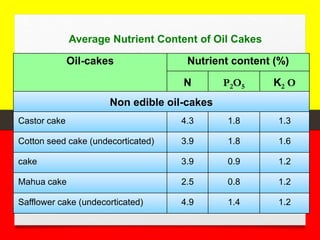
Organic farming relies on techniques like crop rotation, green manure, compost, and biological pest control to maintain soil fertility without using harmful chemicals. It defines organic farming and discusses its history, principles, and methods. Key aspects covered include using organic manures and pesticides, maintaining soil health, and rotating crops to replenish nutrients. Both advantages like increasing soil fertility long-term and reducing pollution, and disadvantages like potential lower initial yields are addressed.