Embed presentation
Downloaded 247 times



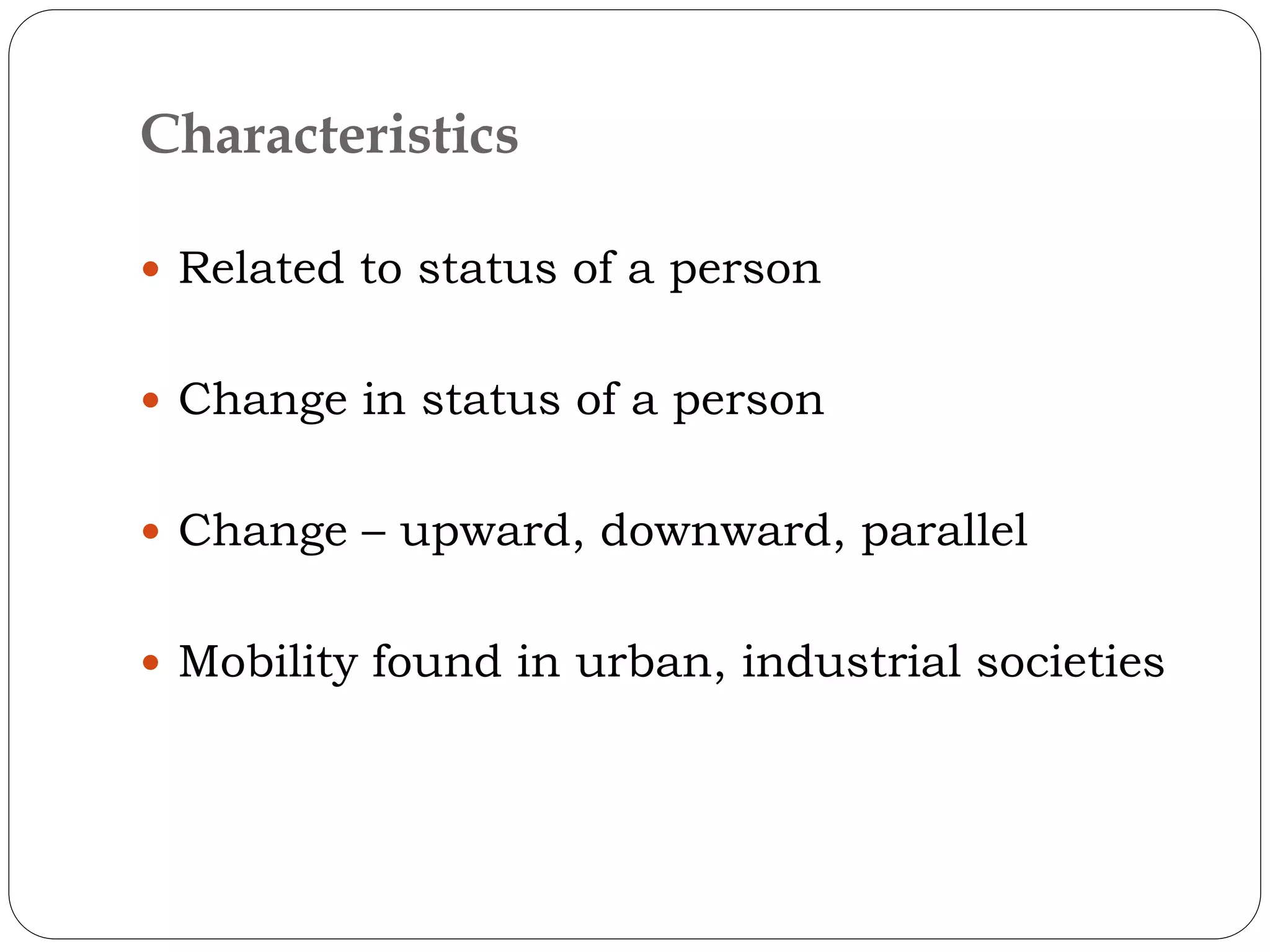



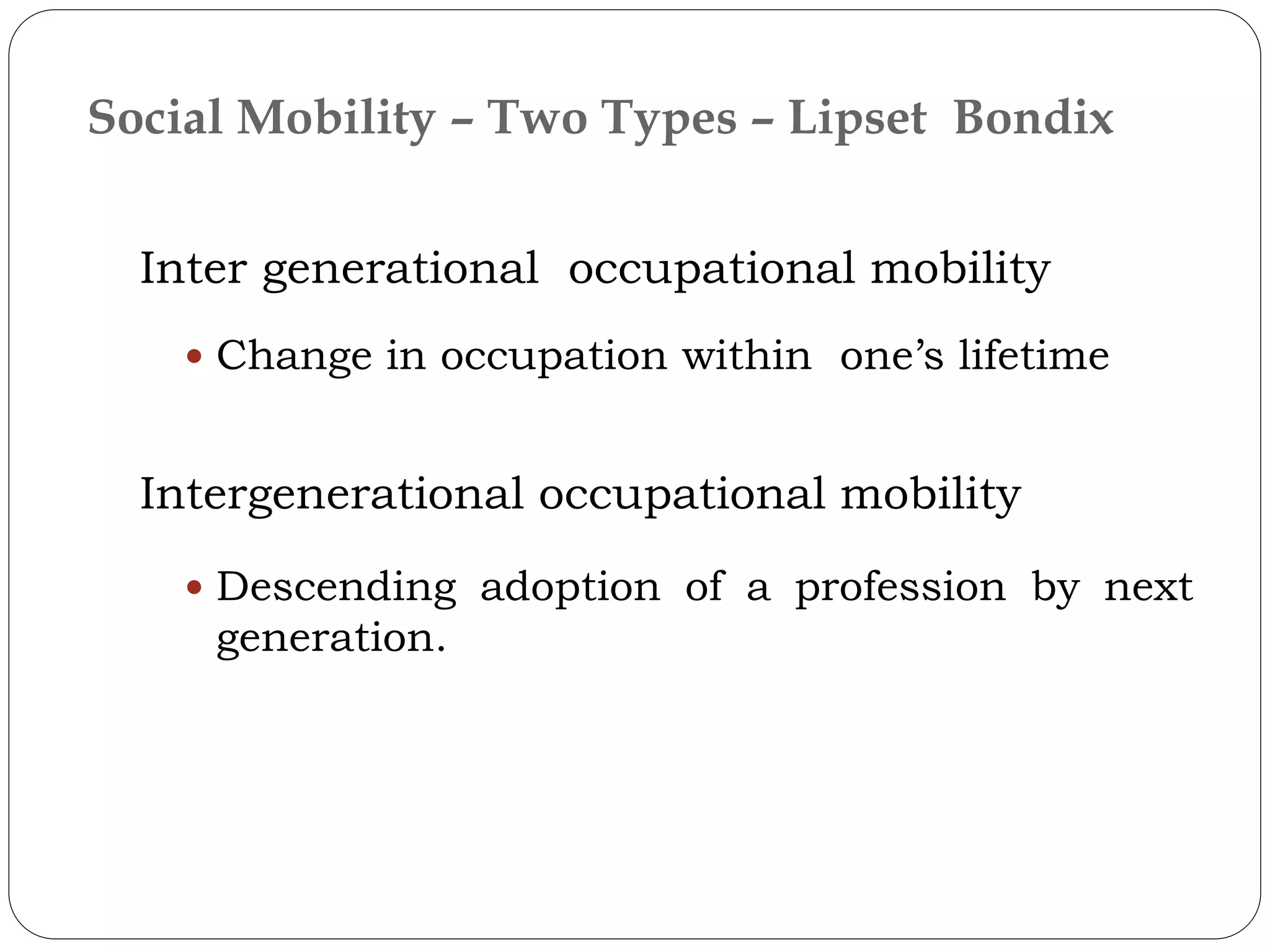


Social mobility refers to changes in social status or position, such as upward, downward, or parallel movements. It is related to changes in a person's social status and is a characteristic of industrial or urban societies. There are different types of social mobility including horizontal (movement within the same social level), vertical (movement up or down levels), and inter-generational occupational mobility (a change or adoption of occupations between generations). Sources of vertical social mobility include institutions like the army, religious groups, schools, politics, businesses, and families.









