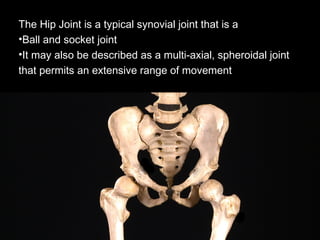
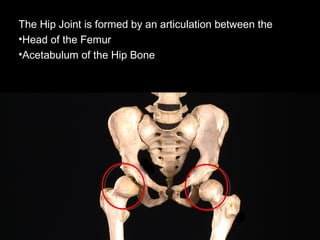
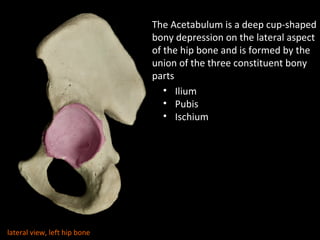
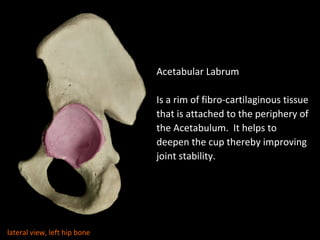
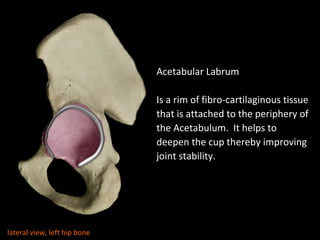
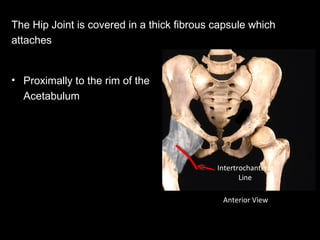
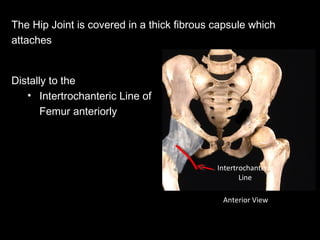
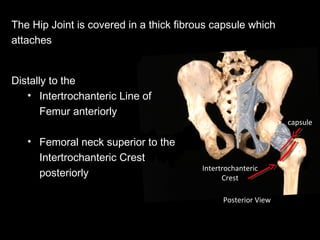
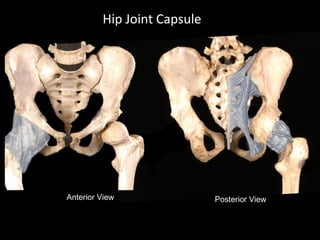
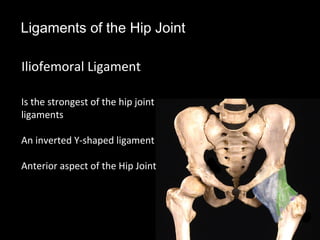
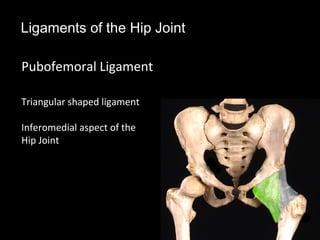
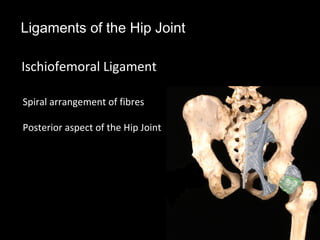
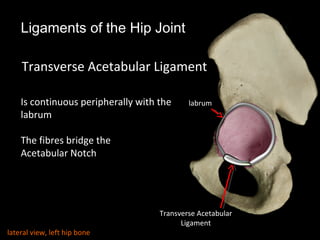
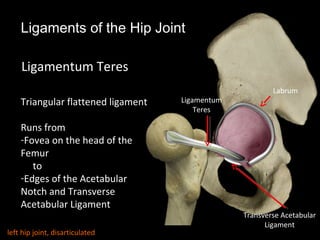
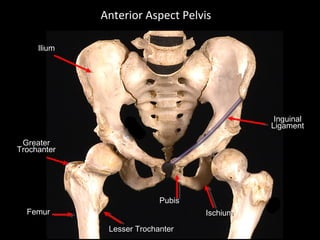
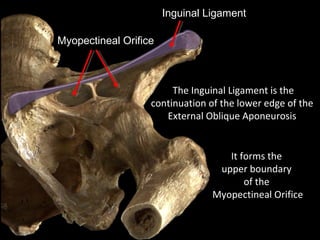
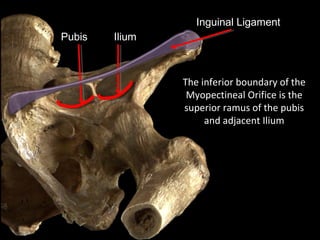
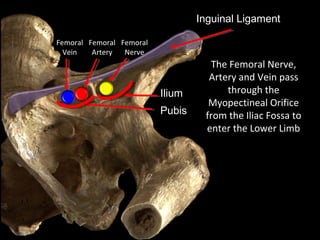
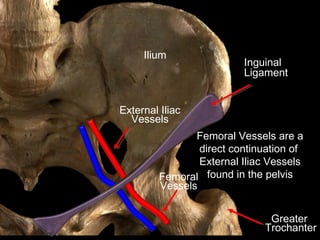
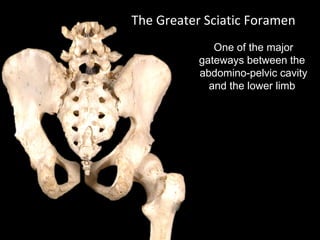
