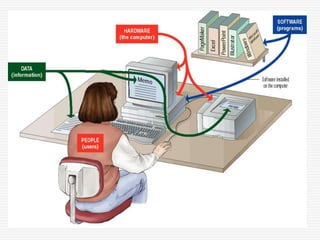
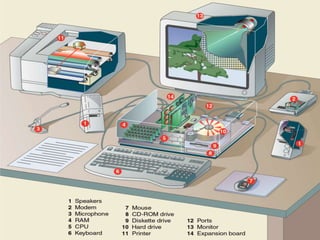
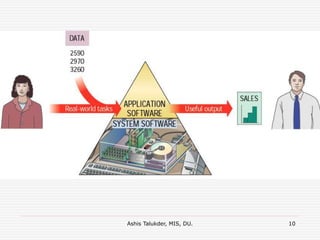
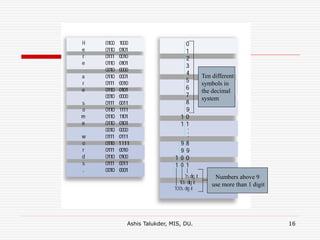
The document explains the fundamental components of a computer system, which includes hardware, software, data, and users. It highlights the process of data processing, consisting of capturing, manipulating, and managing data to create useful information. Additionally, it details the types of software, such as system and application software, and describes different user roles in operating computers.