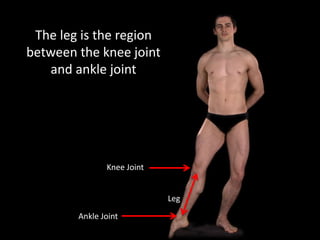
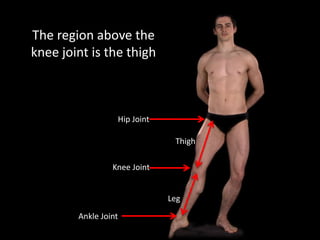
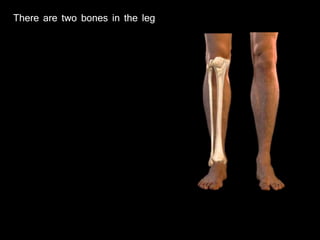
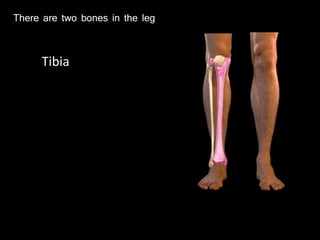
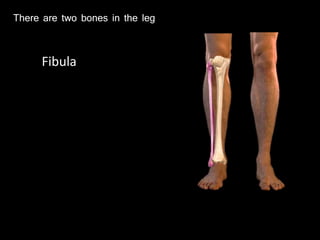
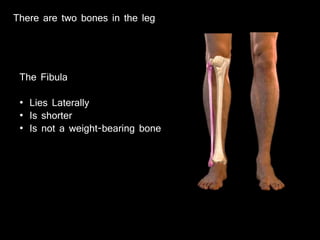
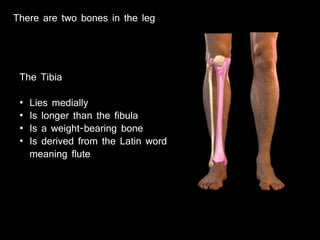
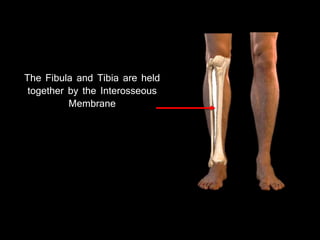
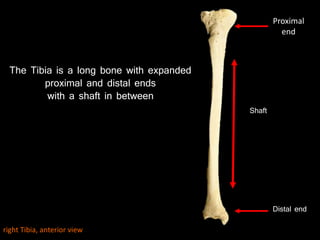
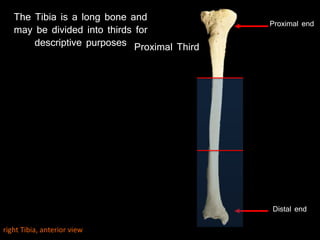
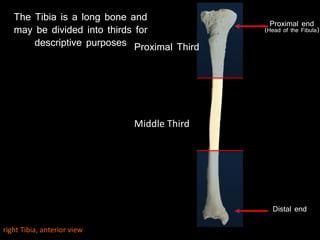
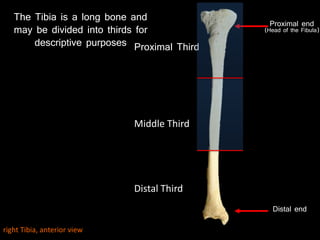
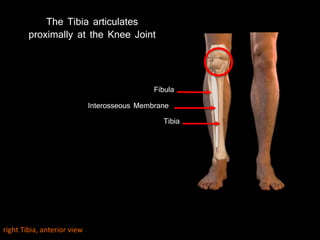
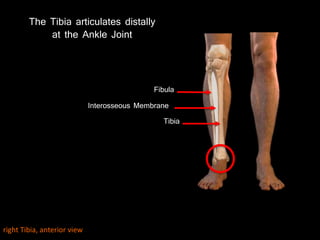
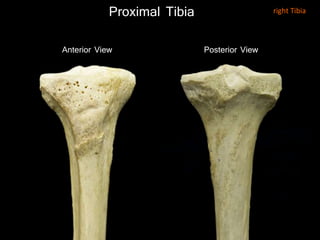
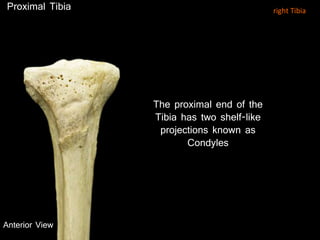
