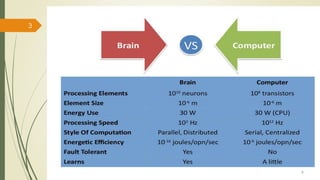
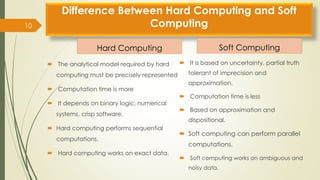
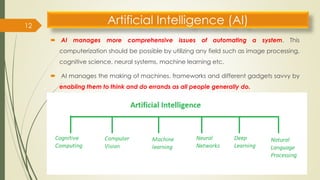
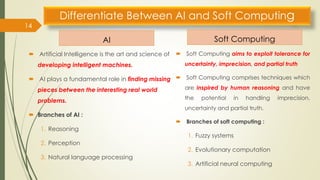
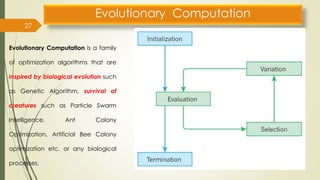
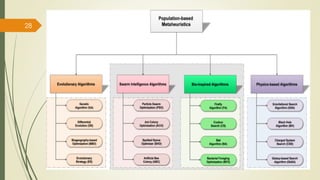
The document provides an overview of soft computing, which utilizes approximate calculations to solve complex problems where traditional computing falls short due to imprecision and uncertainty. It distinguishes soft computing from hard computing by highlighting its adaptability, tolerance for partial truths, and efficient solutions across various applications such as image processing, fuzzy logic control, and artificial intelligence. Additionally, it discusses key concepts like artificial neural networks and evolutionary computation methods inspired by biological processes.















![30
Haykin, Simon S. "Neural networks and learning machines/Simon
Haykin." (2009).
Sivanandam, S. N., and S. N. Deepa. Principles of soft
computing (with CD). John Wiley & Sons, 2007.
Jang, Jyh-Shing Roger, Chuen-Tsai Sun, and Eiji Mizutani. "Neuro-
fuzzy and soft computing-a computational approach to
learning and machine intelligence [Book Review]." IEEE
Transactions on automatic control 42.10 (1997): 1482-1484.
Books
Ross, Timothy J. Fuzzy logic with engineering applications. Vol. 2.
New York: wiley, 2004.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecturer-1introductiontosoftcomputing-201224120104/85/Introduction-to-soft-computing-30-320.jpg)

