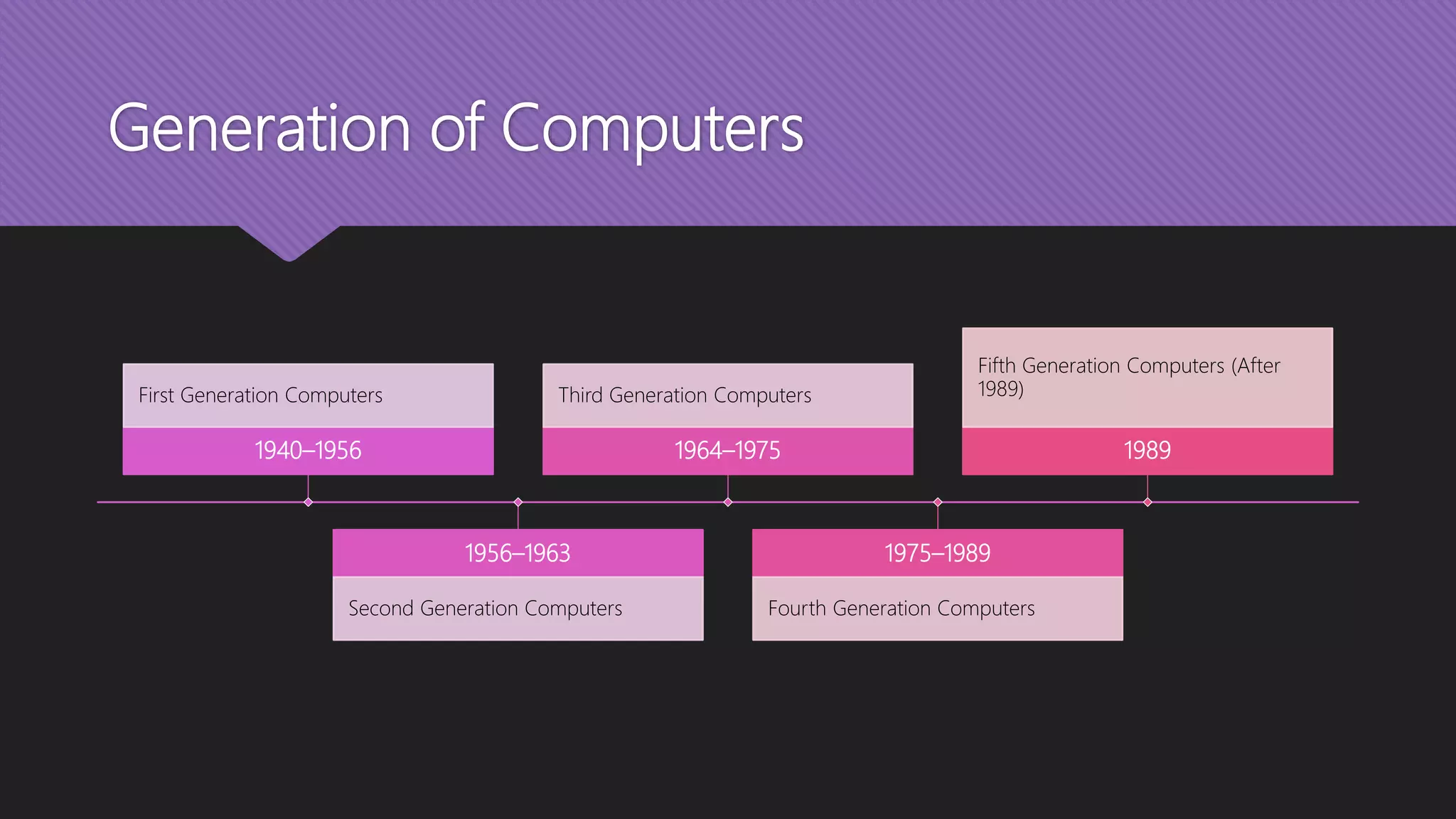
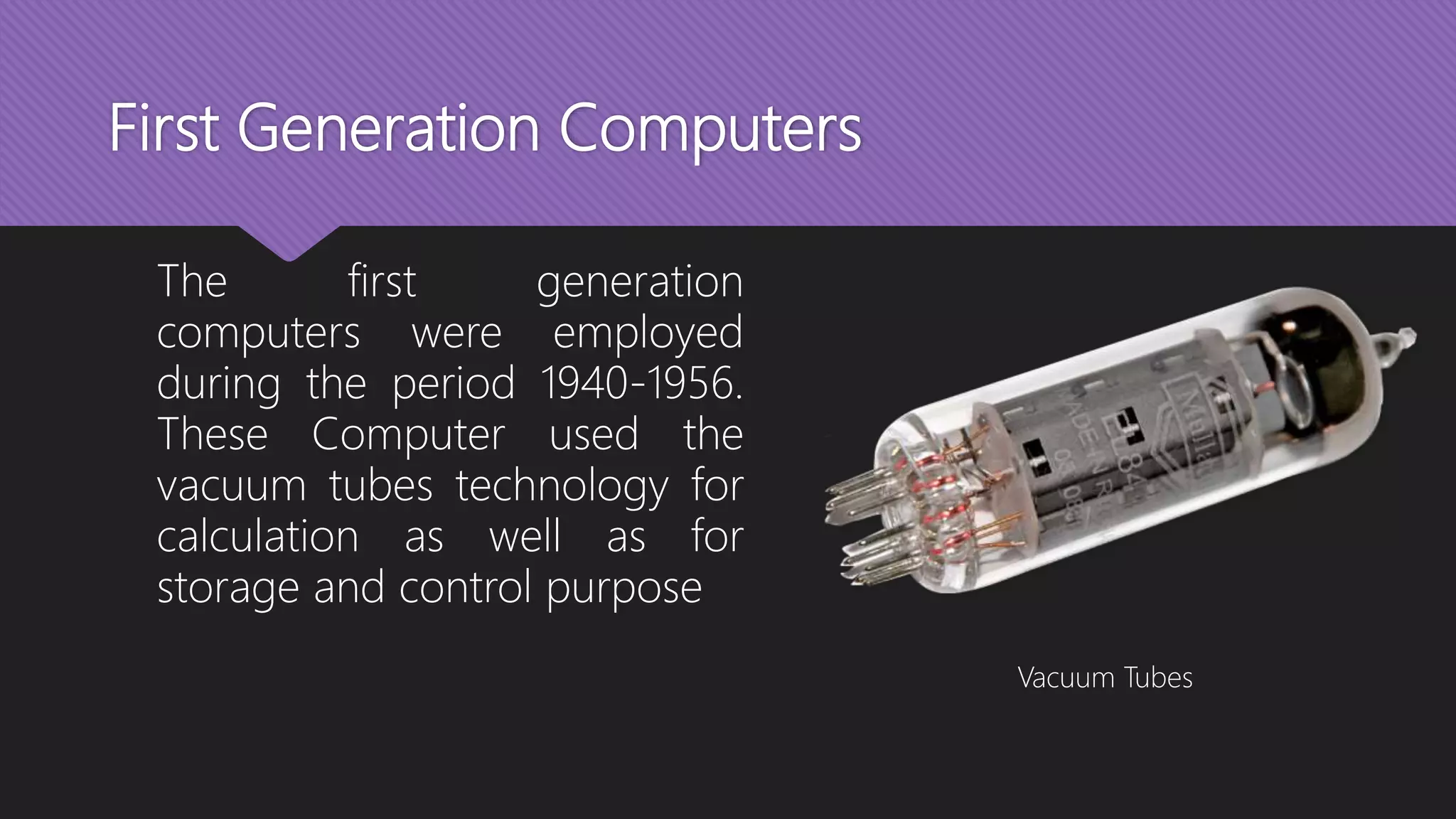
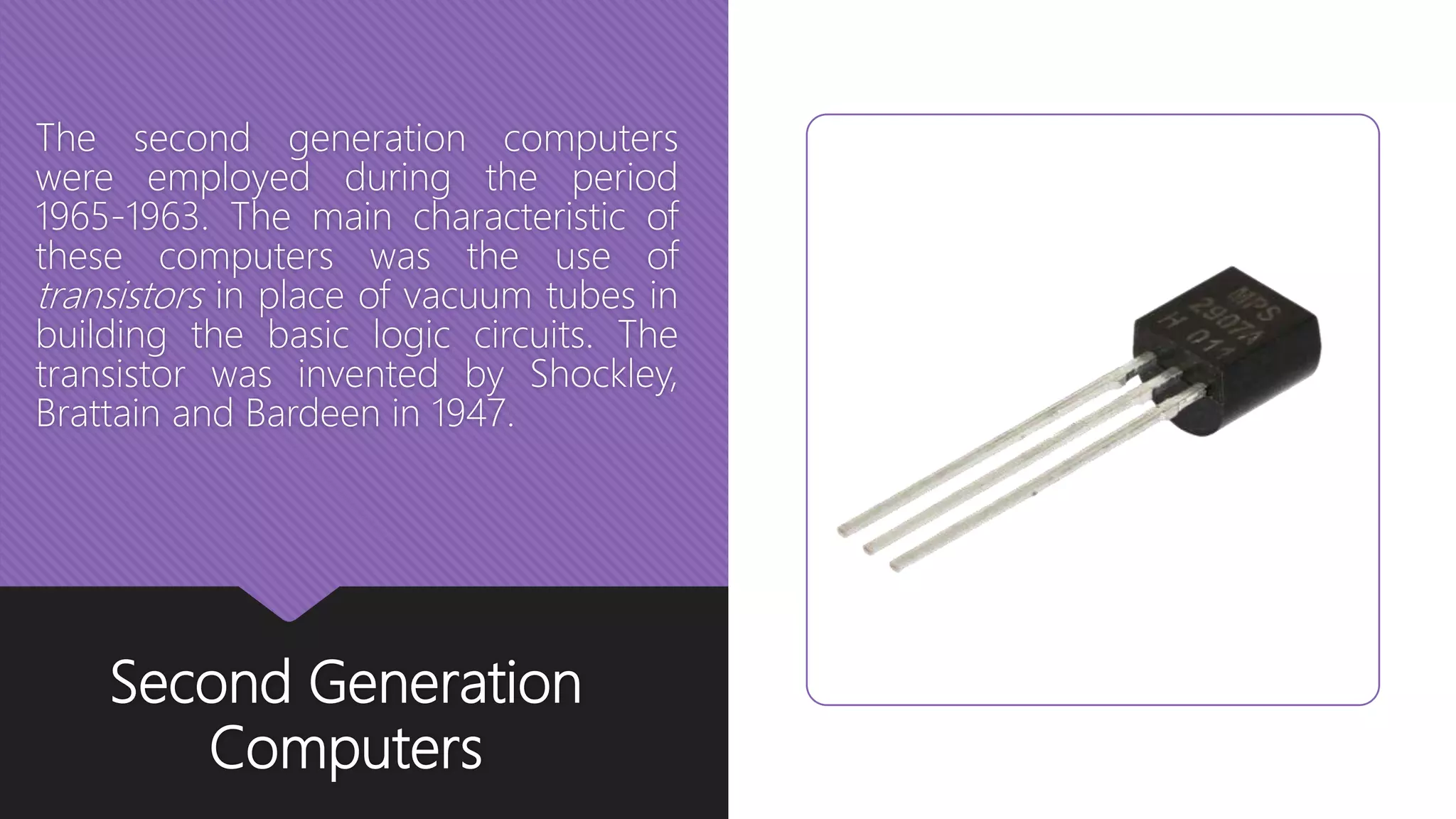
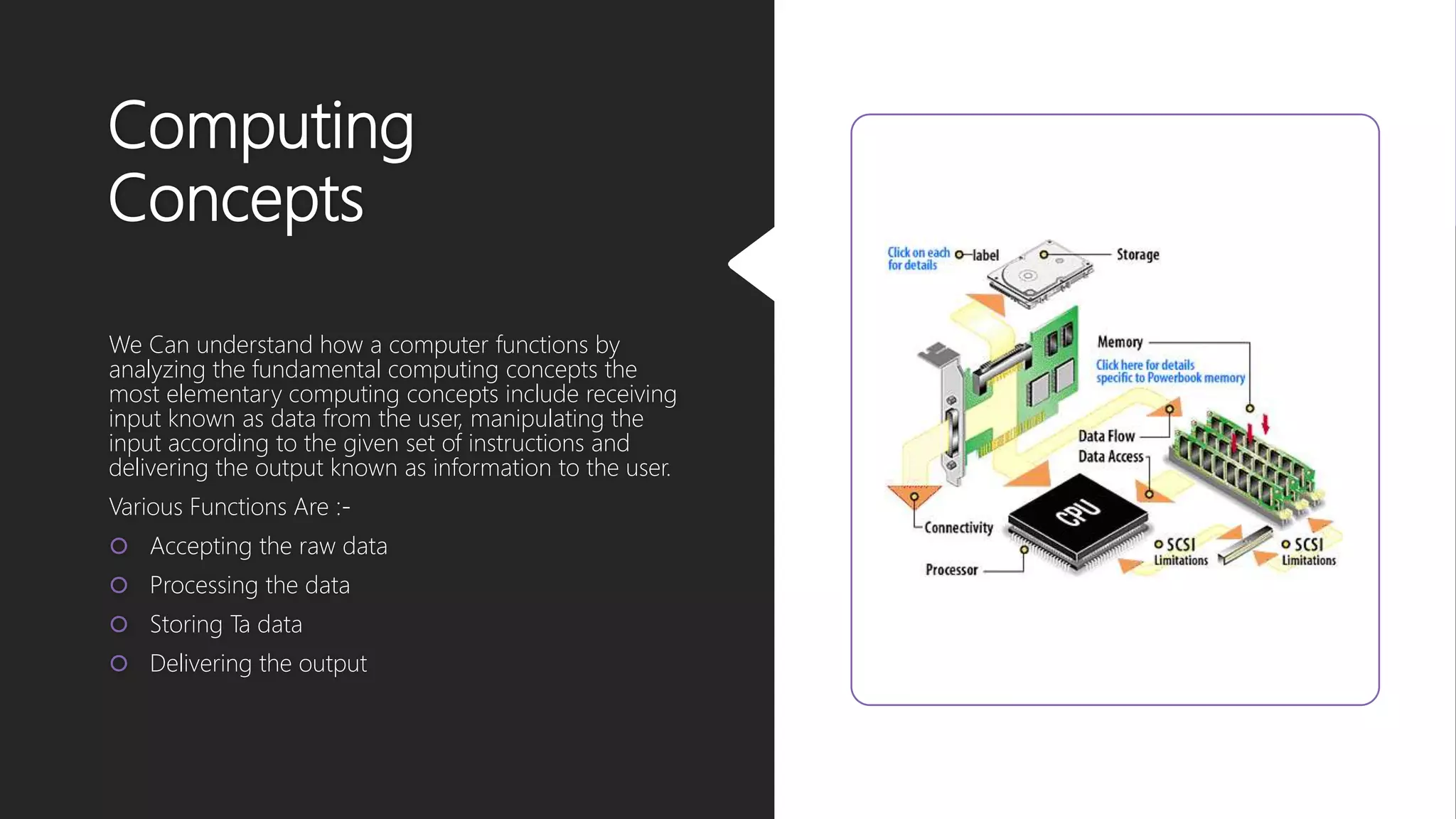
The document outlines the evolution and classification of computers through five generations from the 1940s to the present, highlighting key technological advancements such as the transition from vacuum tubes to transistors and integrated circuits. It details the various classifications of computers based on operation principles, applications, size, and capability. Additionally, it mentions the integral components of a computer system, including hardware, software, and data, alongside the application of computers across various sectors.