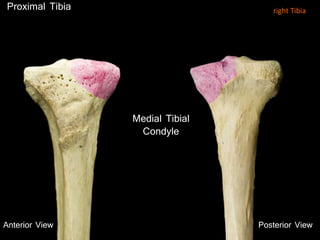
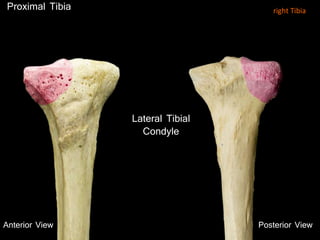
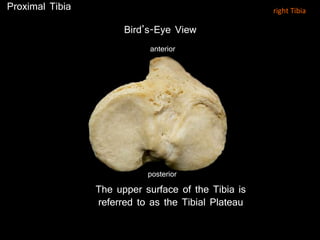
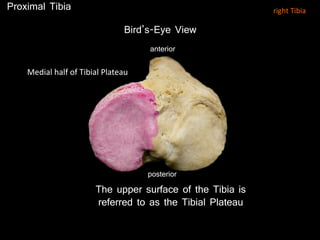
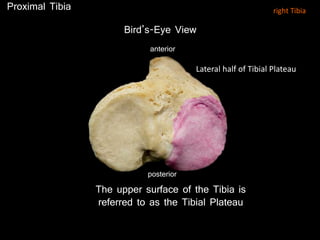
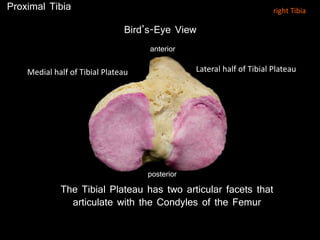
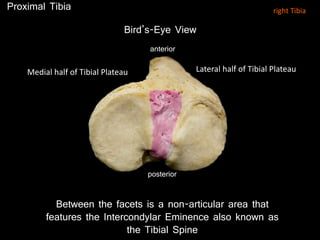
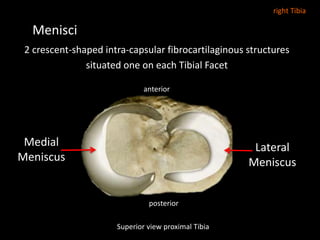
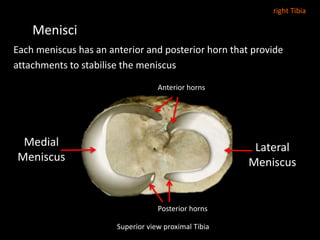
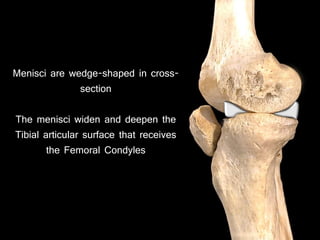
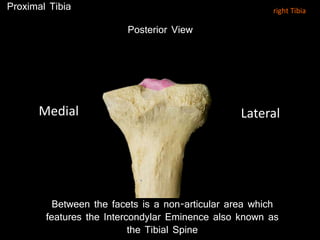
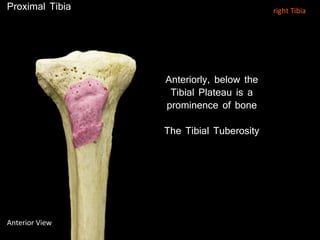
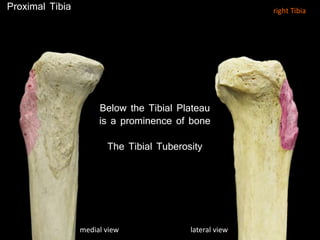
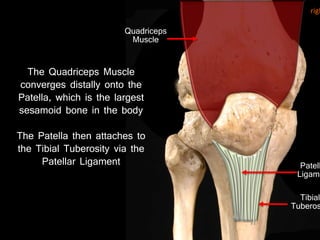
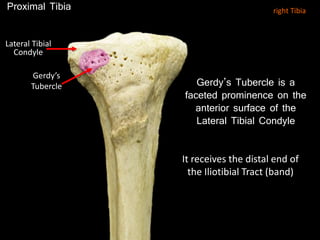
