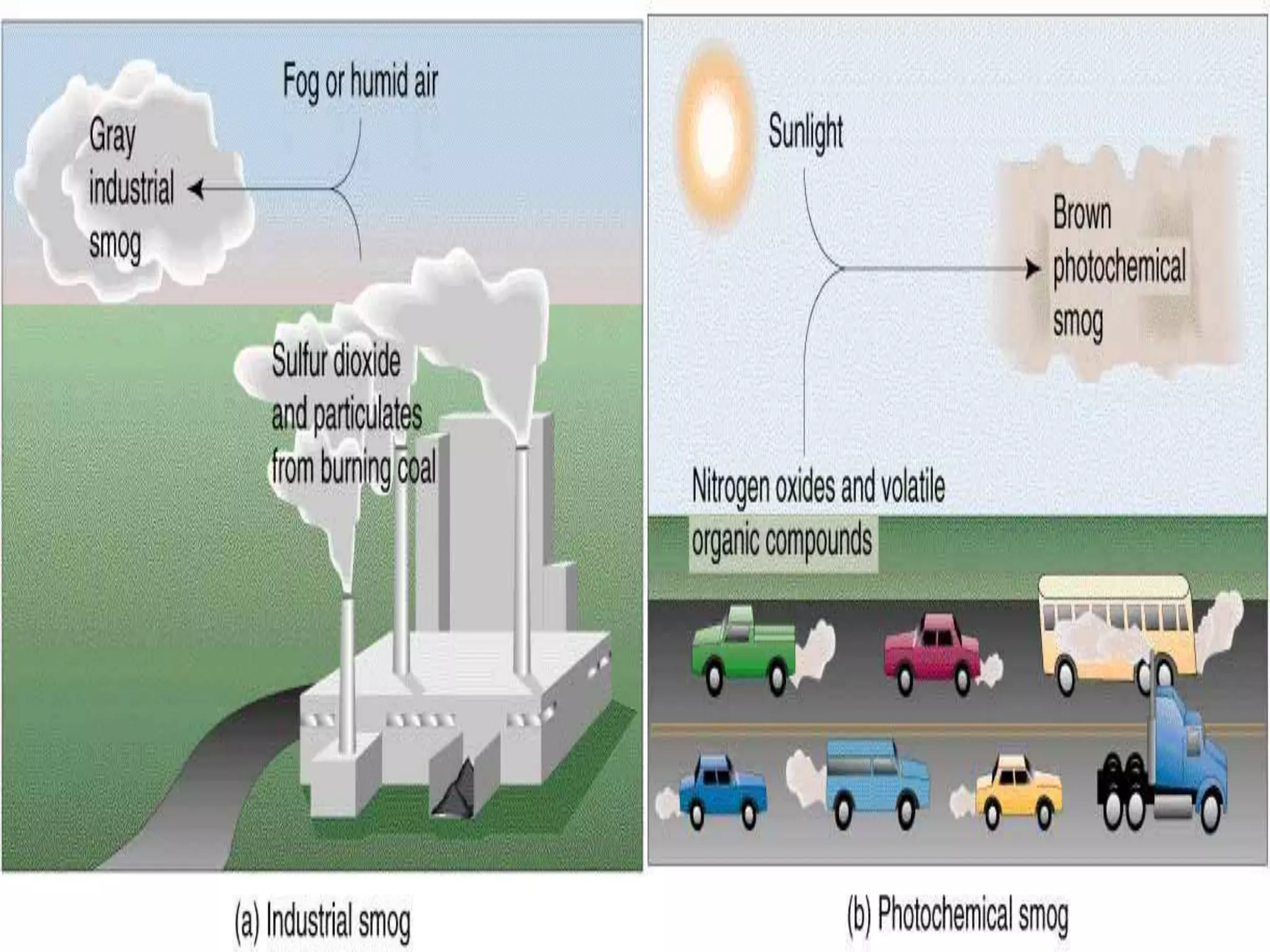
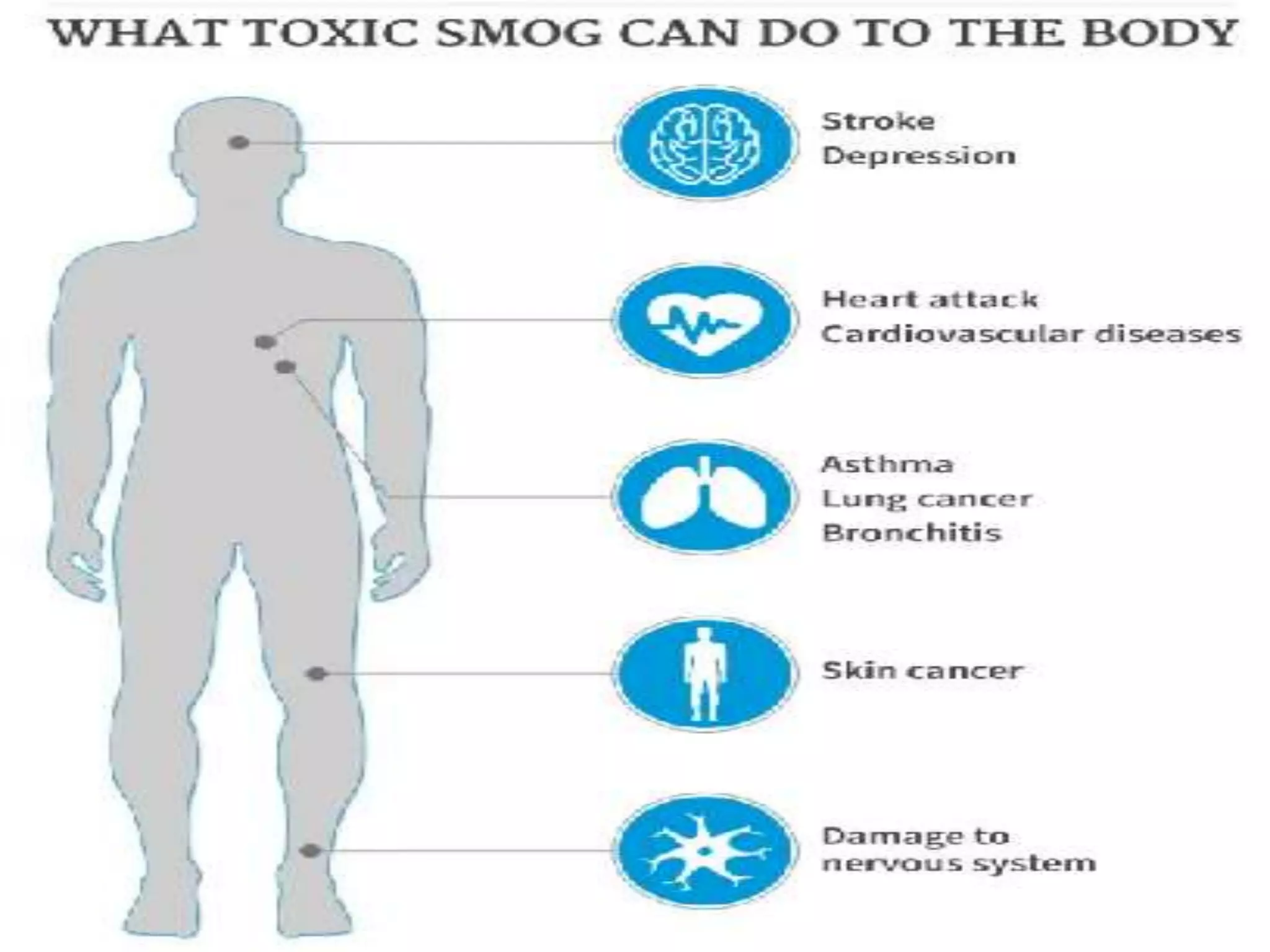
Smog is air pollution that reduces visibility and is caused by a combination of smoke and fog. It forms when pollutants from vehicles, factories, and other sources are released into the atmosphere and remain suspended under certain conditions. There are two main types of smog: sulfurous smog, which results from high sulfur oxide levels from burning coal and causes London-style smog; and photochemical smog, also called Los Angeles smog, which forms from nitrogen oxides and organic compounds reacting in sunlight to create secondary pollutants. Smog has negative health effects like respiratory issues and is a problem in some Pakistani cities due to industrial and transportation pollution.