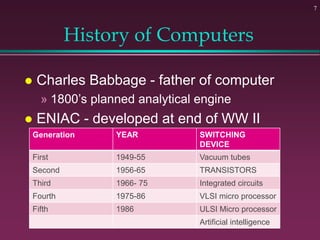
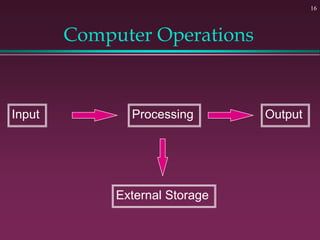
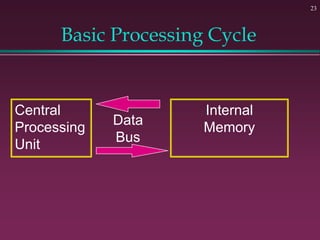
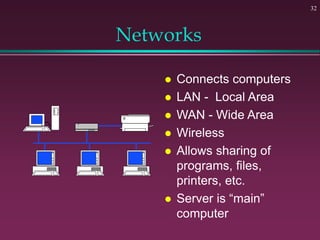
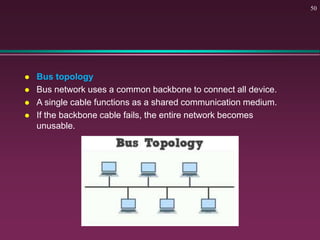
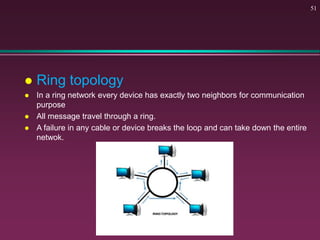
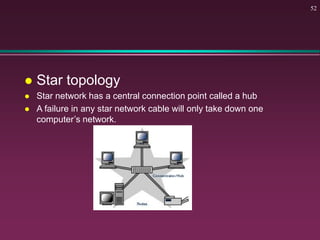
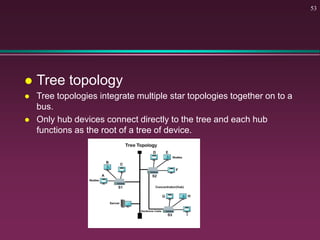
This document provides an overview of basic computer concepts. It defines what a computer is and describes its main components like the CPU, memory, input/output devices, and software. It also discusses operating systems, applications, networks, security concepts like viruses and protection, and basic network topologies. The document is intended as an introductory guide to fundamental computer terms and technologies.