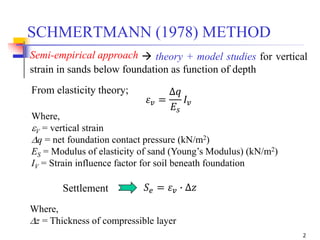
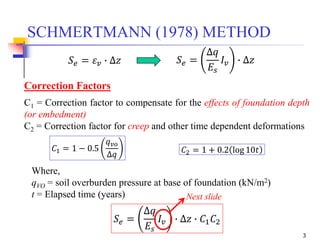
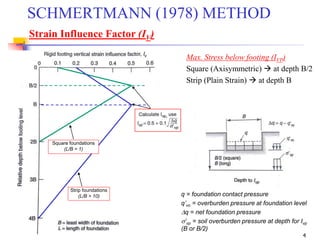
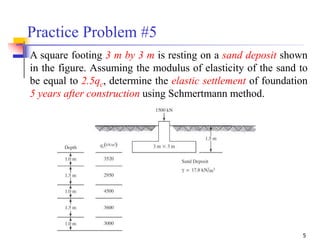
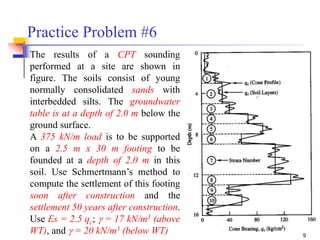
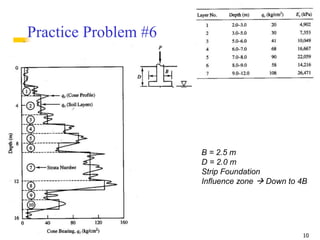
The document discusses the Schmertmann method for calculating vertical strain and settlement in sandy soils beneath foundations, detailing the equations and correction factors involved. Various examples, including practice problems and parameters like modulus of elasticity, are provided to illustrate the application of the method. References to foundational texts in geotechnical engineering are included for further reading.
![1
Geotechnical Engineering–II [CE-321]
BSc Civil Engineering – 5th Semester
by
Dr. Muhammad Irfan
Assistant Professor
Civil Engg. Dept. – UET Lahore
Email: mirfan1@msn.com
Lecture Handouts: https://groups.google.com/d/forum/geotech-ii_2015session
Lecture # 15
25-Oct-2017](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/15-181020124920/75/Geotechnical-Engineering-II-Lec-15-16-Schmertmann-Method-1-2048.jpg)