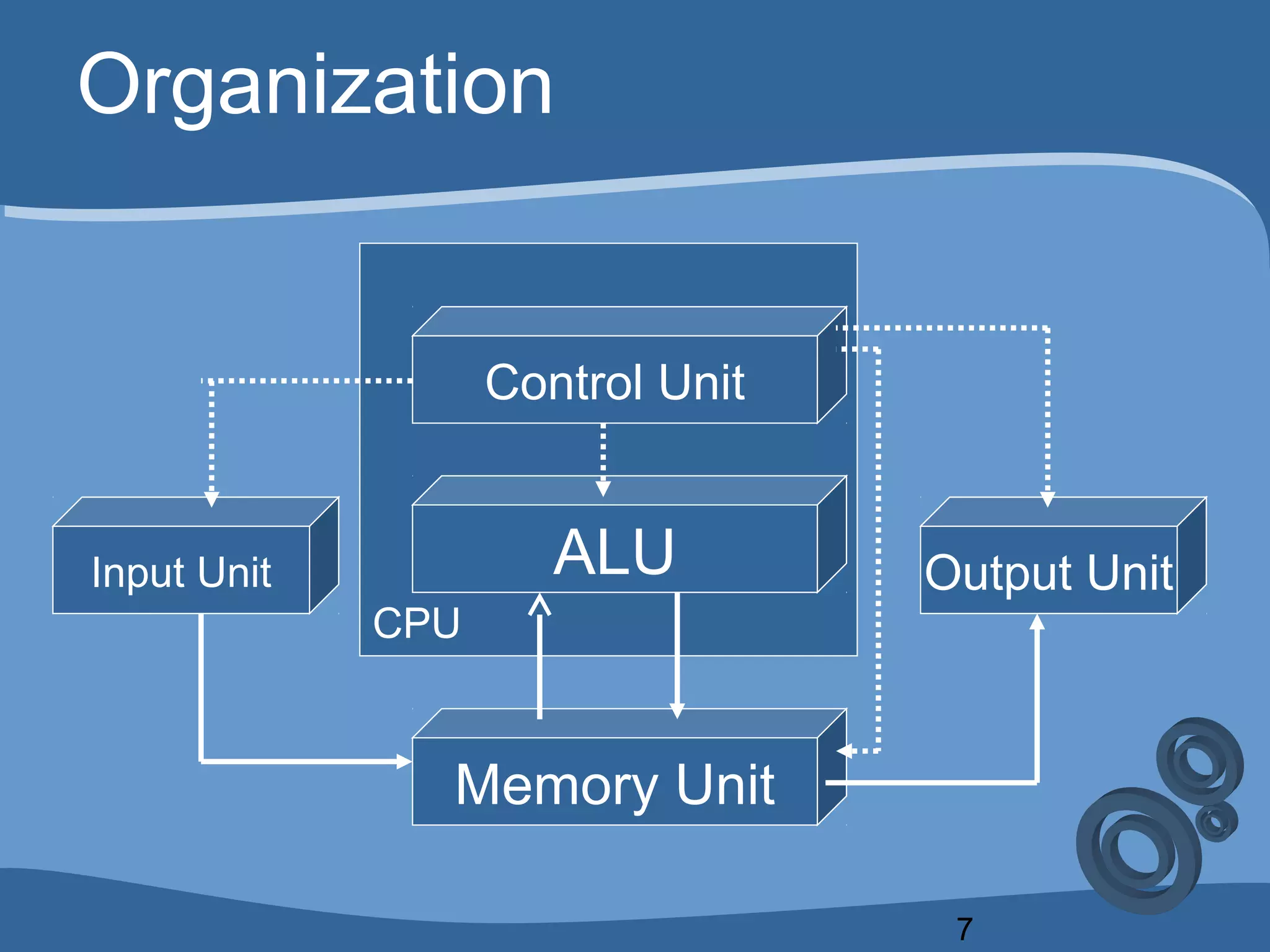
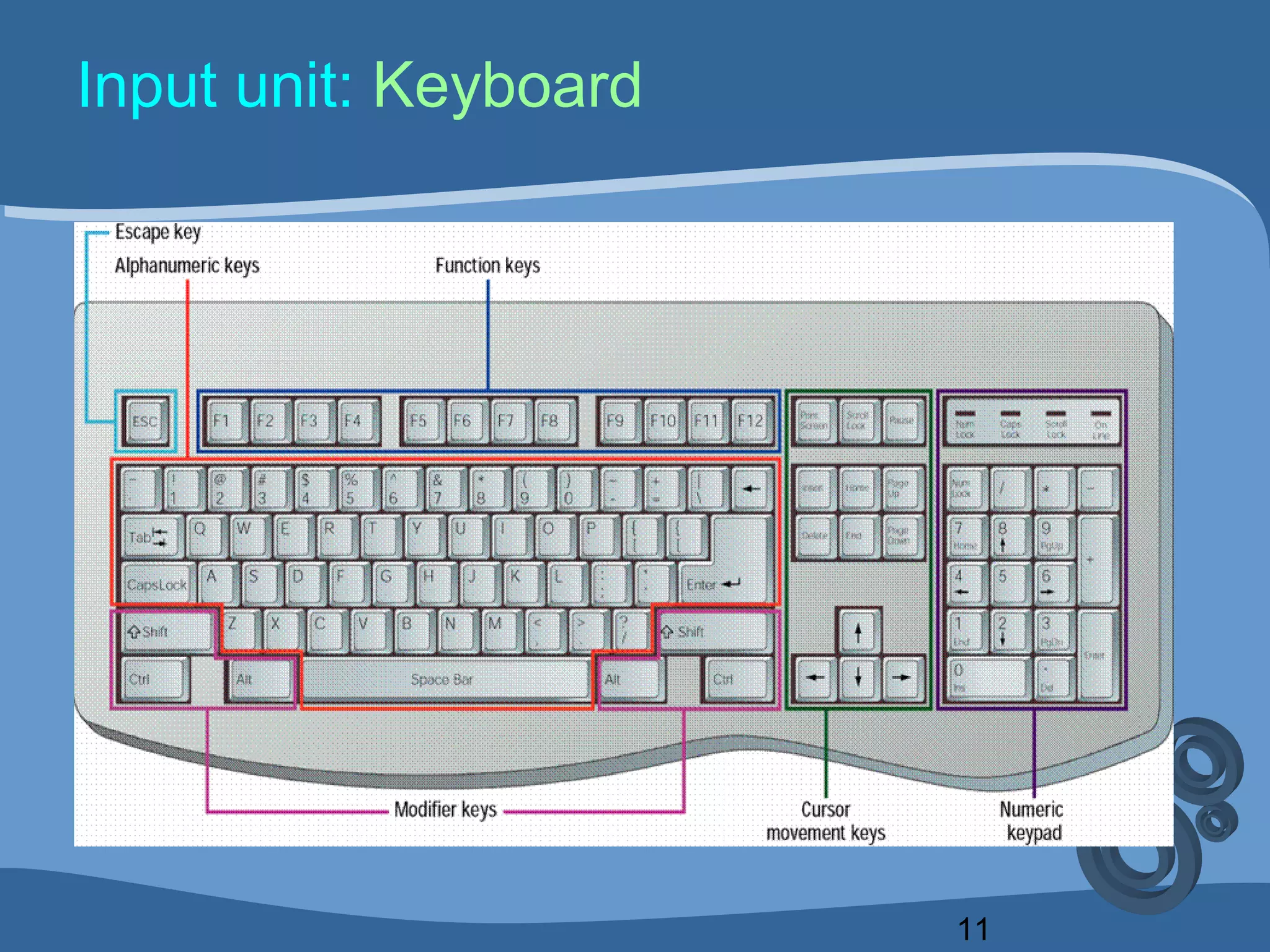
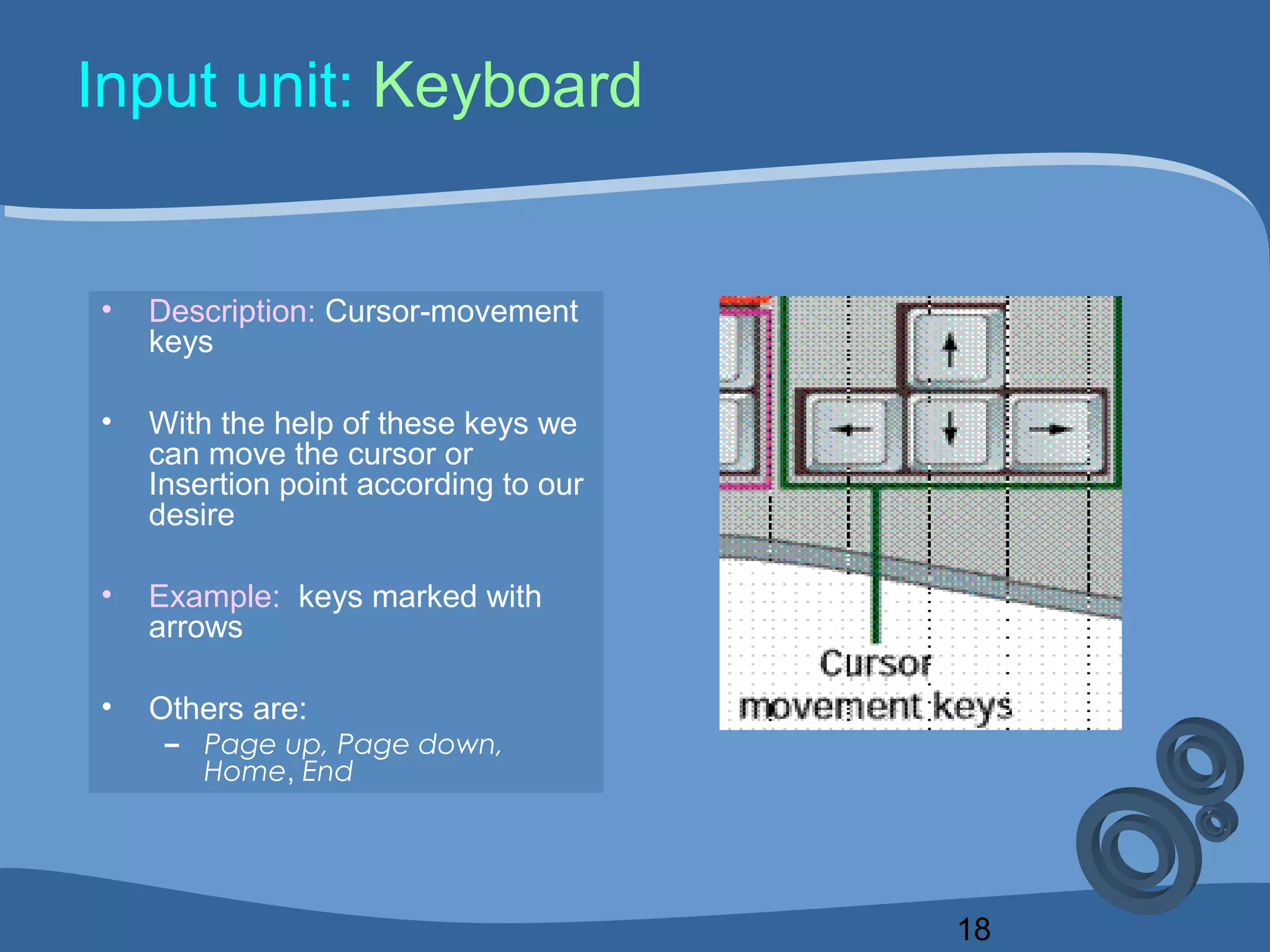
