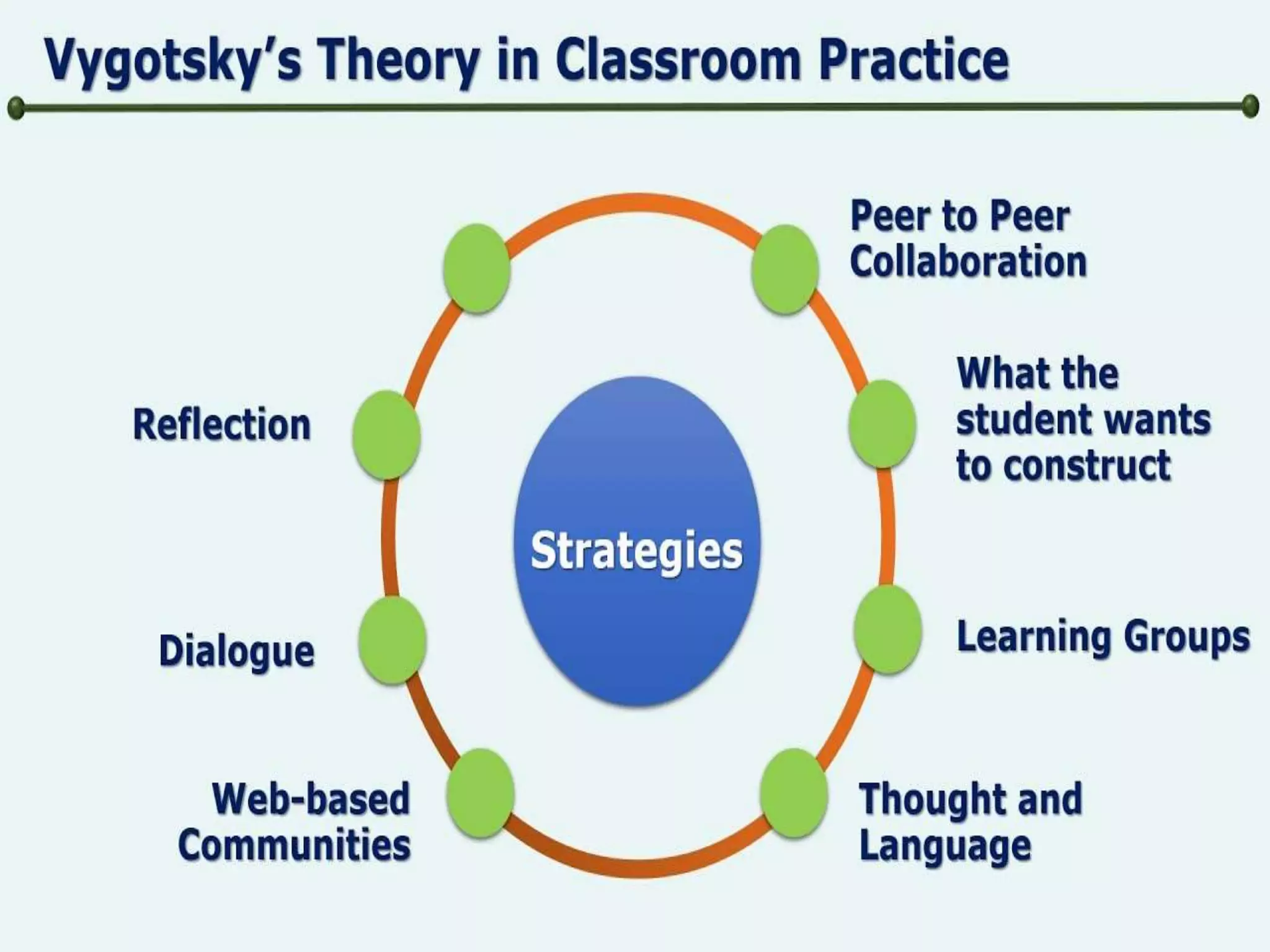
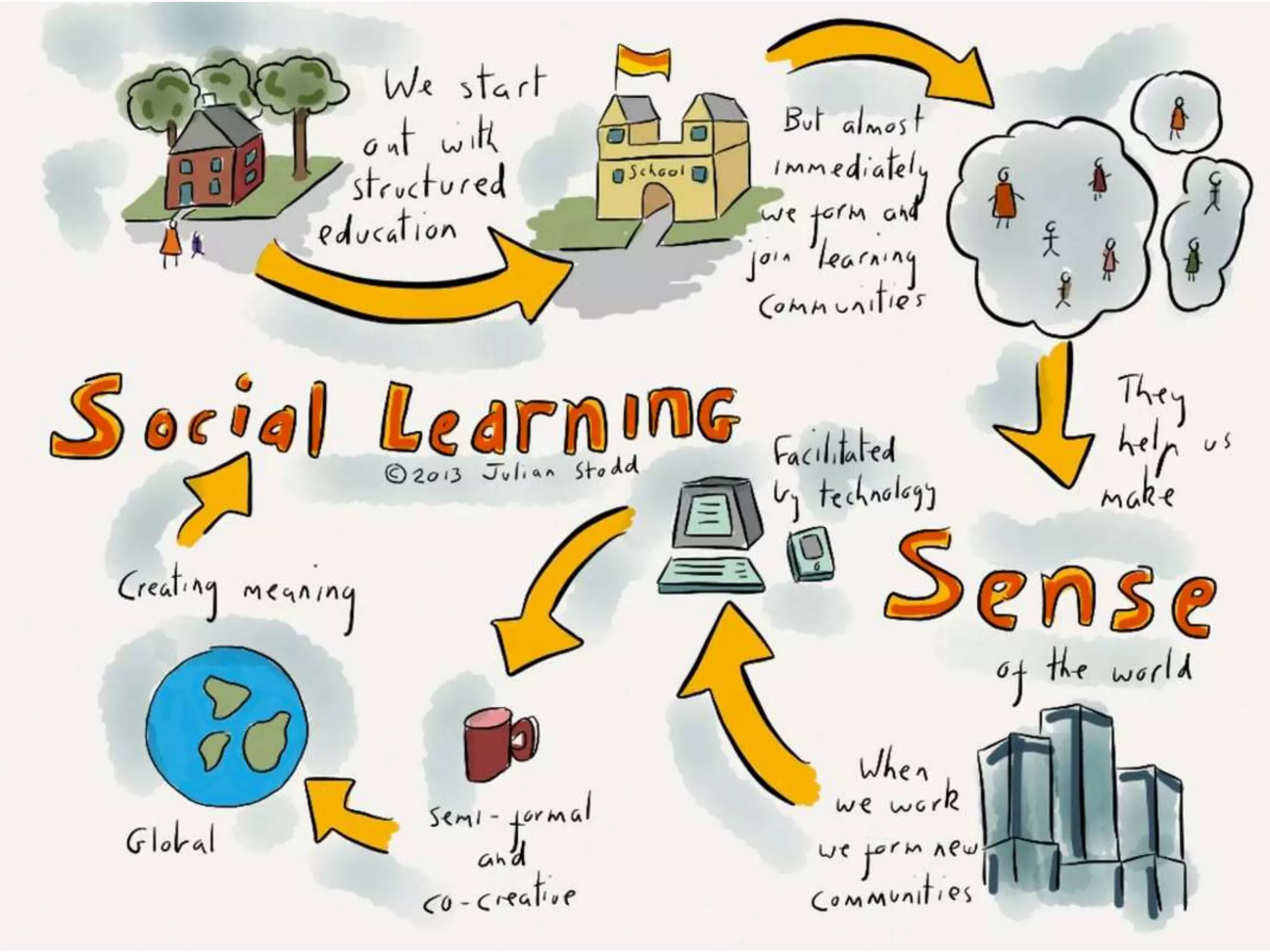
Social constructivism is a theory of learning proposed by Lev Vygotsky that views learning as a social process where children construct knowledge through interaction with others in shared experiences and language. According to Vygotsky, learning occurs in the Zone of Proximal Development with assistance from teachers or more capable peers. Within the ZPD, scaffolding aids can help students solve problems they cannot yet solve independently. Language plays a central role in learning as it allows children to internalize knowledge from their social and cultural environment.