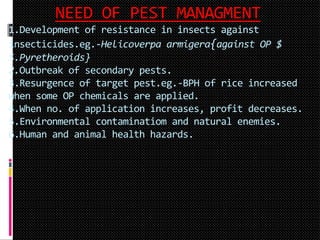
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) uses multiple methods to control pests in an agricultural system. The backbone of IPM is the economic injury level concept. Reasons for adopting IPM include the development of pest resistance, secondary pest outbreaks from overuse of pesticides, and environmental and human health hazards from chemical contamination. IPM involves understanding the agricultural ecosystem, planning for low-cost and environmentally friendly pest control, and using a variety of control methods like cultural practices, host plant resistance, biological and chemical methods to maintain pest populations below economic thresholds. The objective of IPM is to reduce pest damage in a sustainable way without complete elimination of pests.