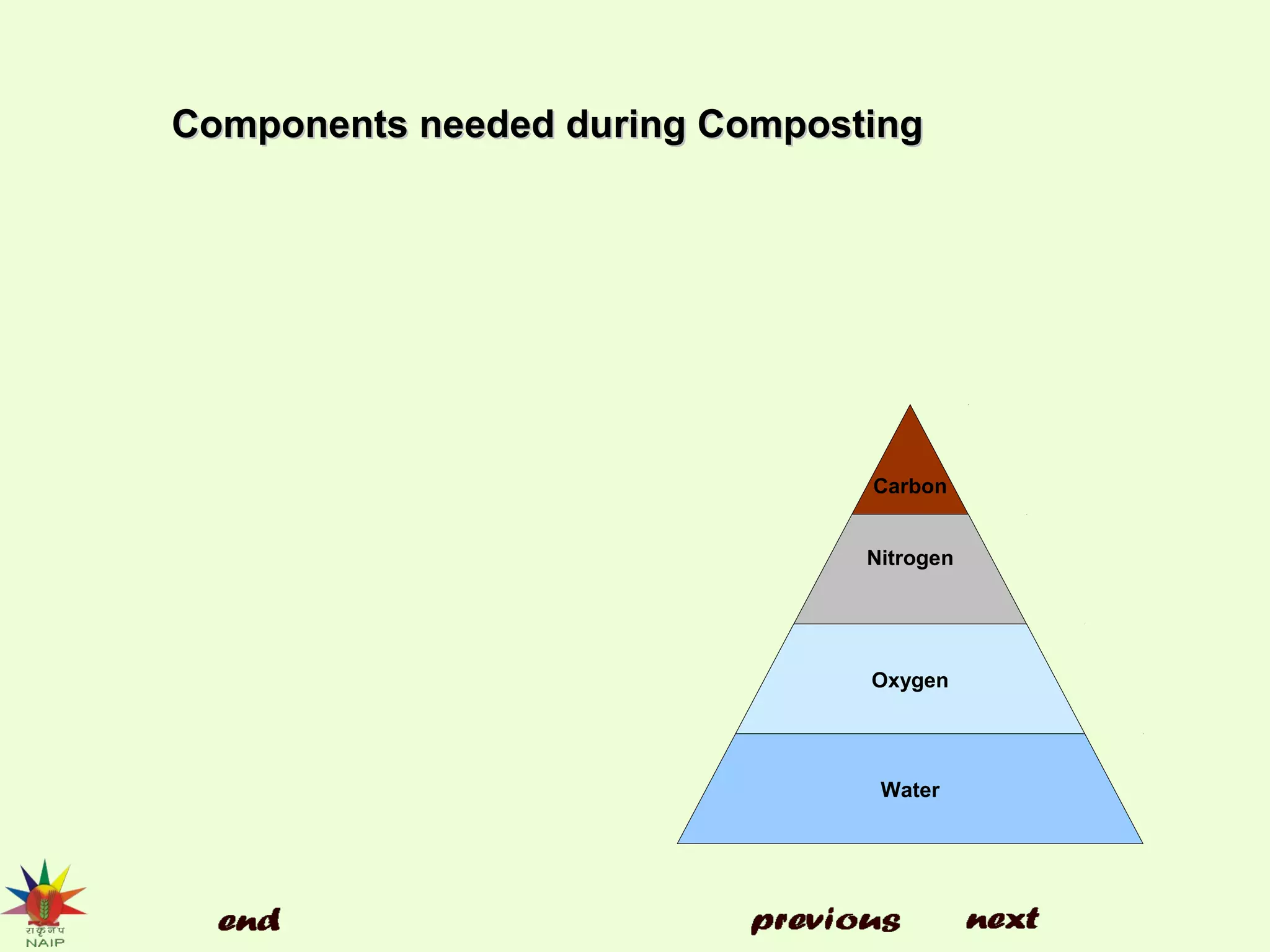
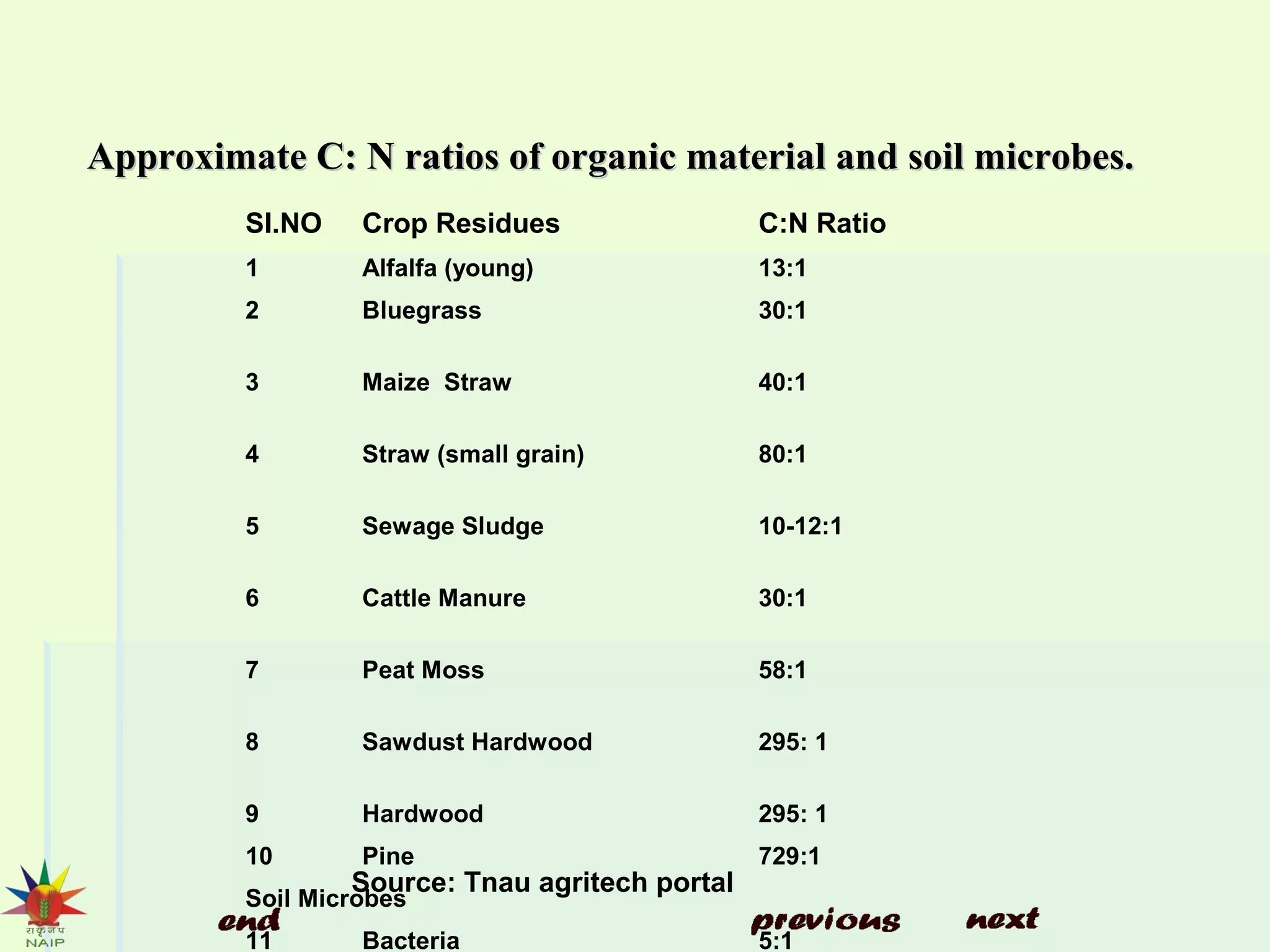
The document discusses soil conditioners or amendments, detailing their importance in enhancing soil quality for improved plant growth. It describes various types of organic and inorganic conditioners, their functions, benefits, and examples such as compost, manure, and gypsum. Additionally, it emphasizes the role of green manuring in enriching soil and boosting crop yields.