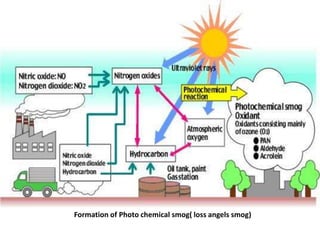
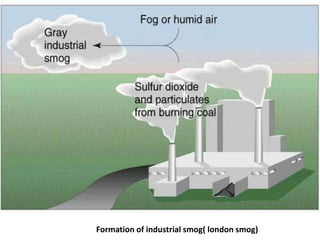
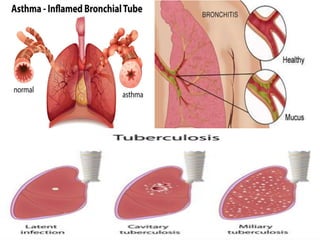
Smog is a combination of smoke and fog formed when pollutants from sources like automobiles, factories, and the burning of coal react with sunlight and moisture in the air. There are two main types of smog:
Industrial smog, like the 1952 London Smog, forms when coal smoke and sulfur dioxide combine with fog. It can be extremely toxic. Photochemical smog forms when nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds from fossil fuel combustion react with sunlight to produce secondary pollutants. Conditions like sunlight, temperatures over 18 degrees Celsius, and the presence of nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds are needed for photochemical smog formation. The reactions produce ozone and other toxic chemicals that can harm human