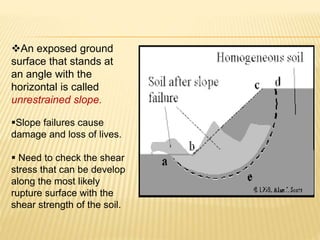
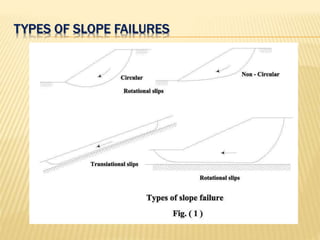
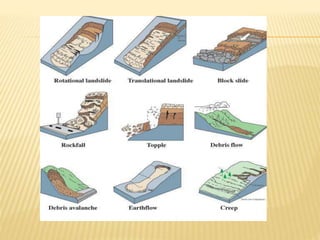
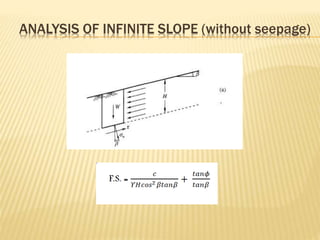
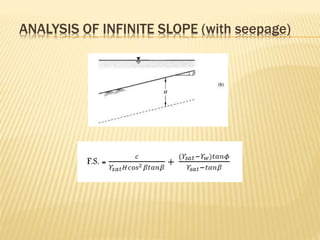
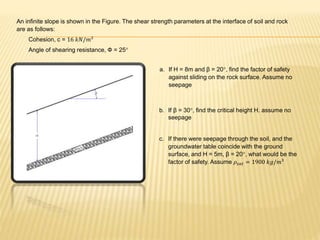
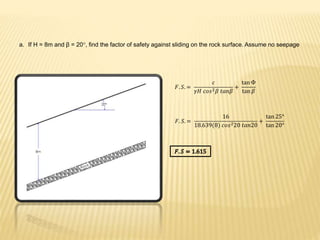
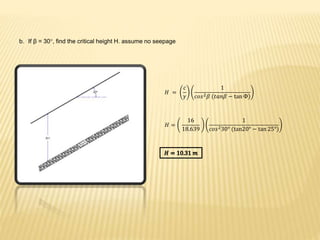
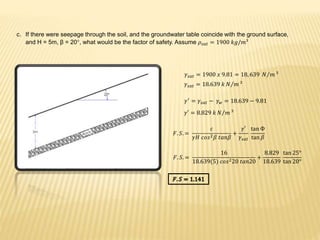
The document discusses slope stability and factors that influence it. It defines an unrestrained slope and describes different types of slope failures such as base failure and midpoint circle failure depending on where the surface of sliding intersects the slope. Factors that influence slope stability include soil/rock strength, groundwater, external loading, slope geometry. Slope failures can be triggered by erosion, rainfall, earthquakes, construction activities, and more. Methods to improve slope stability include flattening slopes, adding weight/retaining walls, lowering the water table, soil improvement. Stability analysis procedures include mass and methods of slices approaches. The factor of safety is defined and equations for infinite slope analysis with and without seepage are provided.