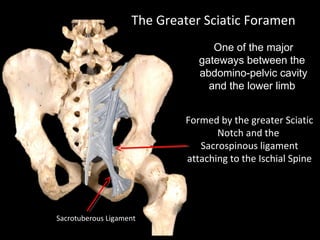
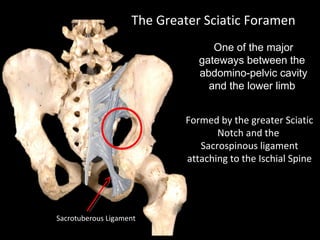
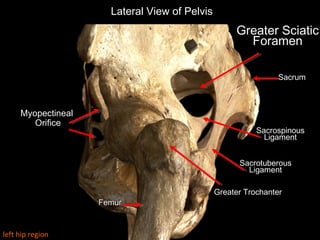
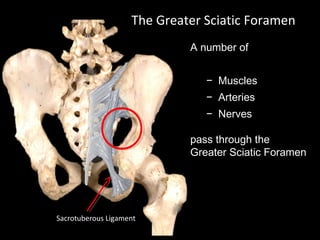
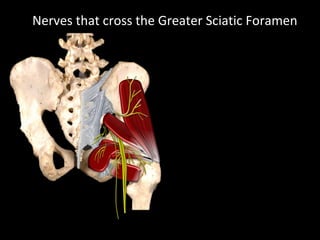
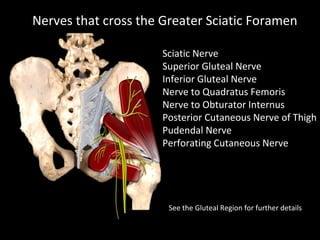
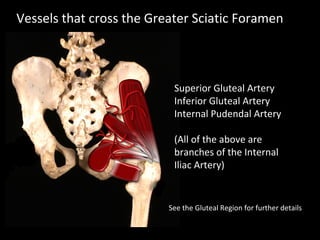
The hip joint is a synovial ball and socket joint formed by the head of the femur and the acetabulum of the hip bone, allowing extensive movement and stability enhanced by the acetabular labrum and a fibrous capsule. It is reinforced by strong ligaments, including the iliofemoral, pubofemoral, and ischiofemoral ligaments, alongside the transverse acetabular ligament and ligamentum teres. The document also discusses two major pelvic gateways—the myopectineal orifice and greater sciatic foramen—transmitting vessels and nerves from the pelvis to the lower limb.