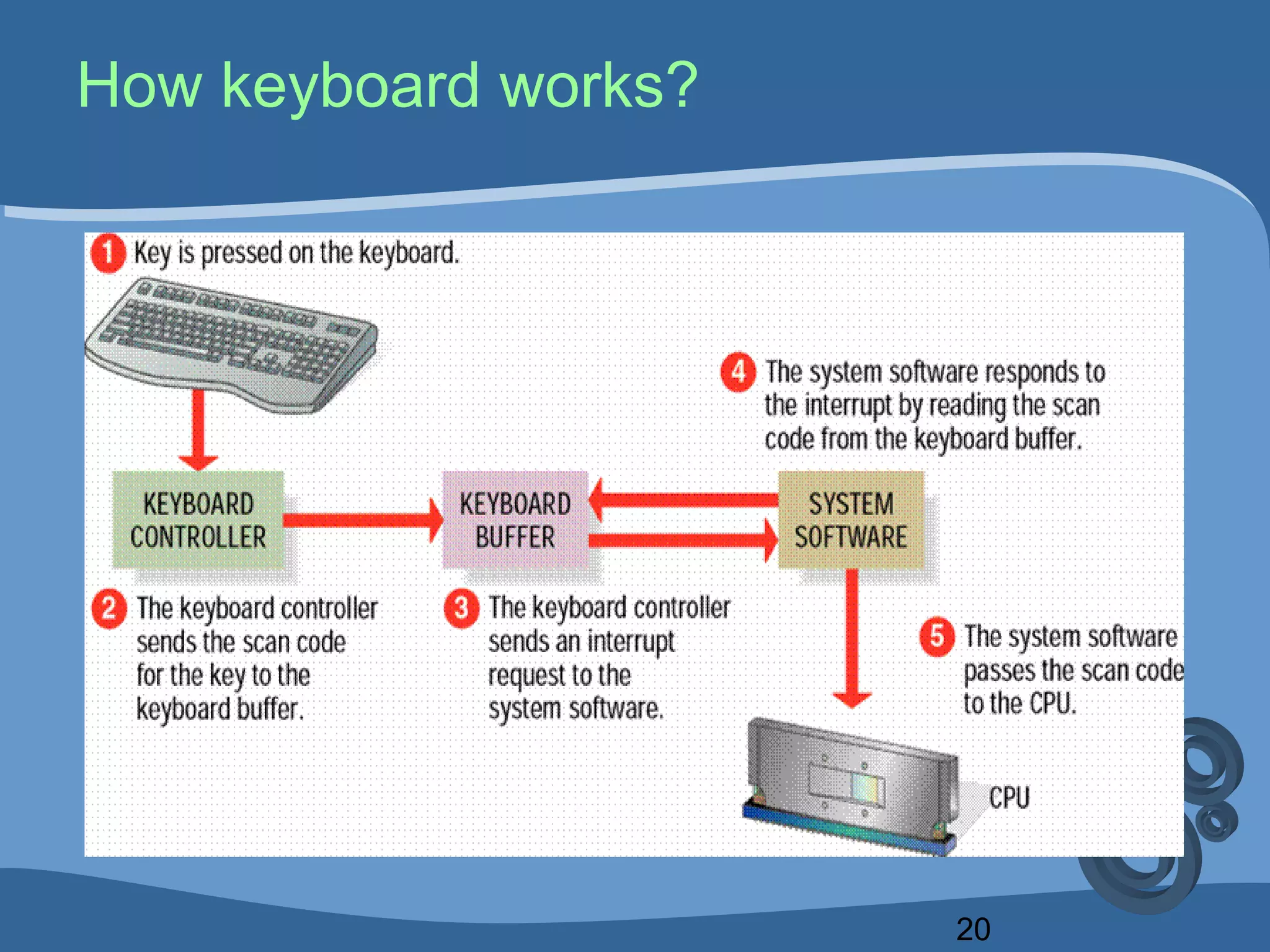
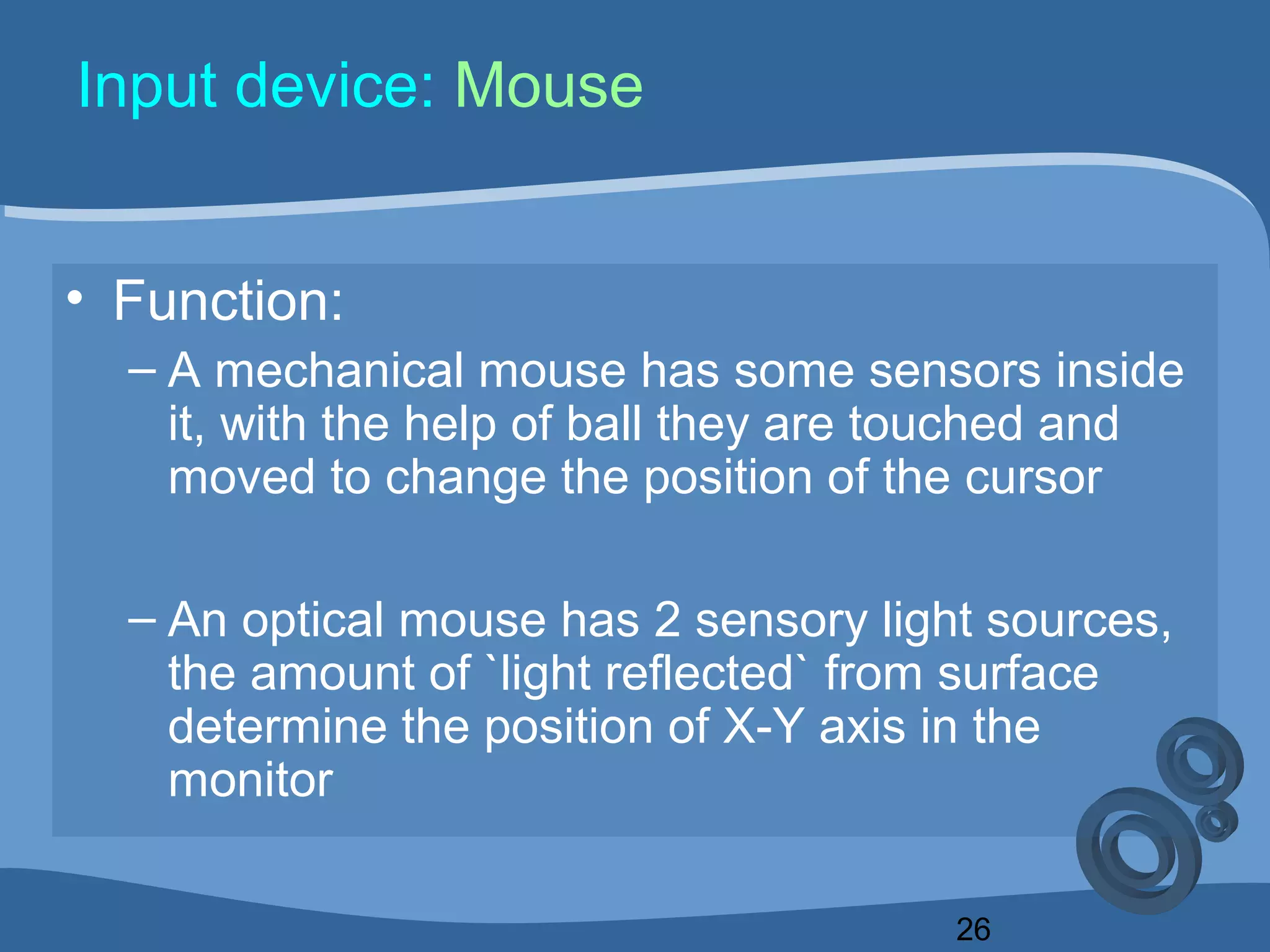
