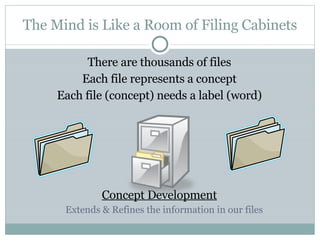
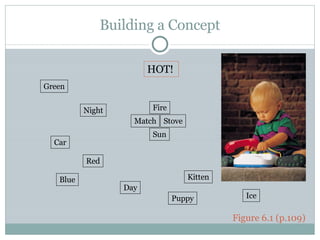
The document discusses the concept development model, which involves building general understandings from specific examples. It describes concept development as acquiring vocabulary through concepts and extending knowledge by refining information in "filing cabinets" that represent concepts. The key steps in concept development are listing associated items, grouping like items, labeling groups, regrouping items under other concepts, and forming generalizations. Teachers can structure and implement concept development lessons flexibly based on student groupings and pacing.