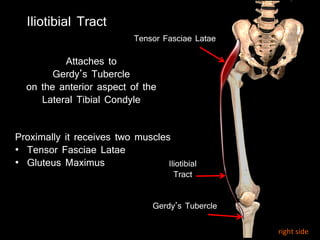
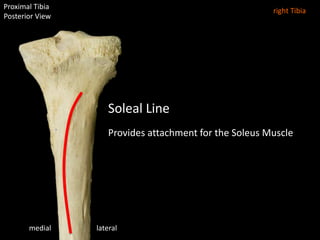
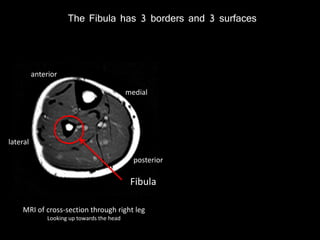
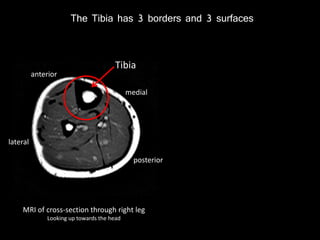
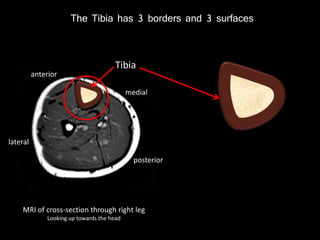
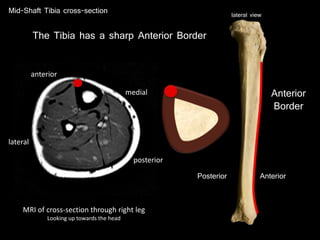
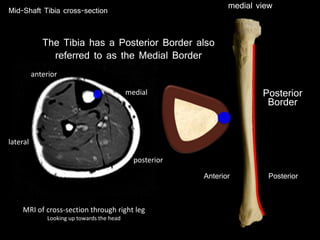
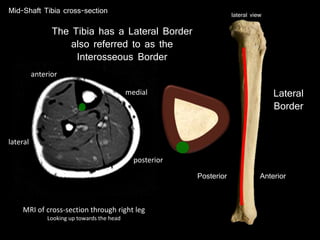
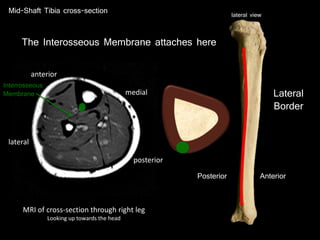
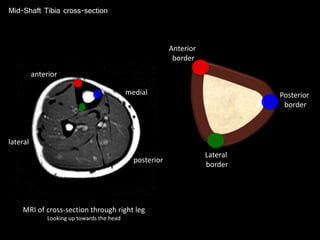
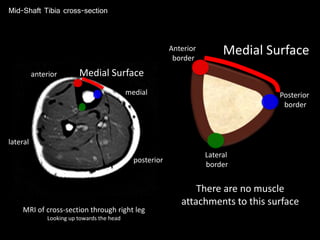
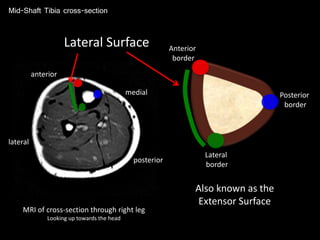
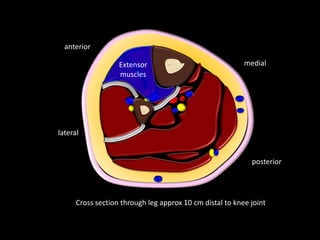
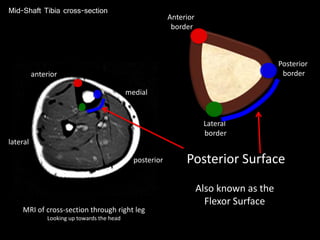
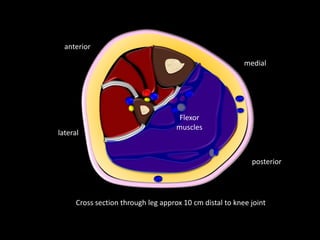
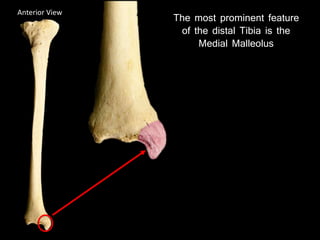