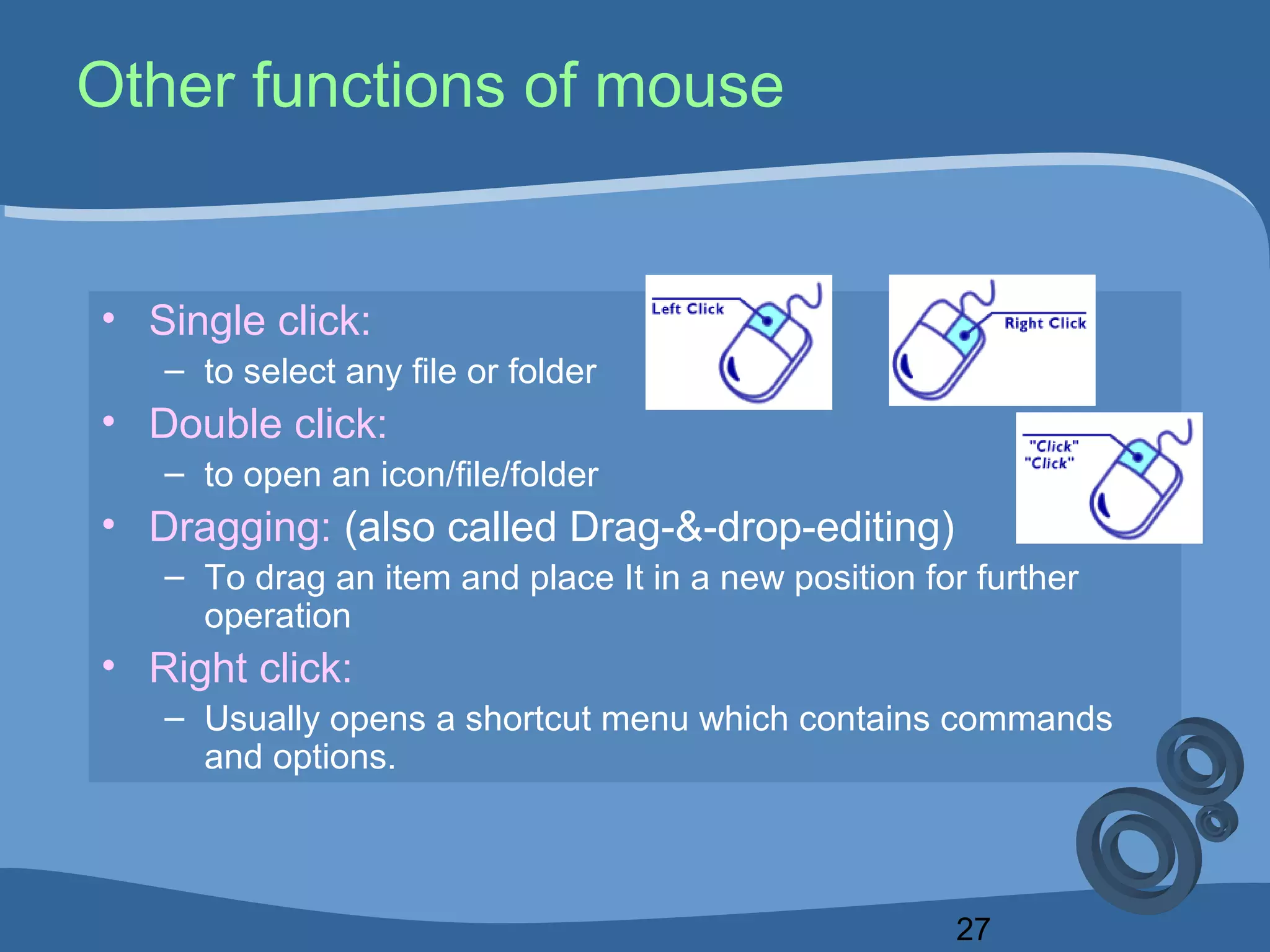
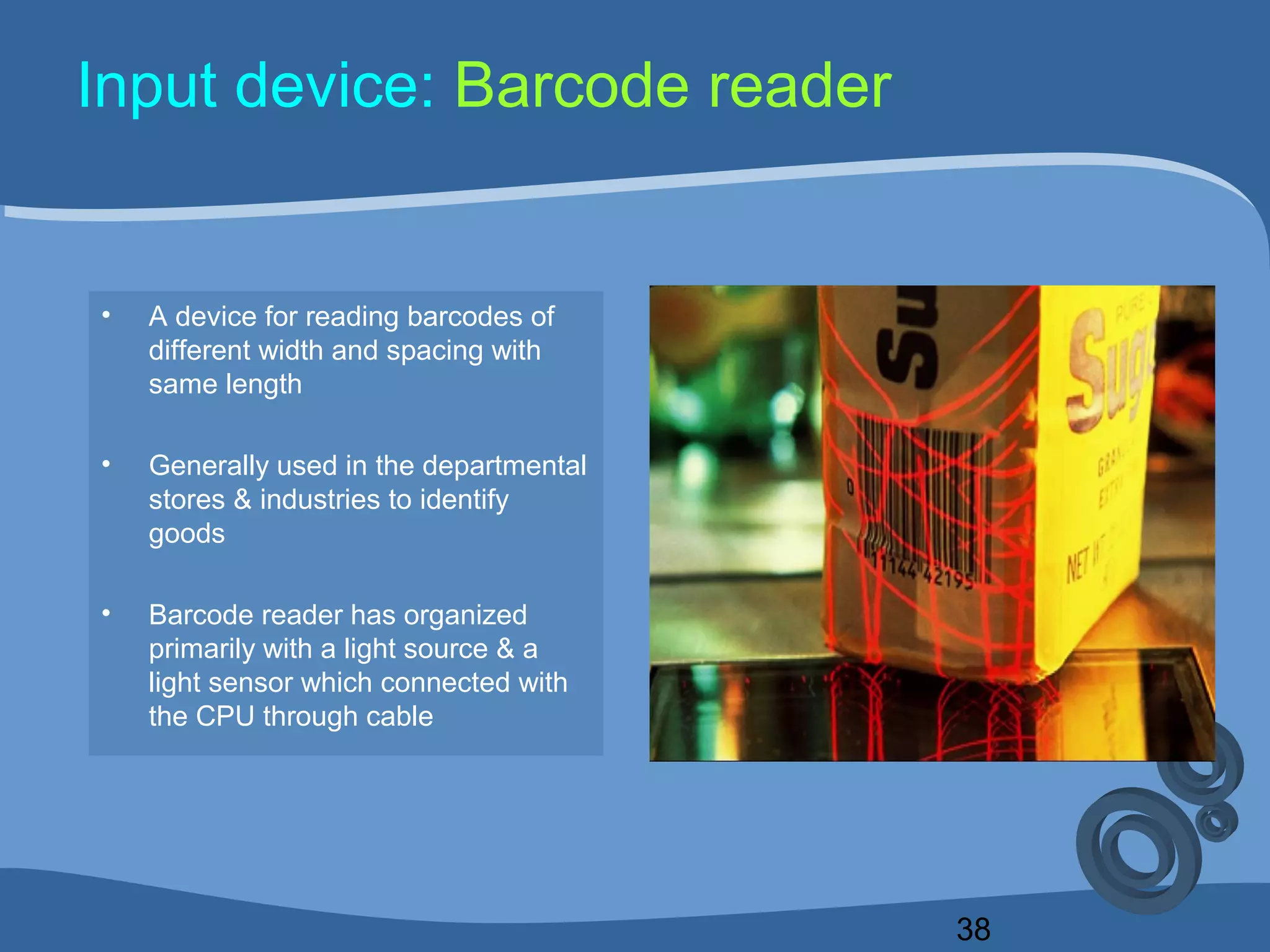
The document outlines a course on computing fundamentals within the BBA program at the University of Dhaka, covering topics such as computer classification, organization, various input devices like keyboards and mice, and how they function. It also discusses additional input devices including scanners, OCR, OMR, MICR, and barcode readers. Key concepts about output units and memory classification are briefly introduced, setting a foundation for further learning about computer systems.