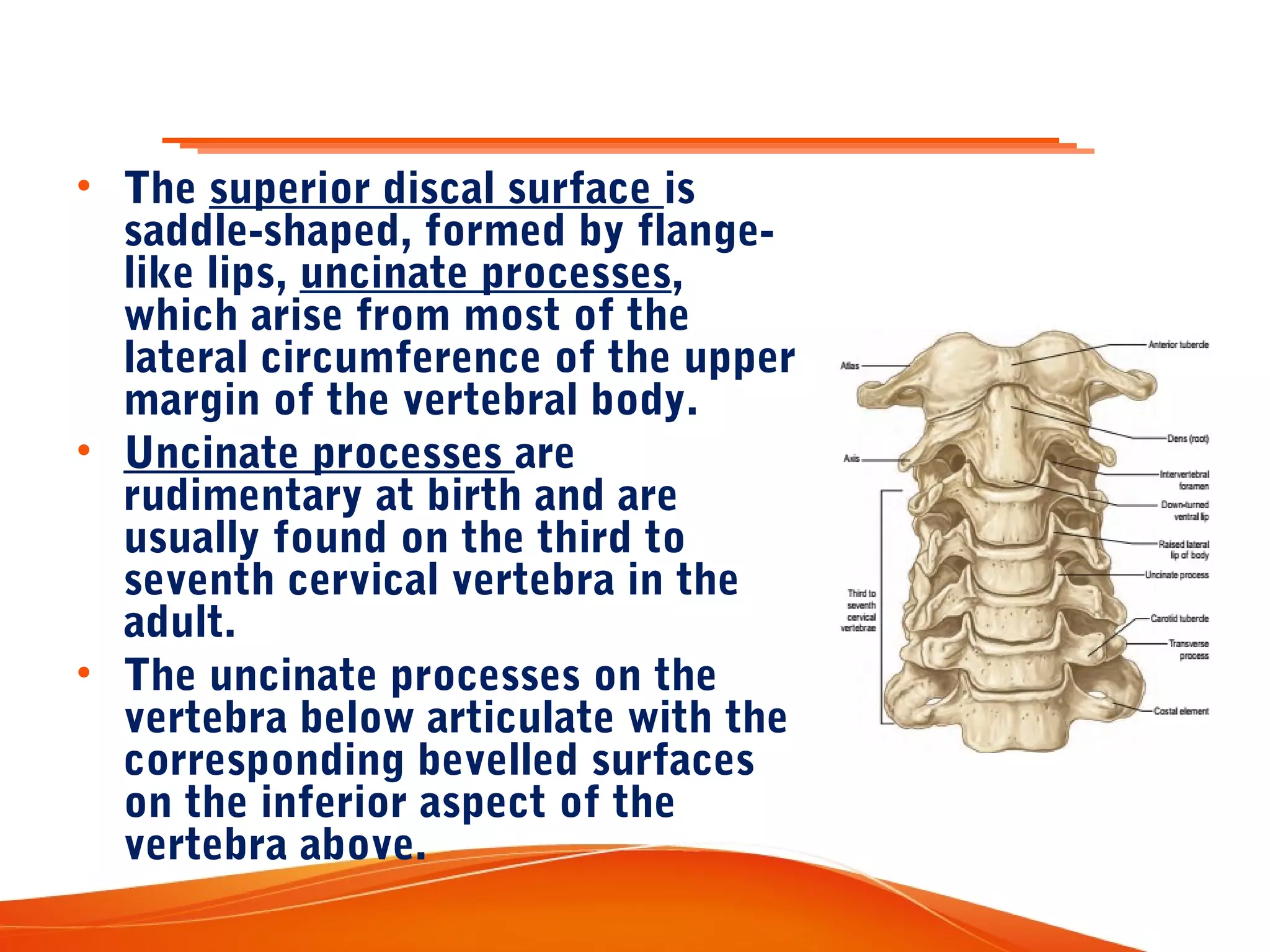
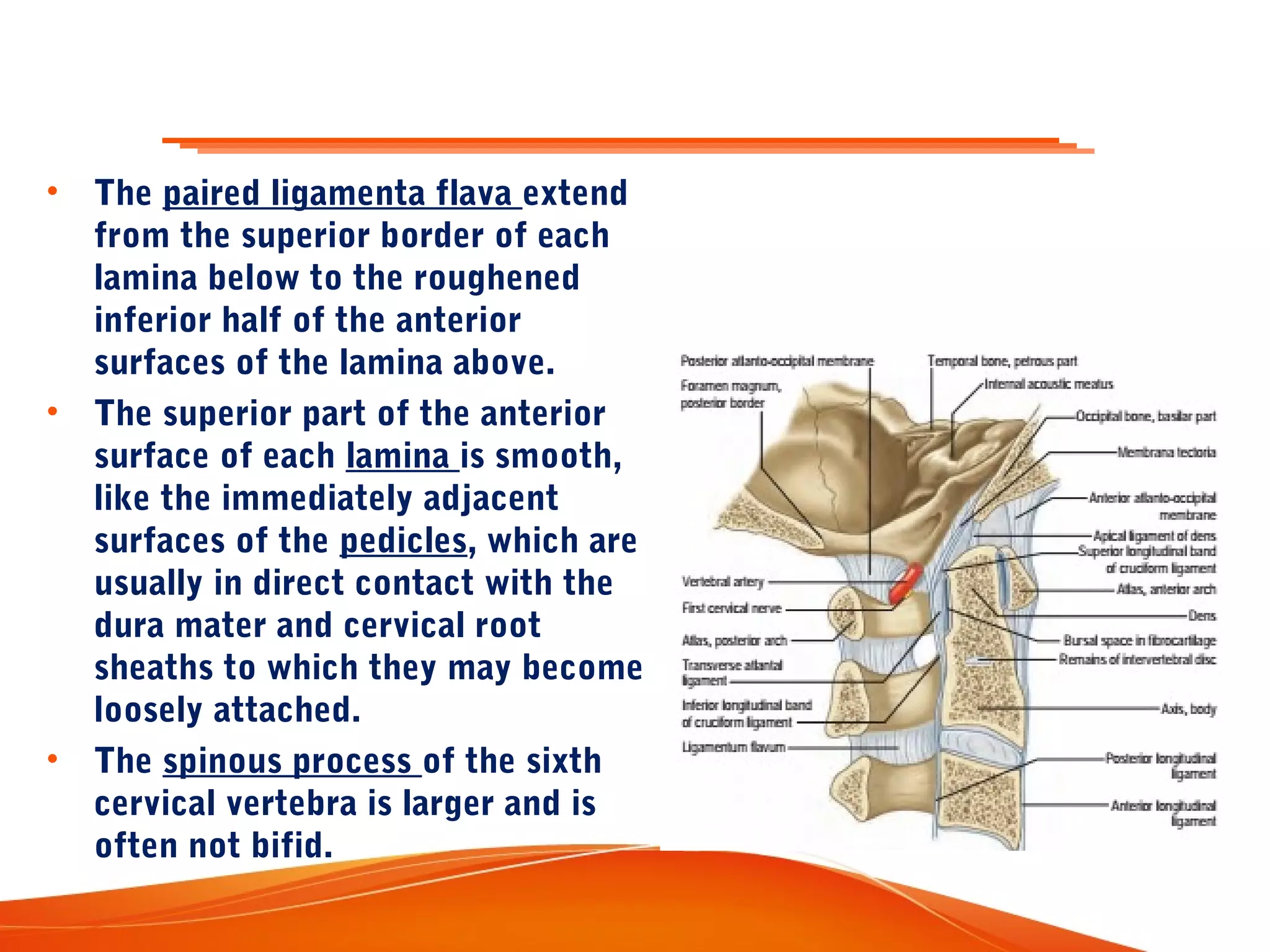
The human spinal column consists of 33 vertebrae organized into five regions. The vertebrae are interconnected by discs and supported by ligaments. Each region has characteristics suited to its location and functions. The cervical region has the greatest flexibility to allow rotation of the head. Facet joints and curvatures of the spine constrain and guide its range of motion. The vertebrae, discs, ligaments, muscles and curvatures work together to support the structure and movement of the spine.