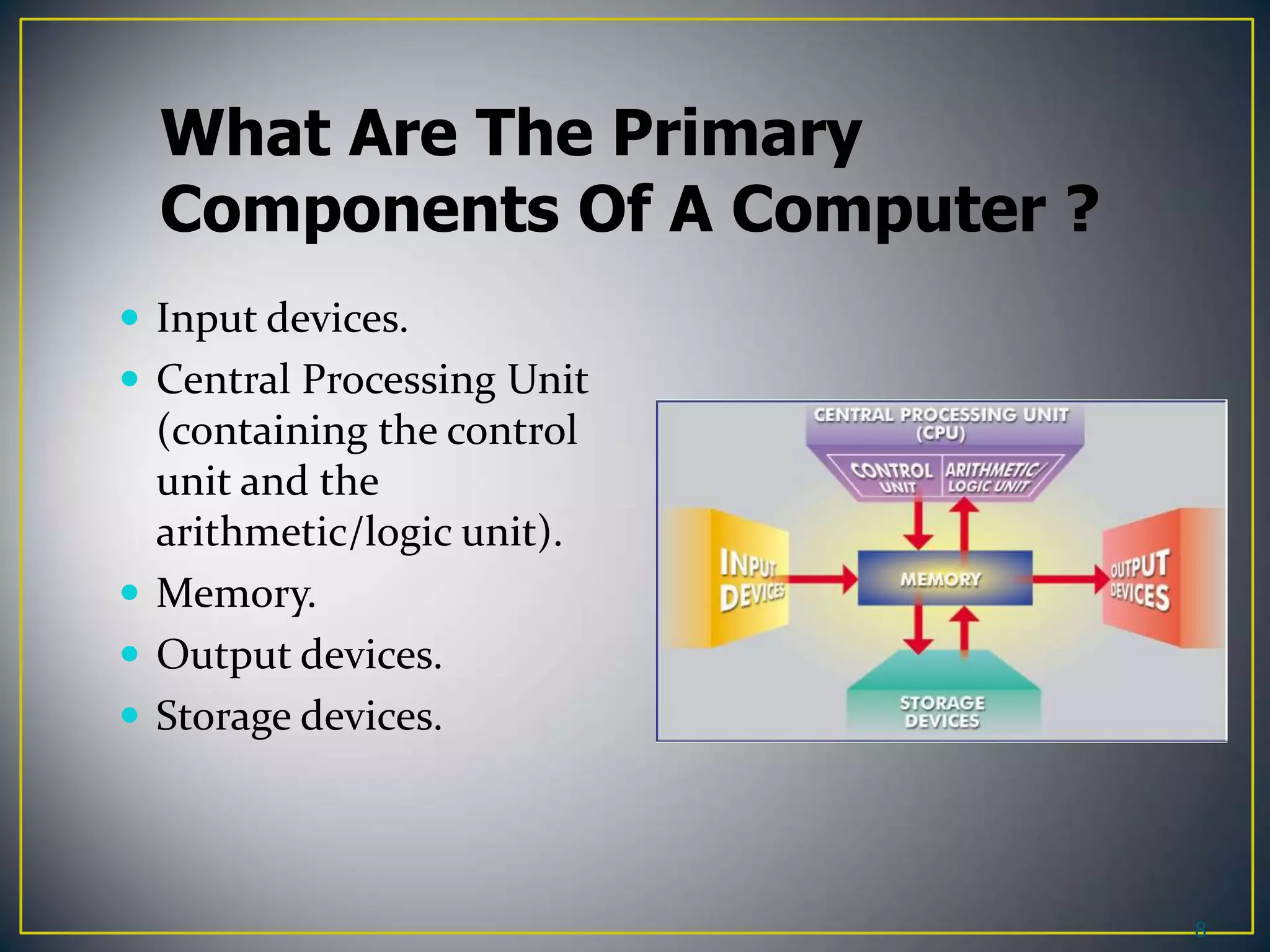
A computer is an electronic device that can accept data as input, process that data, and produce output in the form of information. It consists of central processing, memory, storage, and input/output devices. A computer performs four main functions: input, processing, output, and storage. It is able to manipulate large amounts of data at high speeds very accurately to create useful information.