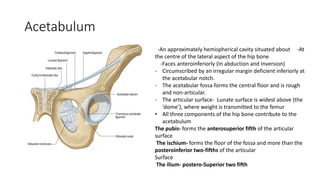
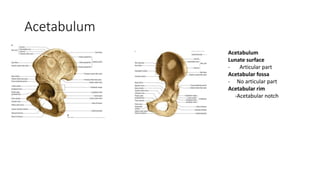
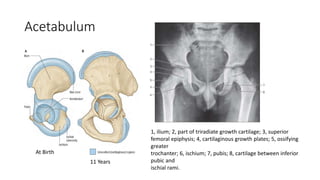
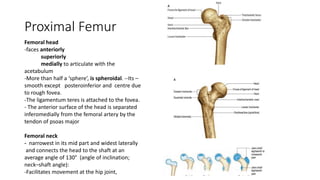
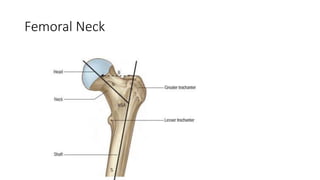
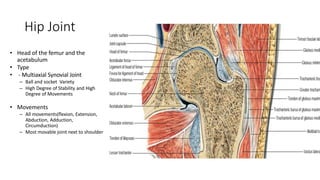
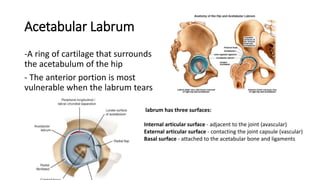
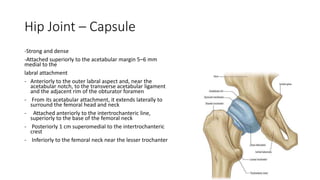
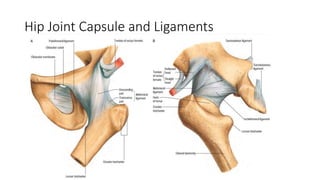
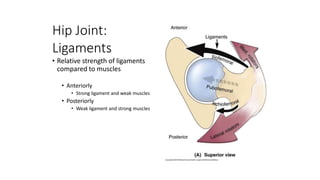
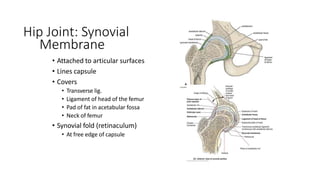
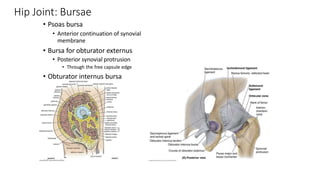
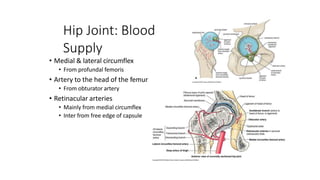
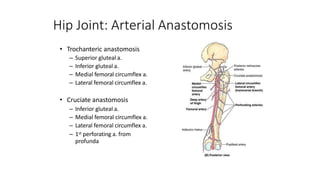
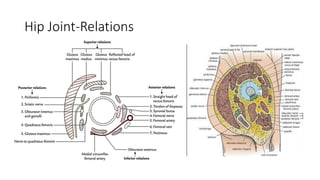
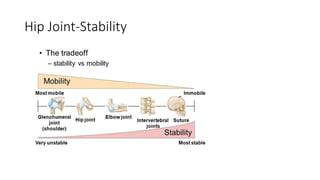
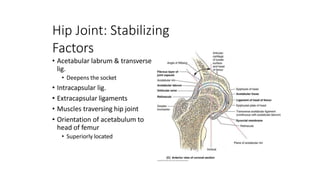
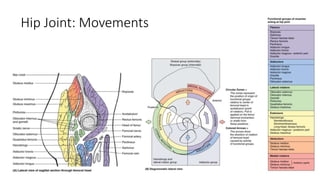
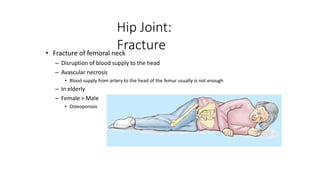
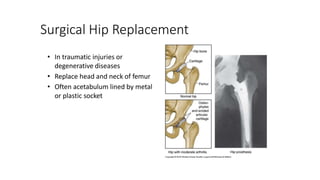
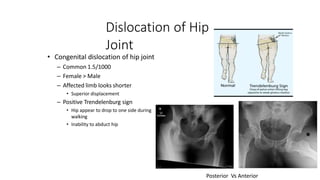
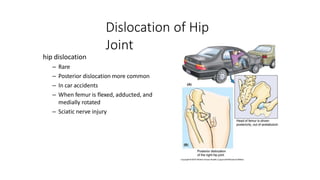
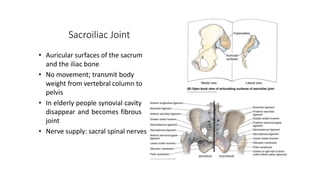
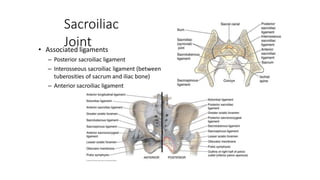
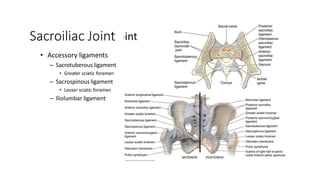
The document summarizes the anatomy of the hip joint. It describes the components of the hip joint including the acetabulum, femoral head, and femoral neck. It discusses the ligaments, capsule, synovial membrane, muscles, blood supply, innervation and relations of the hip joint. It also briefly covers stability, movements, fractures, hip replacements, dislocations, and the sacroiliac joint.