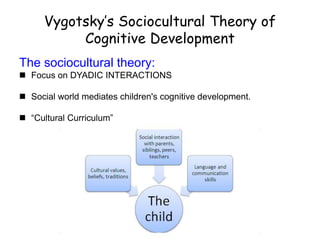
The document discusses sociocultural theory of cognitive development, which posits that cognition is shaped by social and cultural contexts. It focuses on Vygotsky's view that cognitive development occurs through interactions with others and the use of cultural tools like language. A key concept is the Zone of Proximal Development, which is the difference between what a child can do independently versus with guidance, and represents the child's potential development. Within the ZPD, scaffolding from a more knowledgeable person can help a child learn skills they are not yet able to master alone.