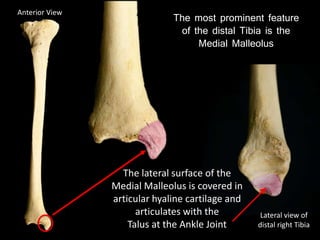
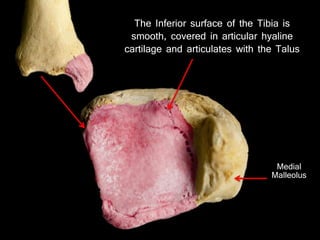
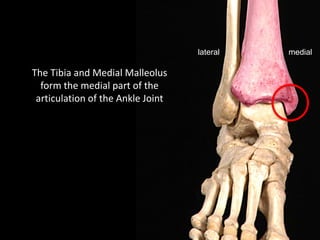
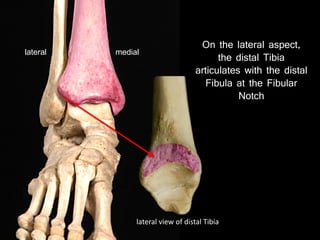
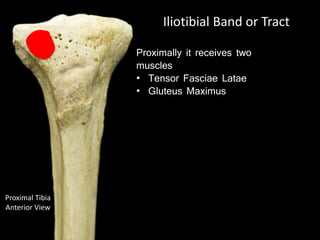
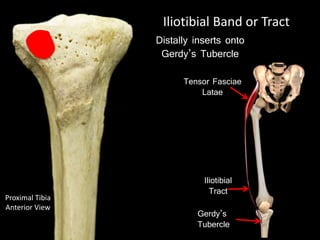
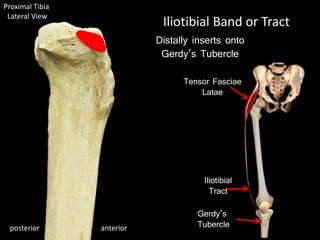
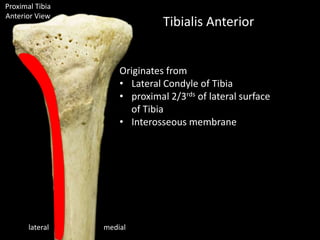
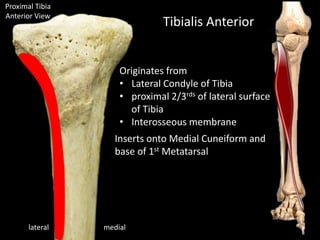
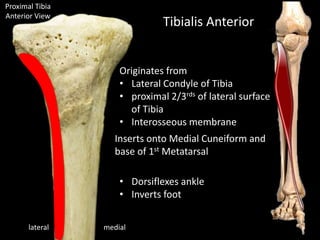
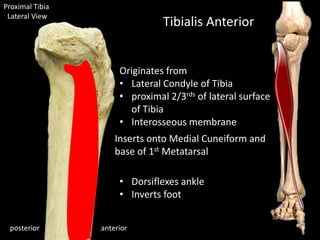
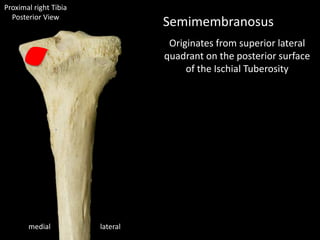
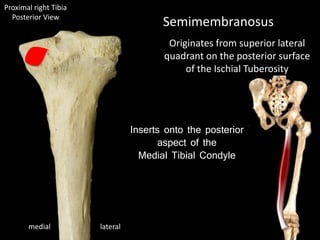
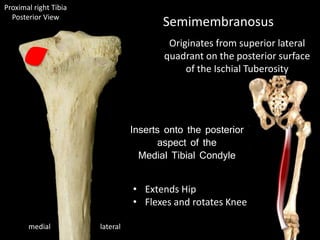
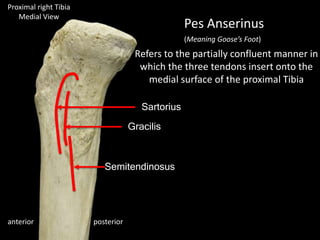
