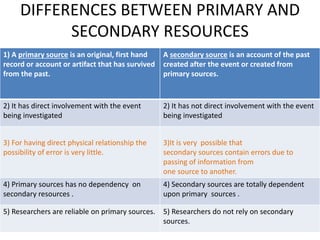
The document discusses historical research as a systematic method to uncover, evaluate, and synthesize evidence about past events. It emphasizes the importance of distinguishing between primary and secondary sources, outlines the steps involved in conducting historical research, and highlights its significance in education by addressing contemporary problems and understanding past theories and practices. Additionally, it recognizes potential challenges and criticisms in the process of historical inquiry.