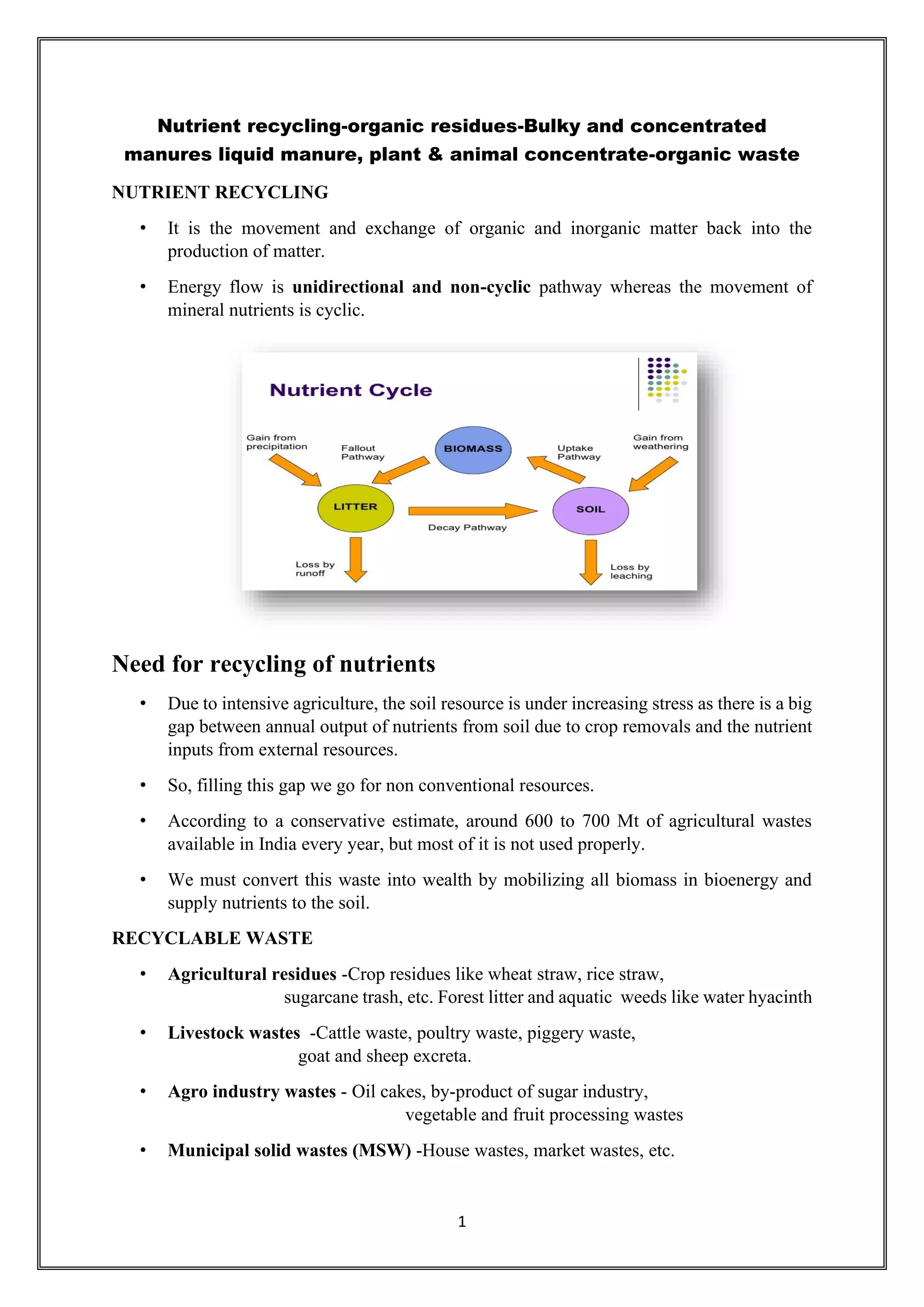
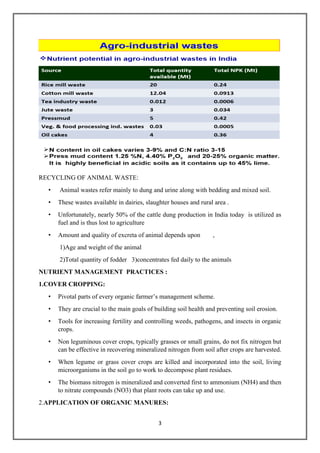
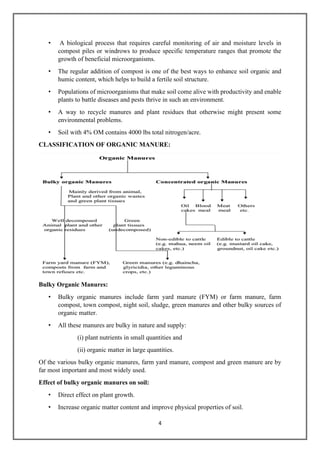
This document discusses various methods of nutrient recycling in agriculture, including the use of crop residues, animal wastes, agro-industry wastes, municipal solid wastes, and industrial wastes. It describes different types of organic manures like farm yard manure, compost, green manures, night soil, sewage sludge, and concentrated organic manures like oilcakes and bone meal. Nutrient recycling is important for sustainable agriculture to replenish soil nutrients removed by crops. Organic manures improve soil health by increasing organic matter content and supporting beneficial soil microorganisms.