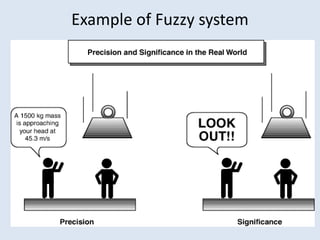
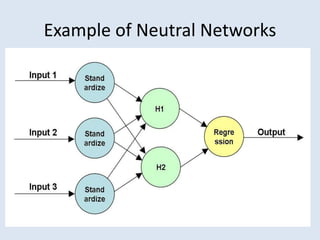
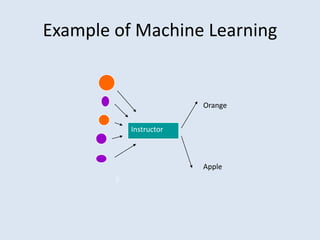
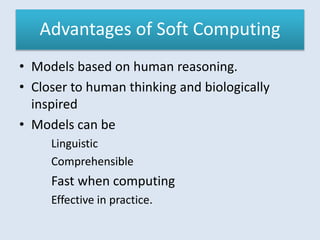
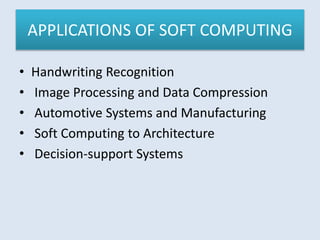
This document discusses soft computing techniques. Soft computing deals with inexact solutions and uses techniques like fuzzy systems, neural networks, machine learning, and probabilistic reasoning. It summarizes the key differences between hard and soft computing, providing examples of each technique. The document concludes by listing some common applications of soft computing such as handwriting recognition, image processing, and decision support systems.