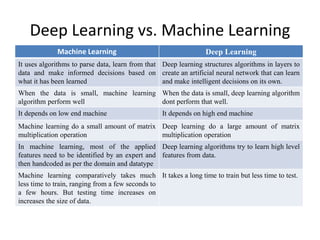
The document provides an overview of machine learning, detailing its history, types, and applications. It distinguishes between supervised, unsupervised, semi-supervised, and reinforcement learning, explaining how each works and their relevance in various tasks. Additionally, it compares machine learning with deep learning, highlighting their operational differences and the conditions under which each performs optimally.