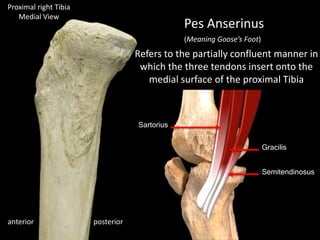
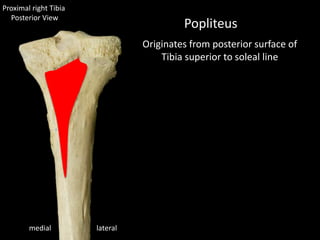
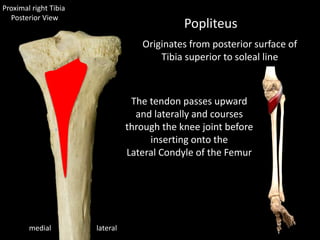
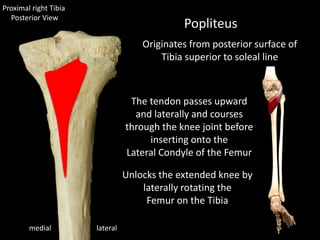
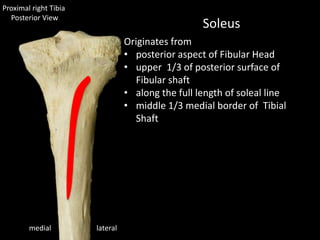
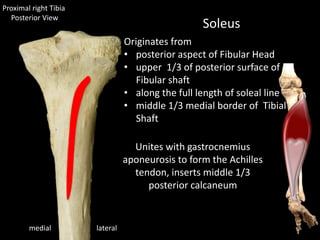
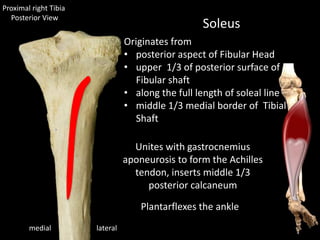
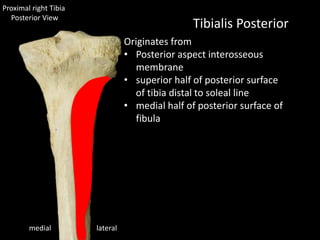
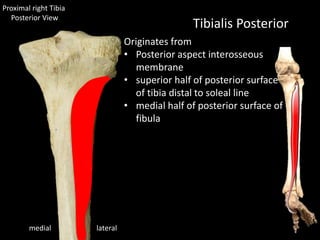
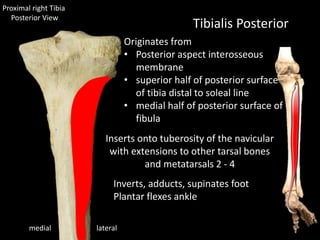
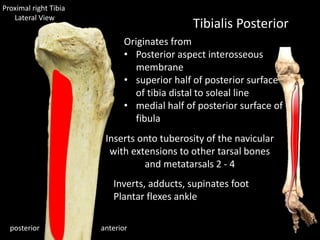
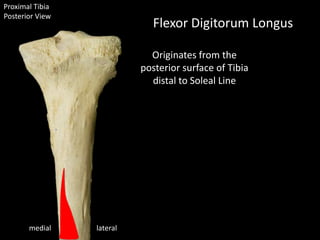
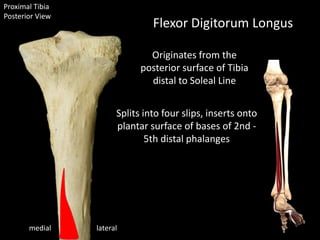
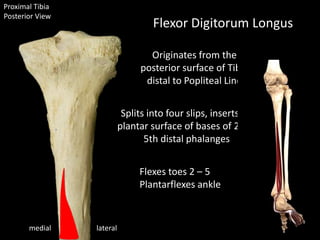
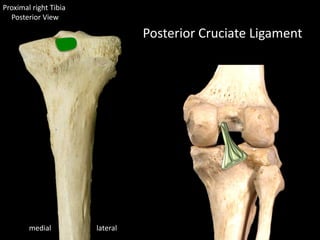
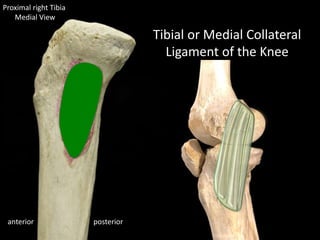
