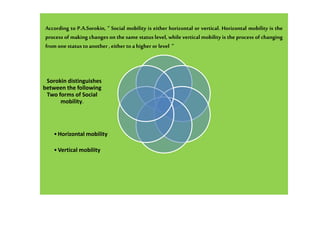
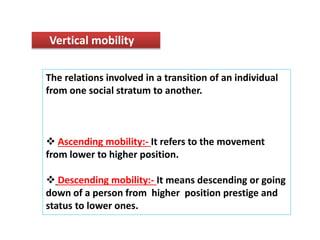
Sorokin distinguishes between horizontal and vertical social mobility. Horizontal mobility refers to changes within the same social status level, such as changing political or religious affiliations. Vertical mobility involves changing social strata, either ascending to a higher level or descending to a lower level. Education promotes social mobility by providing opportunities and motivating people to change occupations. While social mobility can promote individual development and social progress, it can also lead to disorder and discontent within societies.