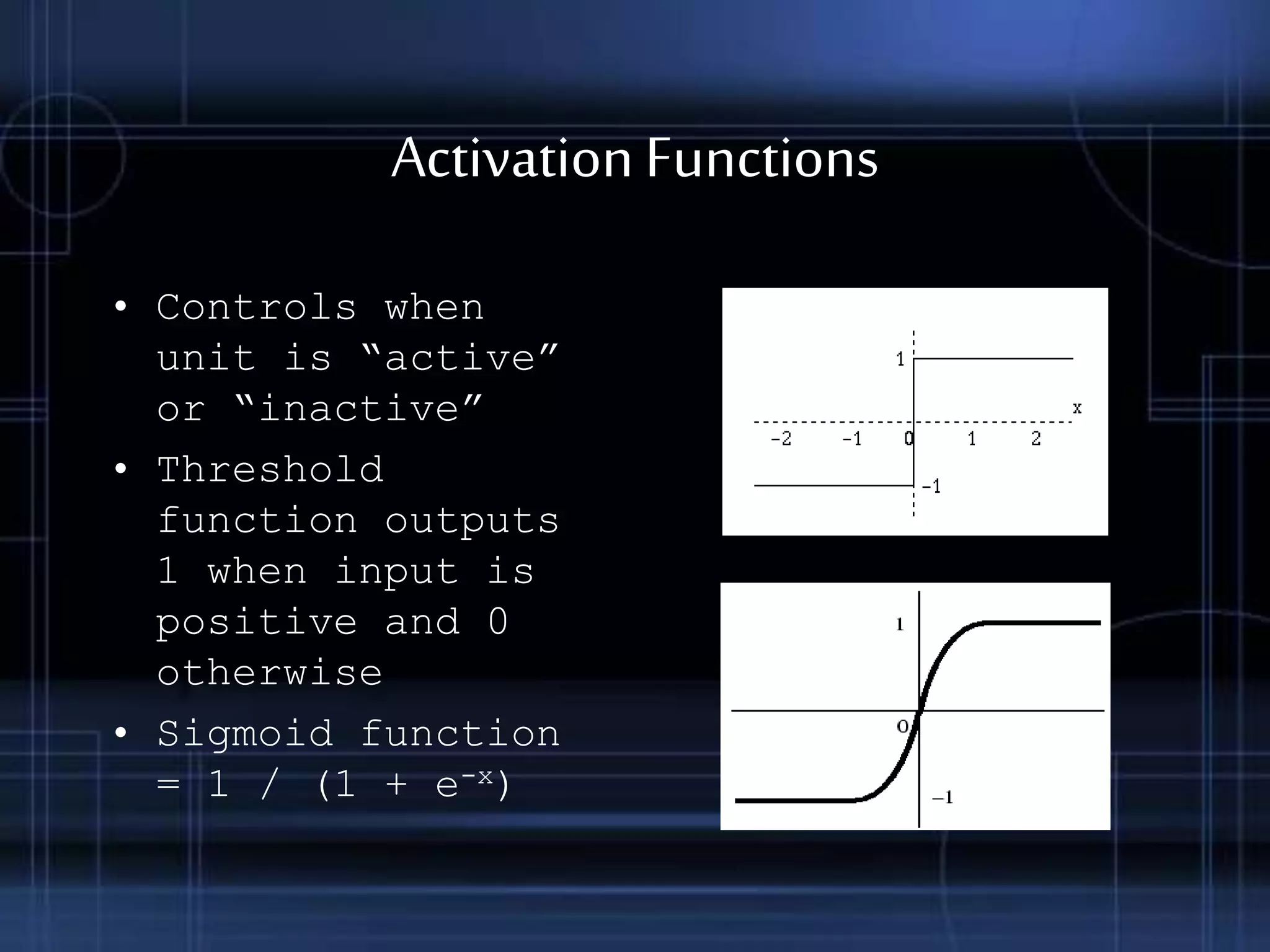
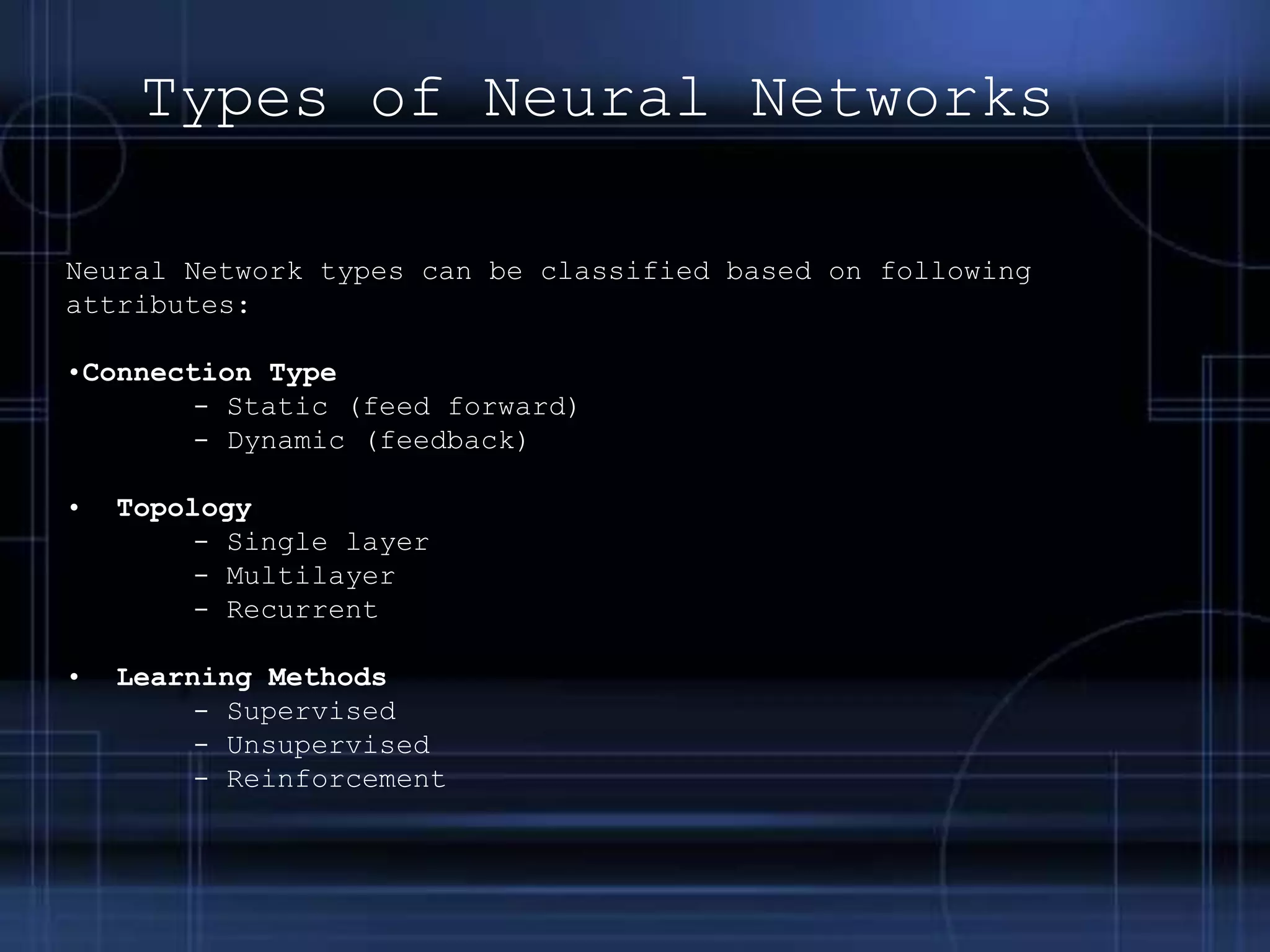
This document provides an overview of neural networks, including their basic components and types. It discusses neurons, activation functions, and different neural network architectures like feedforward and feedback networks. It also covers supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning methods. Applications of neural networks are described along with their advantages in learning from experience and dealing with incomplete information, and disadvantages like long training times.