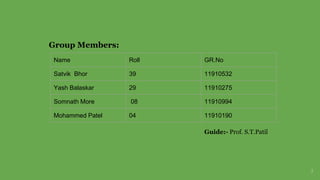
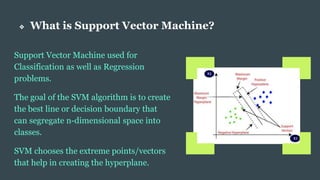
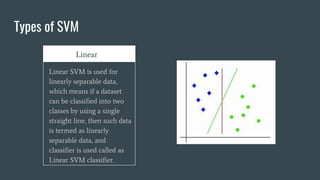
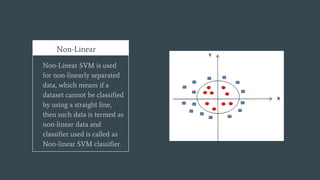
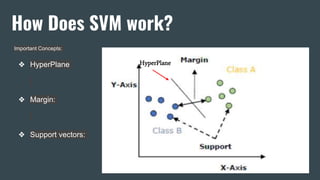
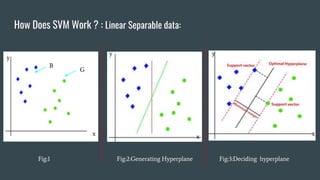
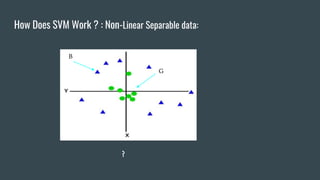
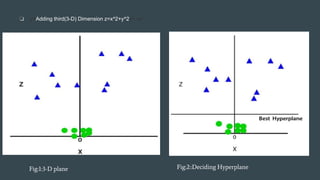
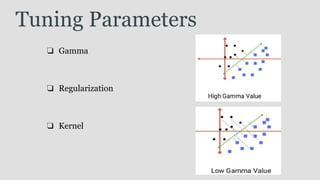
The document provides an overview of Support Vector Machines (SVM), detailing its purpose for classification and regression tasks by creating hyperplanes to segregate data. It outlines the types of SVM (linear and non-linear), compares SVM with other classification methods, and discusses its advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, it highlights real-world applications of SVM, including face detection, text categorization, and bioinformatics.