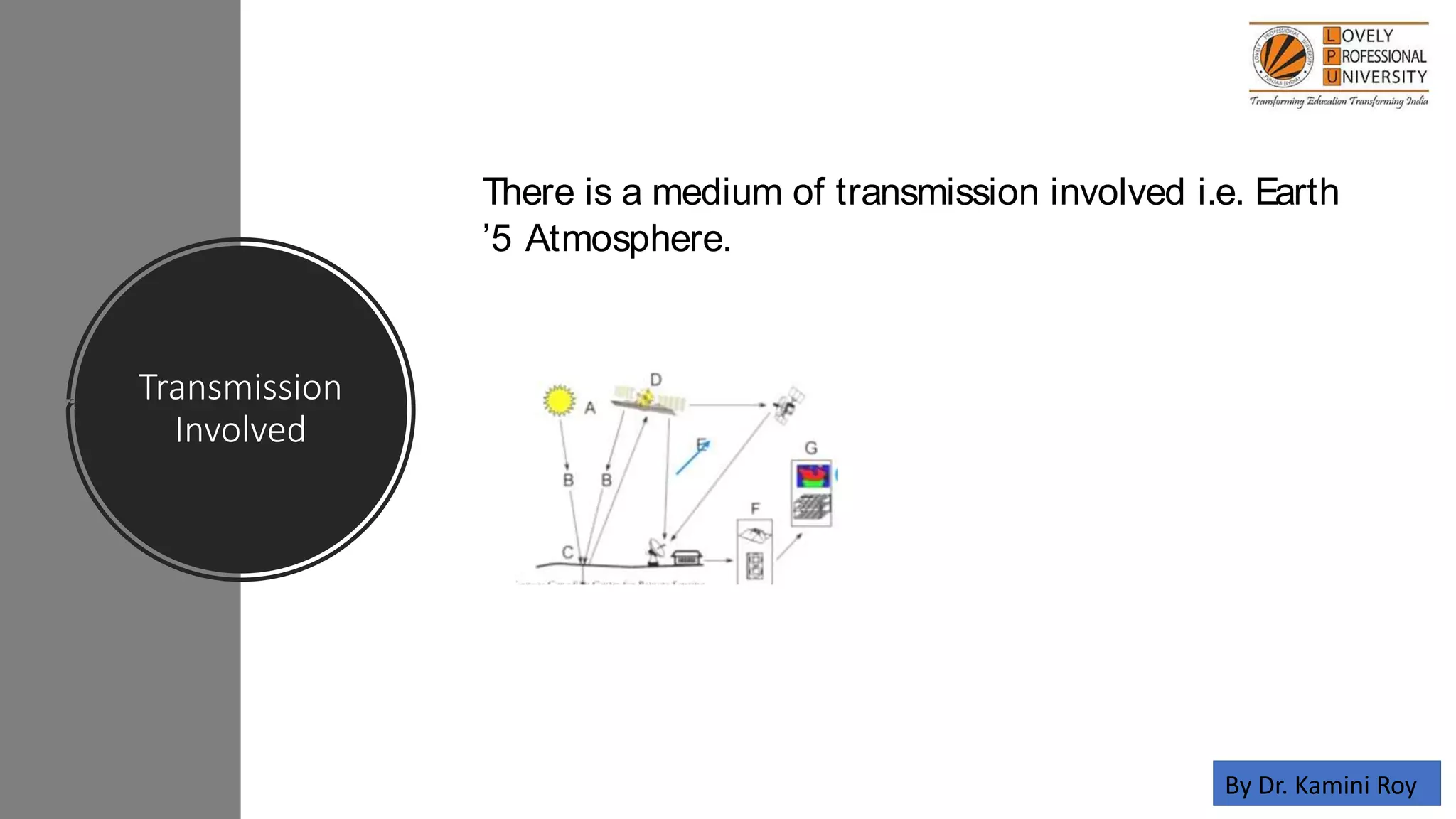
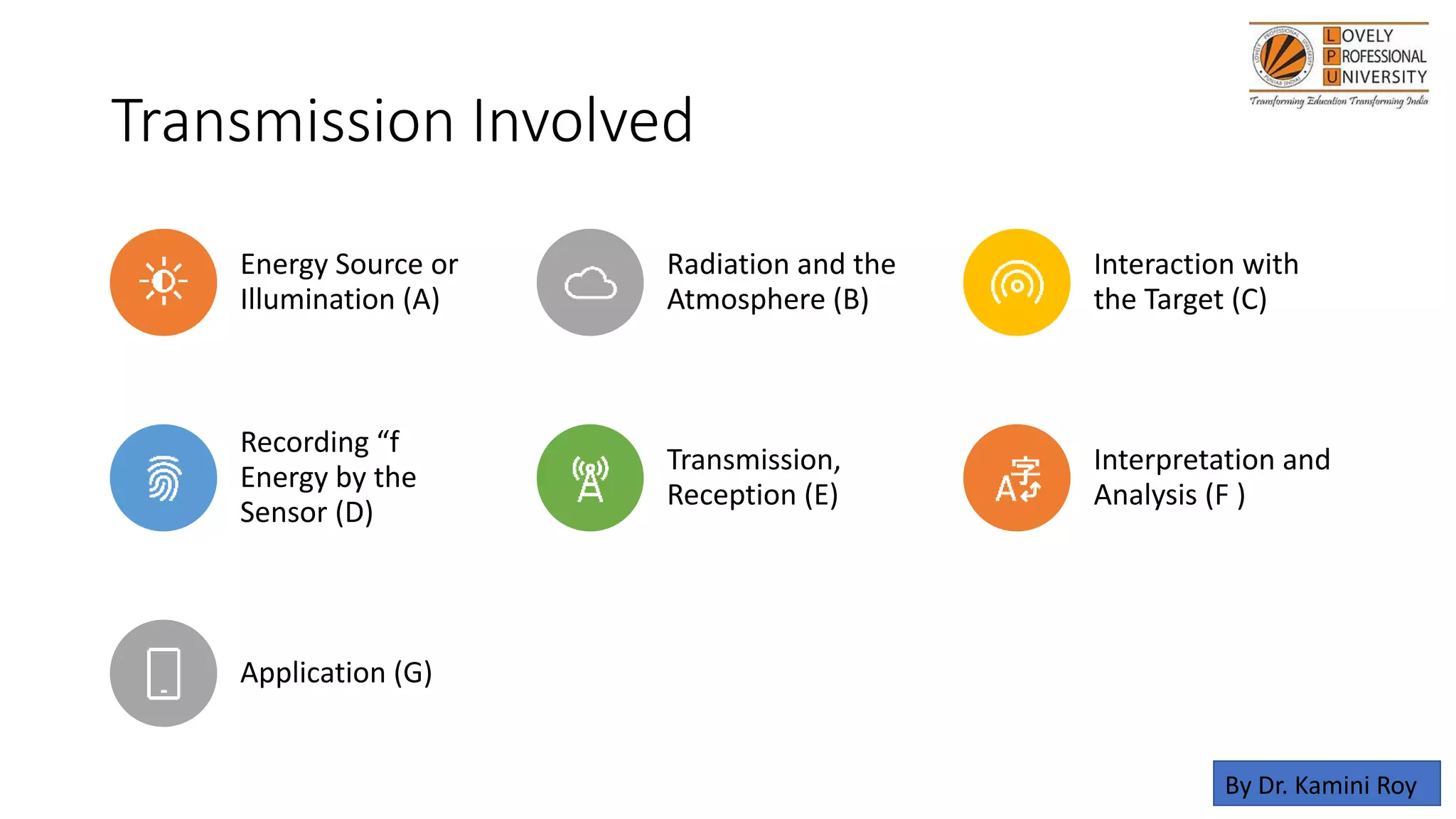
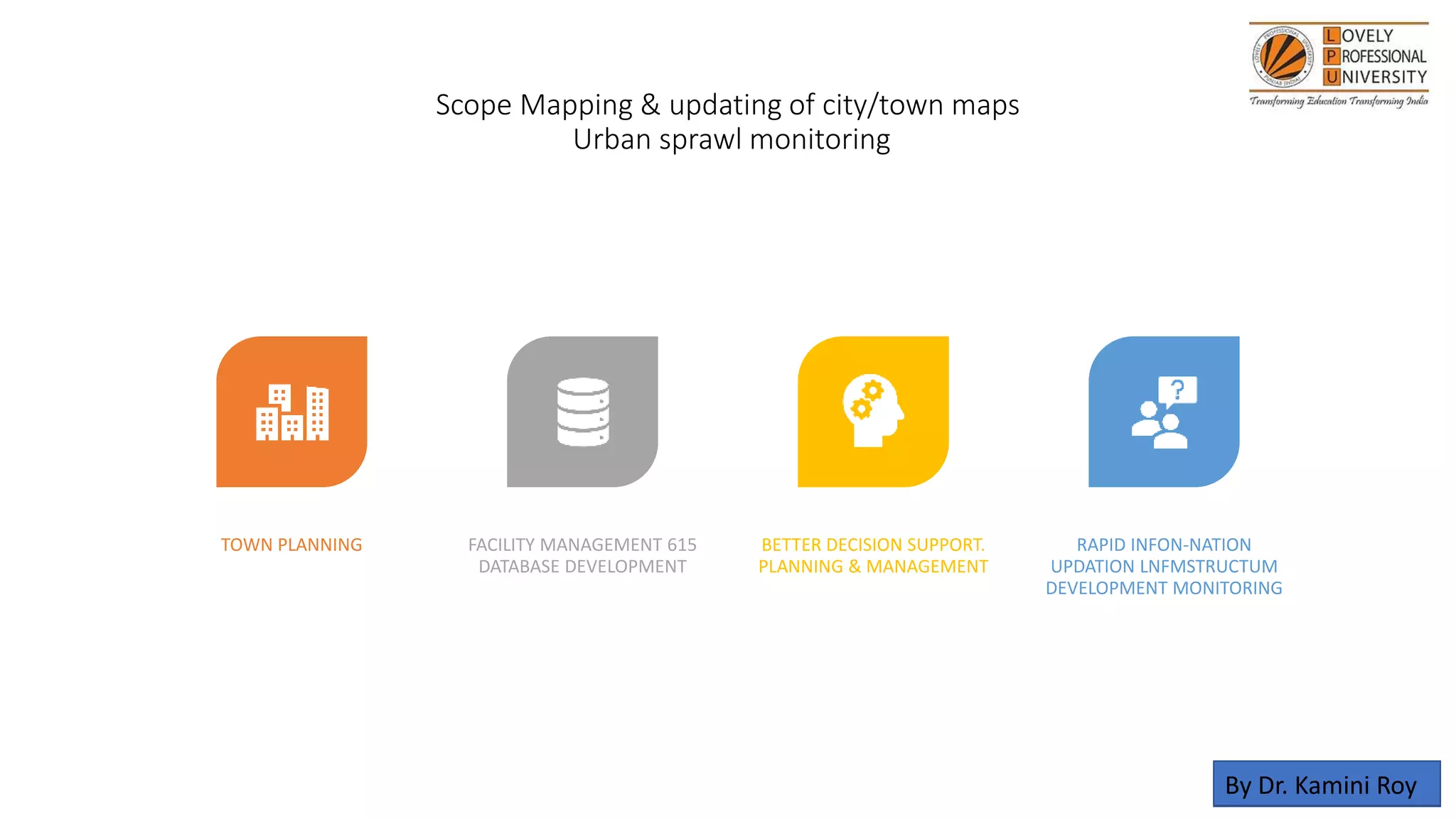
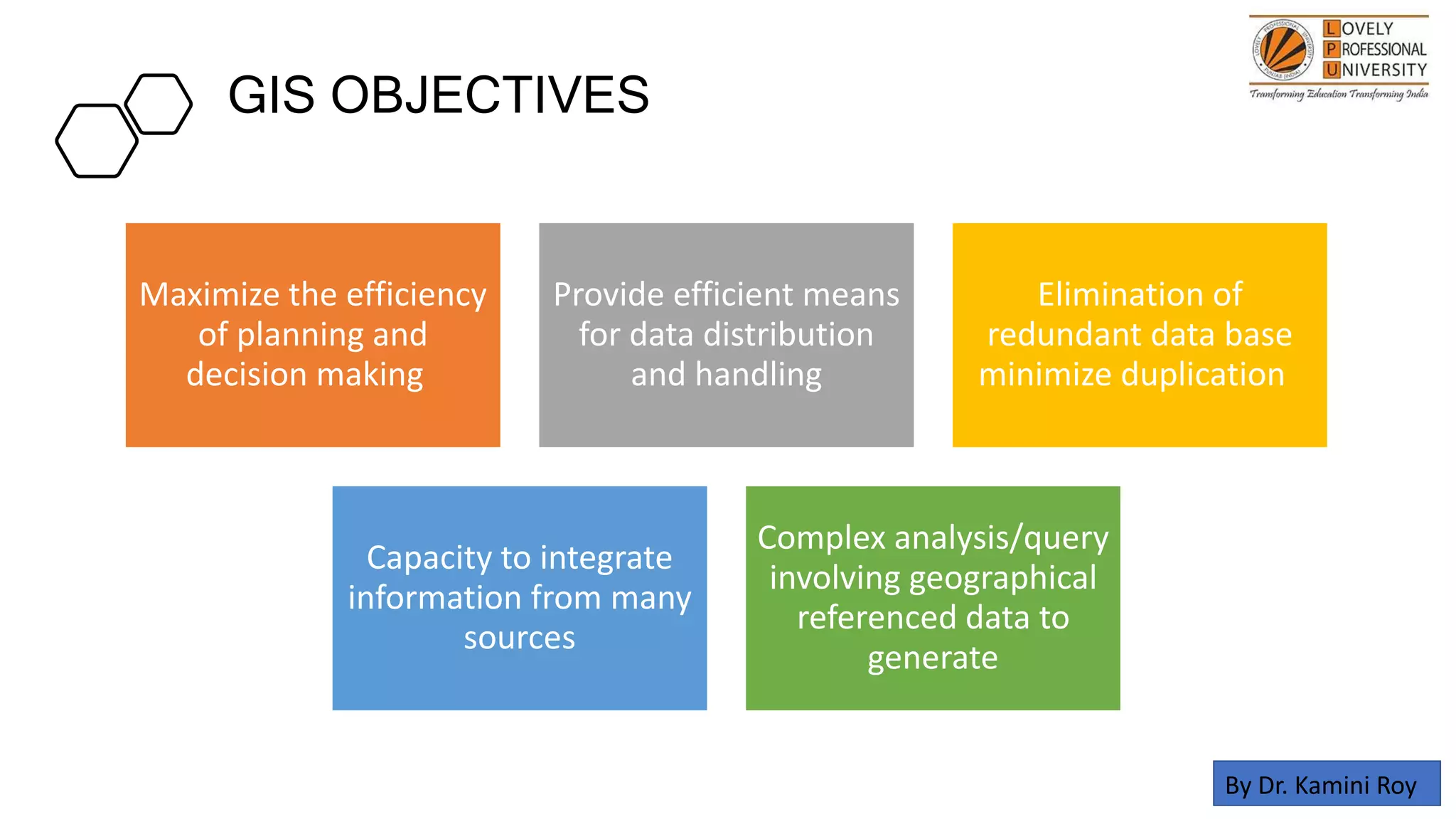
The document discusses the applications of remote sensing and GIS in diagnosing and managing problem soils, highlighting their roles in agriculture, forestry, geology, and urban planning. It covers processes involved in remote sensing, such as data collection and analysis, as well as the objectives of GIS in optimizing decision-making and data management. The author acknowledges various sources that contributed to the content of the presentation.