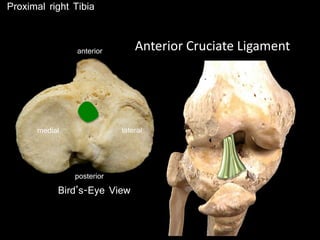
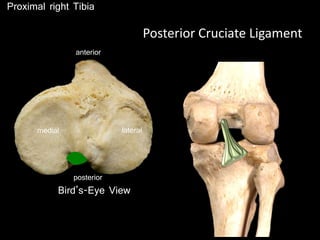
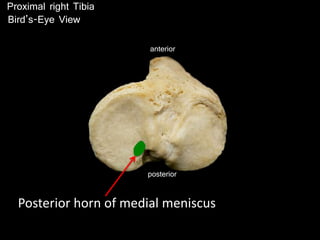
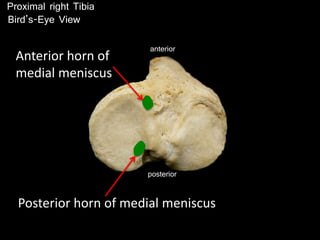
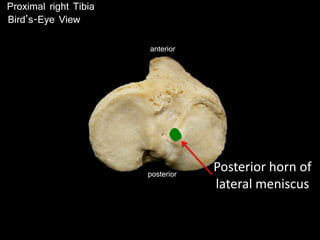
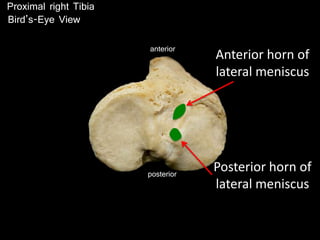
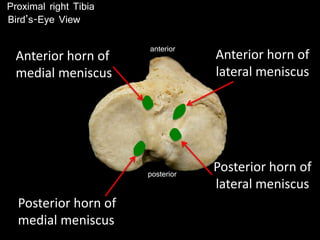
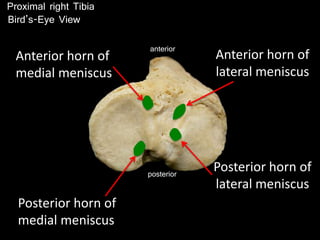
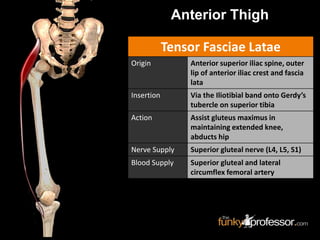
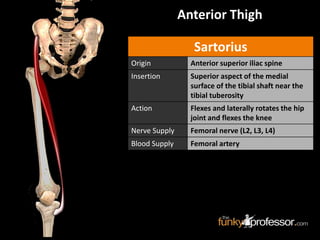
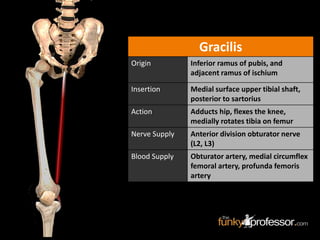
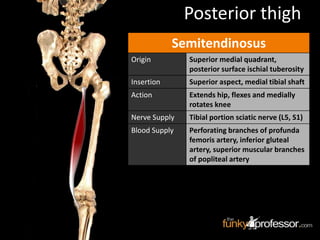
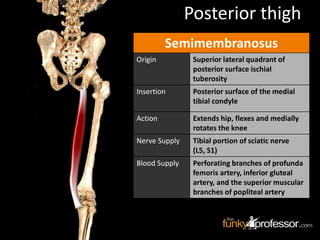
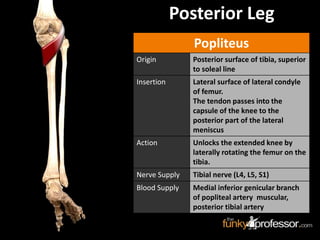
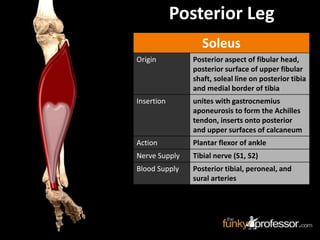
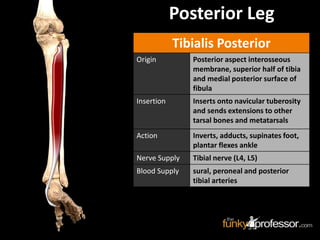
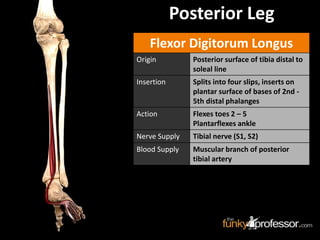
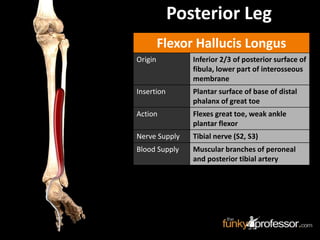
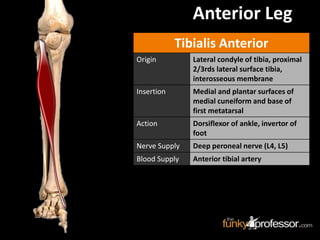
The document provides a detailed anatomical description of the tibia, including its structure, functions, and relationships with other bones and muscles in the leg. It outlines key features such as the tibial plateau, condyles, interosseous membrane, and muscle attachment points, as well as the functions of various muscles associated with the tibia. Additionally, the document discusses ligament attachments and the articulation of the tibia with the knee and ankle joints.